- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад по английскому языку на тему Unemployment
Содержание
- 1. Презентация по английскому языку на тему Unemployment
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. Phonetic exercise Song “Let it be”
- 4. Let it be
- 5. Checking the homeworkChildren at work
- 6. Unemployment
- 7. Measuring UnemploymentA Working Definition of UnemploymentPeople able,
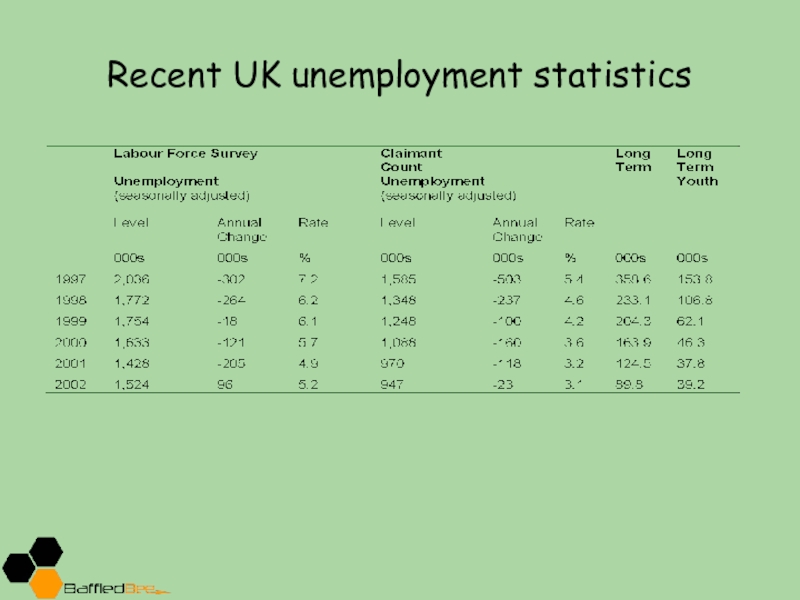
- 8. Recent UK unemployment statistics
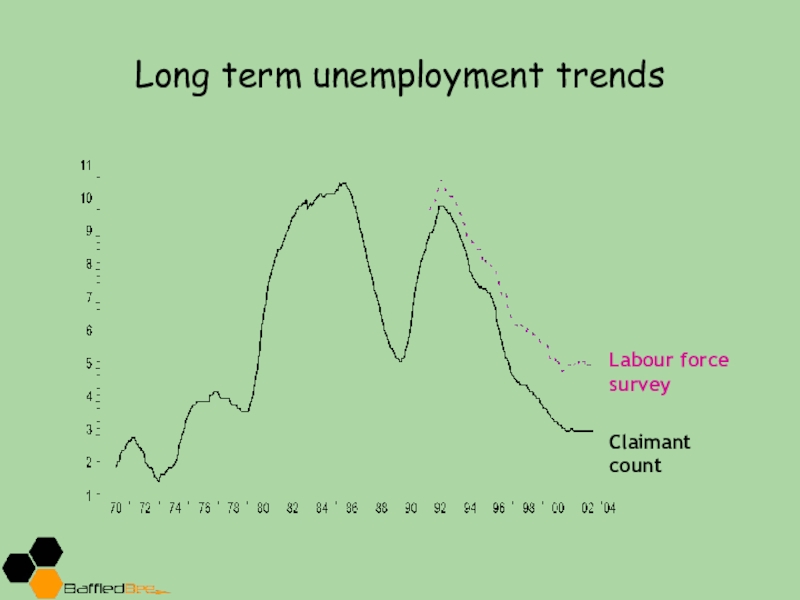
- 9. Long term unemployment trendsLabour force surveyClaimant count
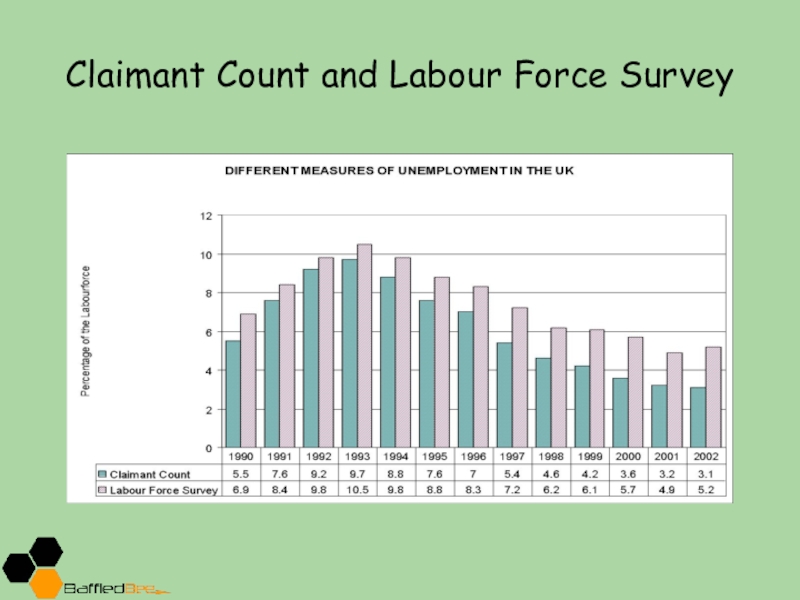
- 10. Claimant Count and Labour Force Survey
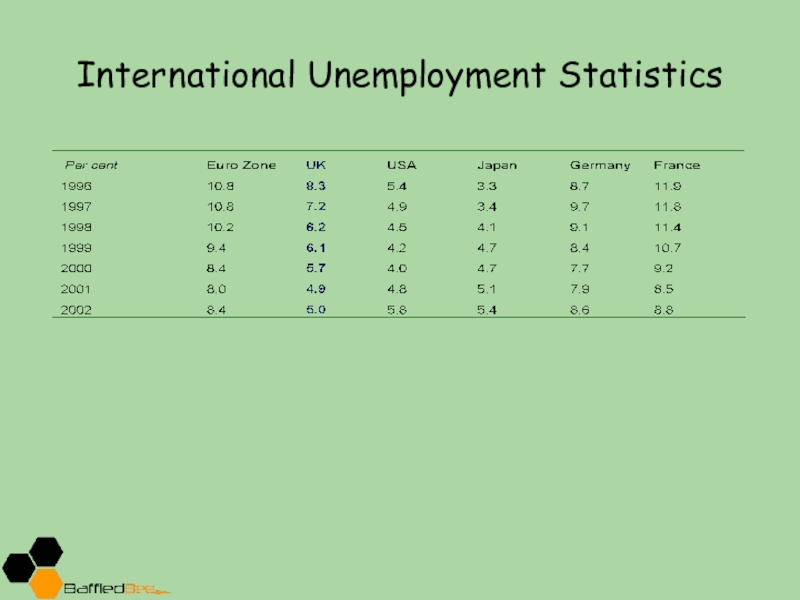
- 11. International Unemployment Statistics
- 12. Types of UnemploymentSeasonal Regular seasonal changes in
- 13. Causes of Unemployment (continued)StructuralArises from the mismatch
- 14. Illustrating cyclical unemployment using AD-AS analysisGeneral Price
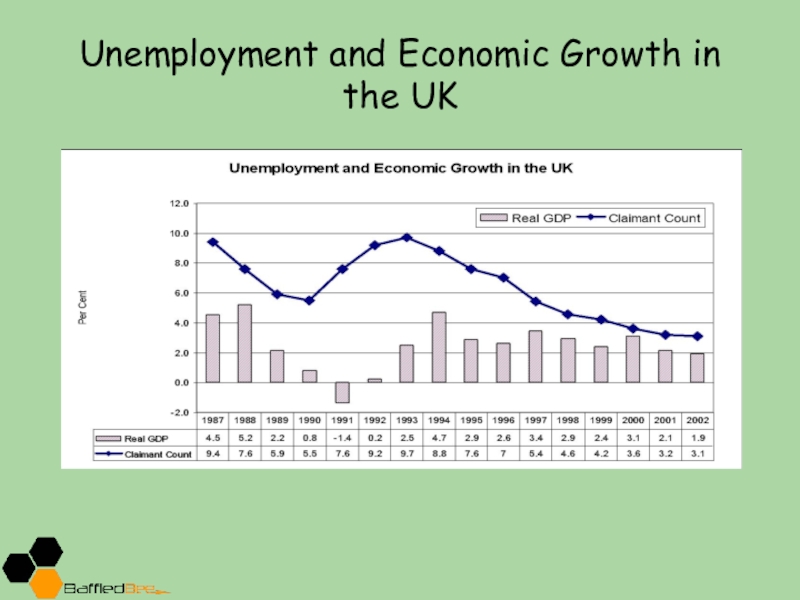
- 15. Unemployment and Economic Growth in the UK
- 16. Economic and Social Costs of UnemploymentPrivate Costs
- 17. Consequences of Unemployment (2)Economic Consequences for BusinessesNegative
- 18. Consequences of Unemployment (3)Consequences for the Government
- 19. Policies to Reduce UnemploymentMeasures to boost labour
- 20. Consequences of falling unemploymentThe circular flow and
- 21. Bloom’s cube1 Why2 Explain3 Call4 Offer5 Think up6 Share
- 22. Complete the table “Insert”
- 23. Слайд 23
