- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад на тему Проект по самостоятельной работе студентки 3 курса отделения Сестриское дело на тему: Беременность. Pregnancy.
Содержание
- 1. Проект по самостоятельной работе студентки 3 курса отделения Сестриское дело на тему: Беременность. Pregnancy.
- 2. When you think about pregnancy, the image
- 3. To know exactly what pregnancy is, it
- 4. Слайд 4
- 5. The semen that gets into the vagina
- 6. Semen travels into the uterus in waves.
- 7. Semen travels into the uterus in waves.
- 8. Sperms move towards the egg cell
- 9. Once in the fallopian tube, the sperm
- 10. Sperm reaches the egg cell
- 11. Sperm penetrates the egg cell
- 12. New research shows that it is the
- 13. So has pregnancy occurred now? Well, not quite.
- 14. ZYGOTE
- 15. When the sperm fertilizes the egg, the
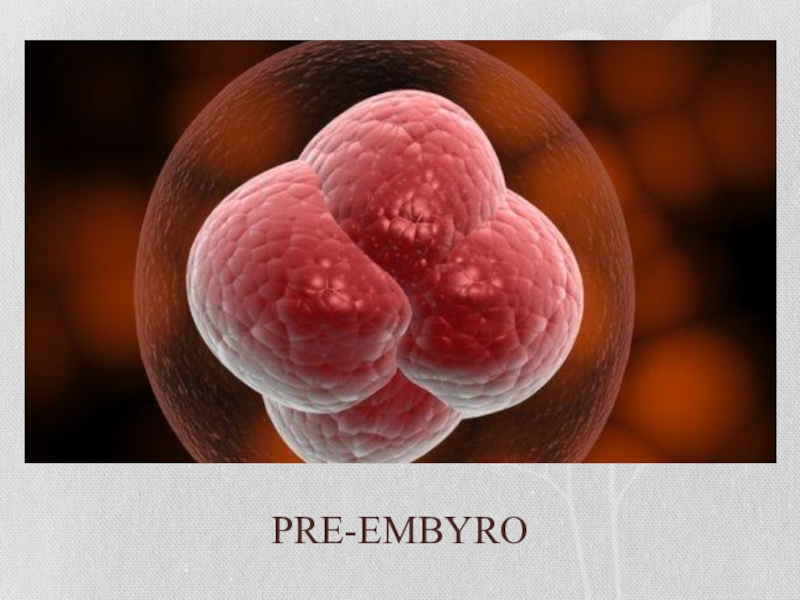
- 16. PRE-EMBYRO
- 17. First, the zygote replicates itself into a
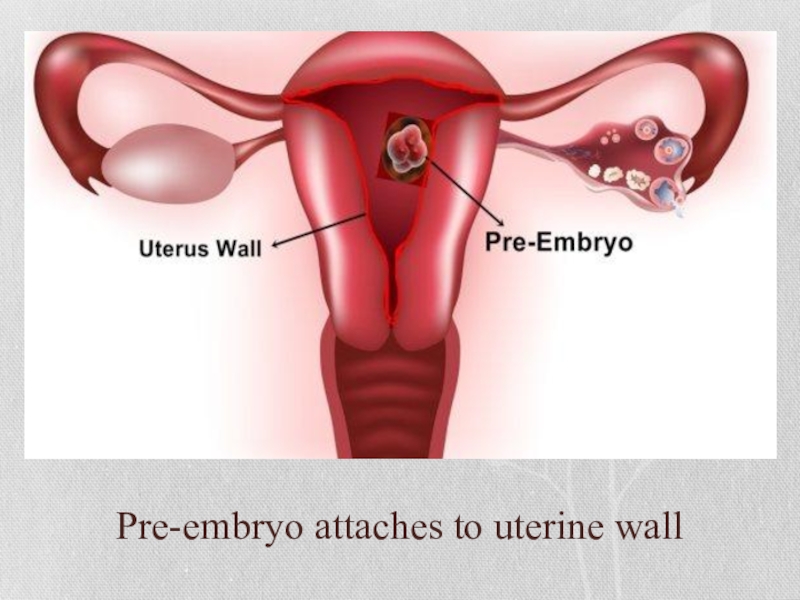
- 18. Pre-embryo attaches to uterine wall
- 19. The pre-embryo, once snuggled comfortably along the
- 20. And it is only once those hormones
- 21. Once firmly implanted in the uterine wall,
- 22. Слайд 22
- 23. Have you missed a period or are
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. During pregnancy, the woman undergoes many physiological
- 26. Pregnancy is typically broken into three periods,
- 27. FIRST TRIMESTERMinute ventilation increases by 40% in
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Although the fetus begins to move during
- 30. Final weight gain takes place, which is
- 31. Head engagement, where the fetal head descends
