9 «А»
Белова Арина.
Руководитель: Муслимова
Заира Саидовна.
- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад проекта по английскому языку на тему Различия между британским и американским английским
Содержание
- 1. Презентация проекта по английскому языку на тему Различия между британским и американским английским
- 2. Introduction.Three centuries ago there was only
- 3. Introduction.Thereby, the aim of my work
- 4. Introduction.A number of problems: -Explore the
- 5. 1. The History of American English.English first
- 6. 2. Modern English.Nowadays there are two main
- 7. 2. Modern English.According to the director of
- 8. 3. Main differences between two variants of
- 9. 3.2. Vocabulary differences. Words and word combinations which are different in British and American English.
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. 3.3. Grammar differences.Speakers
- 12. 3.4. Accent differences. American pronunciation. When people
- 13. British pronunciation. When people talk about
- 14. Conclusion. During the work I
- 15. Literature and used materials. 1. Боварская О.
- 16. Thanks for your attention!
Introduction.Three centuries ago there was only one version of English. British colonizers, merchants, travelers brought it to other continents, where it evolved, changed and enriched. New words were appearing, pronunciation was changing. Immigrants from different
Слайд 1
«Differences between British English and American English».
Исследовательскую работу
выполнила ученица
Слайд 2 Introduction.
Three centuries ago there was only one version of English.
British colonizers, merchants, travelers brought it to other continents, where it evolved, changed and enriched. New words were appearing, pronunciation was changing. Immigrants from different countries, who settled in America, altered English grammar, made it simplier and easier. Despite the prevalence and significance of American English, in Russian schools we study British Standard English, which leads to
a number of difficulties.
a number of difficulties.
Слайд 3 Introduction.
Thereby, the aim of my work is systematization of the
main differences between British and American English.
The object of the research is modern varieties of British and American English.
The subject of the study are grammatical, lexical and phonetic differences in the American and British English.
Слайд 4 Introduction.
A number of problems:
-Explore the scientific and methodological literature;
-Review some
historical aspects of the origin of the English language;
-Reveal some grammar, phonetic and lexical differences between two variants.
Hypothesis of the study: the differences between American and British English are significant, which causes serious difficulties in studying English as a foreign language.
Hypothesis of the study: the differences between American and British English are significant, which causes serious difficulties in studying English as a foreign language.
Слайд 51. The History of American English.
English first entered in North America
in the early XVII century.
There are two major periods of English in America:
the early period from the beginning of the XVII century until the end of the XVIII century, which is characterized by the formation of American dialects;
In the XVII - XVIII centuries flows of immigrants are growing, bringing with them a variety of languages and dialects.The international value of American English began to acquire in the second half of the XX century, as the US position in the world arena is rapidly strengthened.
There are two major periods of English in America:
the early period from the beginning of the XVII century until the end of the XVIII century, which is characterized by the formation of American dialects;
In the XVII - XVIII centuries flows of immigrants are growing, bringing with them a variety of languages and dialects.The international value of American English began to acquire in the second half of the XX century, as the US position in the world arena is rapidly strengthened.
Слайд 62. Modern English.
Nowadays there are two main variants of English -
British English and American English.
Unlike the British version , American English is more flexible. It is the language of the new generation, which unites people through common culture, rock music, movies, dense communication. English tends to be brief and clear.
Unlike the British version , American English is more flexible. It is the language of the new generation, which unites people through common culture, rock music, movies, dense communication. English tends to be brief and clear.
Слайд 72. Modern English.
According to the director of the British School of
Language Link Robert Dzhenski: “Now we can speak about the consolidation of universal average English, This - not the American or British, and no other. It is the language of international communication.”
Слайд 83. Main differences between two variants of English.
3.1. Spelling differences.
Many words
are also spelled differently in American and British English.