- 32. CHILDBIRTHBabies born between 39 and 41 weeks
- 33. HAPPY PRAGNANCY
- 34. Internet-sources: 1. https://www.glamcheck.com/health/2011/08/10/what-is-pregnancy/ 2. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnancy 3. https://stuklopechat.com/zdorove/114266-povyshennyy-gomocistein-pri-beremennosti-chem-eto-grozit.html 4. https://www.whattoexpect.com
When you think about pregnancy, the image that comes to mind is a glowing, mum-to-be with a full belly. While this is right, it is not the full story – it’s the abridged version. There’s a
Слайд 2When you think about pregnancy, the image that comes to mind
is a glowing, mum-to-be with a full belly. While this is right, it is not the full story – it’s the abridged version.
There’s a lot more to pregnancy than that dumbed-down simplification. Pregnancy is complex and miraculous, and knowing what is really going on gives you genuine and awe-inspiring appreciation for the human body and what it is capable of.
There’s a lot more to pregnancy than that dumbed-down simplification. Pregnancy is complex and miraculous, and knowing what is really going on gives you genuine and awe-inspiring appreciation for the human body and what it is capable of.
Слайд 3To know exactly what pregnancy is, it is first important to
learn what is going on in your body to get pregnant in the first place.
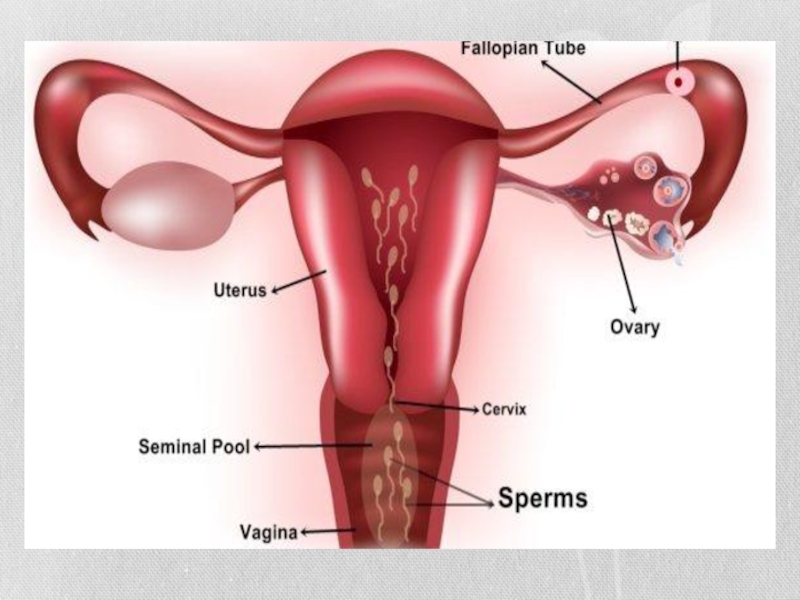
Слайд 5The semen that gets into the vagina during intercourse will form
a pool in the vagina near the cervix. This is called the seminal pool. The location of the pool is right blow the uterus, in an indentation in the vaginal wall. Here, semen wait to go into the uterus.
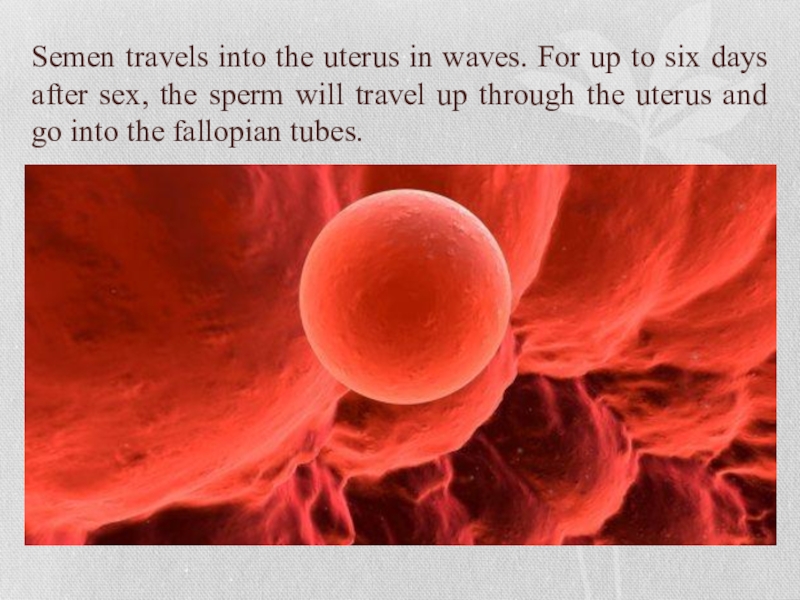
Слайд 6Semen travels into the uterus in waves. For up to six
days after sex, the sperm will travel up through the uterus and go into the fallopian tubes.
Слайд 7Semen travels into the uterus in waves. For up to six
days after sex, the sperm will travel up through the uterus and go into the fallopian tubes.
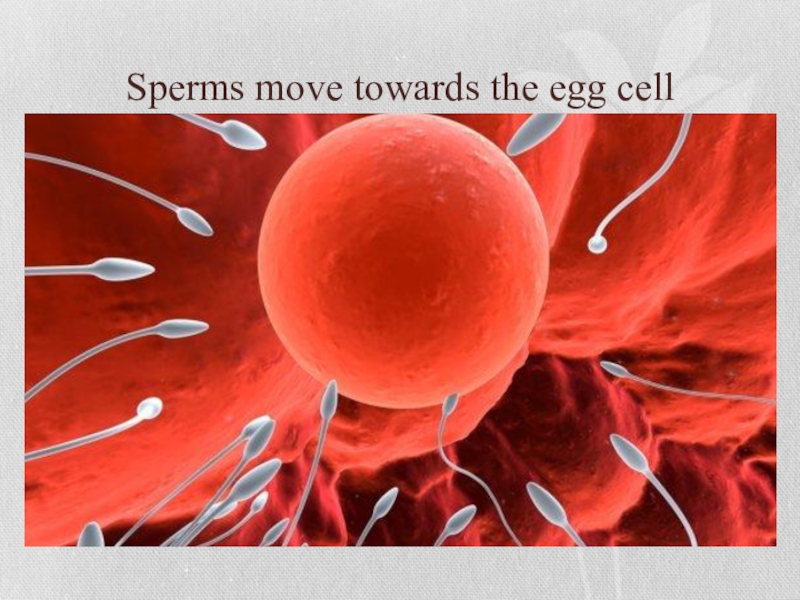
Слайд 9Once in the fallopian tube, the sperm wait for an egg
to descend from the ovaries. If a woman is not ovulating when the sperm are in the fallopian tube, then there will be no egg to fertilize and they will simply die away.
Слайд 12New research shows that it is the egg that decides which
sperm will fertilize it, rather than the other way around. The previous theory stated that it was survival of the fittest i.e. only the strongest sperm that made it past all the others would fertilize the egg. But studies are uncovering that the egg determines which sperm is just right and only allows the chosen one to fertilize it.