• British words that end in -our (colour, flavour and humour) end in -or in American English (color, flavor & humor)
• British words that end in –re (litre, centre, theatre) end in –er in American English (liter, center, theater)
• British words that end in –ise or –yse (minimise, realise, analyse) end in –ize or –yze in American English (minimize, realize, analyze)
• British words that end in –ence (pretence, defence) end in –ense in American English (pretense, defense)
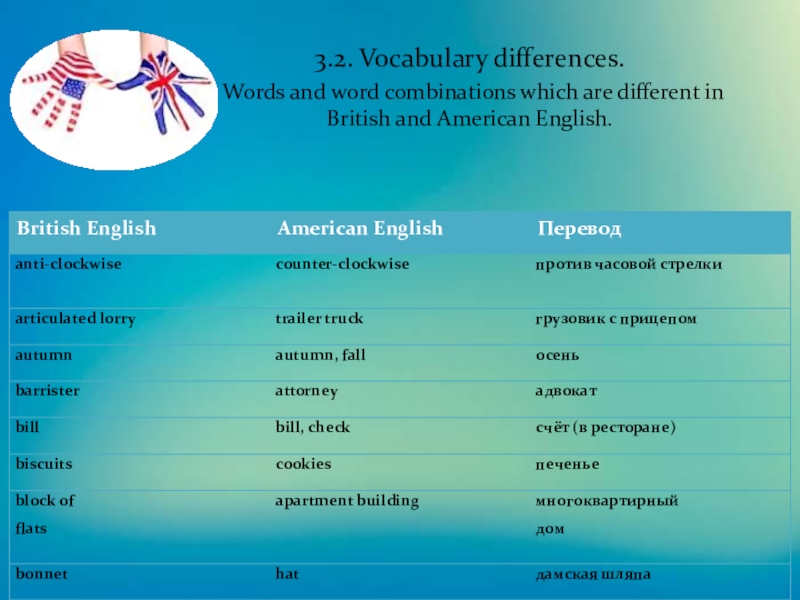
Слайд 93.2. Vocabulary differences. Words and word combinations which are different in
British and American English.
Слайд 11 3.3. Grammar differences.
Speakers of American English generally
use the present perfect tense far less than speakers of British English. In spoken American English it is very common to use the simple past tense. Example:
American English. British English.
1. Are they going to the show tonight? Are they going to the show tonight?
No. They already saw it. No. They’ve already seen it.
2. Is Samantha here? Is Samantha here?
No. She just left. No. She’s just left.
3. Can I borrow your book? Can I borrow your book?
No. I didn’t read it yet. No. I haven’t read it yet.
American English. British English.
1. Are they going to the show tonight? Are they going to the show tonight?
No. They already saw it. No. They’ve already seen it.
2. Is Samantha here? Is Samantha here?
No. She just left. No. She’s just left.
3. Can I borrow your book? Can I borrow your book?
No. I didn’t read it yet. No. I haven’t read it yet.
Слайд 123.4. Accent differences. American pronunciation. When people talk about “learning American pronunciation”, they
mean learning General American (GenAm) pronunciation.
Educated Americans usually speak GenAm 90% of what you’ll hear on American TV, radio, podcasts, movies, Web videos, etc. is GenAm.
General American pronunciation is rhotic /'roʊtɪk/, which means that the letter r is always pronounced. Example: car, tower, inform, first.
Слайд 13British pronunciation. When people talk about learning British pronunciation, they usually think
of Received Pronunciation (RP). This is the pronunciation that you will learn at a British language school.
Only about 5% of Britons speak RP — these are upper-class people, academics, actors, TV personalities, politicians and English teachers. Educated Britons from various regions of the UK sometimes adopt an RP-like accent.
Most “normal” Britons speak with their local accents.
RP is non-rhotic, which means that the letter r is usually “silent”. Here’s how it works:
In words like car, tower, inform and first, r is silent (r is not followed by a vowel).
Слайд 14
Conclusion.
During the work I have studied theoretical research, reviewed the historical
context of the origin of American English. I have stated grammatical, lexical and phonetic features of the American and British English.
The study shows that the hypothesis has been confirmed: the differences between American and British English are significant, which causes serious difficulties in the process of studying English as a foreign language.
The study shows that the hypothesis has been confirmed: the differences between American and British English are significant, which causes serious difficulties in the process of studying English as a foreign language.
Слайд 15Literature and used materials.
1. Боварская О. Pidgit English. U-journal. Журнал
стокгольмской школы экономики в России. №7(1), 2005.
2. Коптелова Е. Варианты английского. Какой учить и как? "Иностранец", №25, 2000.
3. Чернов Г. В. Американский вариант. Англо-русский/русско-английский словарь. М., 2001.
4.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_and_British_English_pronunciation_differences
5. http://www.americanaccent.com/pronunciation.html
http://www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com/about/pronunciation_american_english
6. «Oxford guide to American and British Culture».
7. «Oxford English grammar».
2. Коптелова Е. Варианты английского. Какой учить и как? "Иностранец", №25, 2000.
3. Чернов Г. В. Американский вариант. Англо-русский/русско-английский словарь. М., 2001.
4.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_and_British_English_pronunciation_differences
5. http://www.americanaccent.com/pronunciation.html
http://www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com/about/pronunciation_american_english
6. «Oxford guide to American and British Culture».
7. «Oxford English grammar».