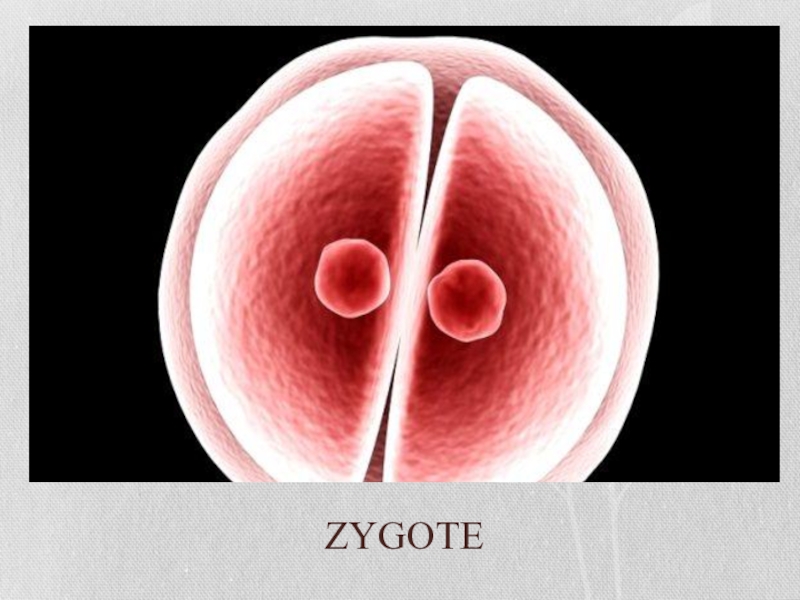
Слайд 15When the sperm fertilizes the egg, the result is a zygote
– a single-celled organism that carries the gene codes of both the parents. The zygote will eventually grow into a baby. But before it can do that, it has to take care of a few other things.
Слайд 17First, the zygote replicates itself into a multi-cellular organism that is
called the pre-embryo. After about 4 days, it will implant itself on the uterine wall. This process can take a couple of days or up to a week. We’re getting closer to the actual pregnancy now
Слайд 19The pre-embryo, once snuggled comfortably along the uterine wall, will start
to release hormones that prevent menstruation from occurring. So it is effectively shutting off the body’s ability to produce more eggs for fertilization. This is why your period stops during pregnancy
Слайд 20And it is only once those hormones have been released that
pregnancy is said to have begun.
Now all your reproductive systems efforts will be focused on nourishing and protecting the embryo.
Слайд 21Once firmly implanted in the uterine wall, the pre-embryo is called
an embryo for about 6 to 8 weeks, after which it will be called a foetus. A human female will carry the embryo and foetus for approximately 38 to 42 weeks or around 9 months before she gives birth to a baby. This carrying of the foetus in the womb is what pregnancy is about. So as to more conveniently calculate the date of birth of the baby, pregnancy may be assumed to begin from the date of conception rather than from the date of implantation, since it is difficult to know when the latter occurs.
Слайд 23Have you missed a period or are you feeling a little
different, and wondering whether you might be pregnant? The most common early signs and symptoms of pregnancy might include:
-Missed period
-Fatigue
-Smell sensitivity
-Morning sickness (nausea)
-Food aversions
-Mood swings
-Tender, swollen breasts
-Darker, bumpy areolas
-Frequent urination
-Bloating
-Raised temperature
-Bleeding
Слайд 25During pregnancy, the woman undergoes many physiological changes, which are entirely
normal, including behavioral, cardiovascular, hematologic, metabolic, renal, and respiratory changes. Increases in blood sugar, breathing, and cardiac output are all required. Levels of progesterone and oestrogens rise continually throughout pregnancy, suppressing the hypothalamic axis and therefore also the menstrual cycle.
Слайд 26Pregnancy is typically broken into three periods, or trimesters, each of
about three months. Each trimester is defined as 14 weeks, for a total duration of 42 weeks, although the average duration of pregnancy is 40 weeks. While there are no hard and fast rules, these distinctions are useful in describing the changes that take place over time.
Слайд 27FIRST TRIMESTER
Minute ventilation increases by 40% in the first trimester. The
womb will grow to the size of a lemon by eight weeks. Many symptoms and discomforts of pregnancy like nausea and tender breasts appear in the first trimester
Слайд 28
SECOND TRIMESTER
Weeks 13 to 28 of the pregnancy are called the second trimester. Most women feel more energized in this period, and begin to put on weight as the symptoms of morning sickness subside and eventually fade away. The uterus, the muscular organ that holds the developing fetus, can expand up to 20 times its normal size during pregnancy.
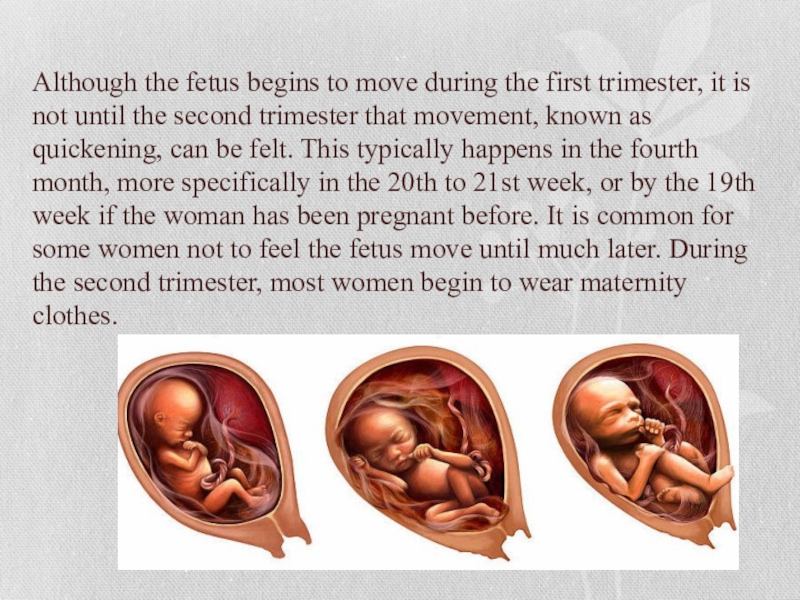
Слайд 29Although the fetus begins to move during the first trimester, it
is not until the second trimester that movement, known as quickening, can be felt. This typically happens in the fourth month, more specifically in the 20th to 21st week, or by the 19th week if the woman has been pregnant before. It is common for some women not to feel the fetus move until much later. During the second trimester, most women begin to wear maternity clothes.
Слайд 30Final weight gain takes place, which is the most weight gain
throughout the pregnancy. The woman's abdomen will transform in shape as it drops due to the fetus turning in a downward position ready for birth. During the second trimester, the woman's abdomen would have been upright, whereas in the third trimester it will drop down low. The fetus moves regularly, and is felt by the woman. Fetal movement can become strong and be disruptive to the woman. The woman's navel will sometimes become convex, "popping" out, due to the expanding abdomen.
THIRD TRIMESTER
Слайд 31Head engagement, where the fetal head descends into cephalic presentation, relieves
pressure on the upper abdomen with renewed ease in breathing. It also severely reduces bladder capacity, and increases pressure on the pelvic floor and the rectum.
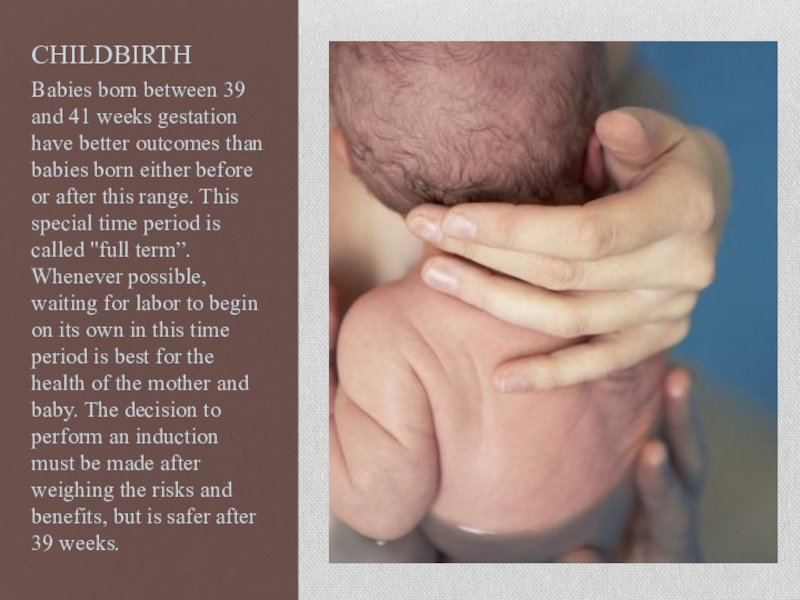
Слайд 32CHILDBIRTH
Babies born between 39 and 41 weeks gestation have better outcomes
than babies born either before or after this range. This special time period is called "full term”. Whenever possible, waiting for labor to begin on its own in this time period is best for the health of the mother and baby. The decision to perform an induction must be made after weighing the risks and benefits, but is safer after 39 weeks.