- 24. ReflectionWhat can you tell me about today’s lesson?What is sensible ,useful…?
- 25. Home taskUnemployment-retellingGrammar
Phonetic exercise Song “Let it be”
Слайд 4Let it be
Мудрые слова
Broken-hearted Темные времена
Words of wisdom Разбитые сердца
May be parted Звуки музыки
Hour of darkness Могут быть разлучены
The sounds of music Пришла ко мне
Comes to me Да будет так
Broken-hearted Темные времена
Words of wisdom Разбитые сердца
May be parted Звуки музыки
Hour of darkness Могут быть разлучены
The sounds of music Пришла ко мне
Comes to me Да будет так
Осылай болсын
Жараланған жүректермен
Дана сөздер
Олар айырылуы мүмкін
Түнелген күндері
Музыка әуені
Маған келді
Слайд 7Measuring Unemployment
A Working Definition of Unemployment
People able, available and willing to
find work and actively seeking work – but not employed
The Claimant Count Measure
The number of people claiming the Jobseekers’ Allowance
The Labour Force Survey
Must have actively sought work in the previous four weeks and be available to start work immediately
Labour Market Slack
Includes all those who want to work, those on government training schemes, and part-timers who could not get a full-time job
The Claimant Count Measure
The number of people claiming the Jobseekers’ Allowance
The Labour Force Survey
Must have actively sought work in the previous four weeks and be available to start work immediately
Labour Market Slack
Includes all those who want to work, those on government training schemes, and part-timers who could not get a full-time job
Слайд 12Types of Unemployment
Seasonal
Regular seasonal changes in employment / labour demand
Affects
certain industries more than others
Catering and leisure
Construction
Retailing
Tourism
Agriculture
Frictional
An irreducible minimum unemployment in a dynamic economy
Includes people experiencing short spells of unemployment
Includes new and returning entrants into the labour market
Imperfect information about available job opportunities can lengthen the period of job search
Frictional unemployment also affected by incentives / disincentives to search and accept paid work
Catering and leisure
Construction
Retailing
Tourism
Agriculture
Frictional
An irreducible minimum unemployment in a dynamic economy
Includes people experiencing short spells of unemployment
Includes new and returning entrants into the labour market
Imperfect information about available job opportunities can lengthen the period of job search
Frictional unemployment also affected by incentives / disincentives to search and accept paid work
Слайд 13Causes of Unemployment (continued)
Structural
Arises from the mismatch of skills and job
opportunities as the pattern of labour demand in the economy changes over time
Occupational immobility of labour is a major cause of structural unemployment – labour market failure
Often involves long-term unemployment
Prevalent in regions where industries go into long-term decline
Cyclical (Keynesian)
There is a clear cyclical relationship between demand, output, employment and unemployment
Caused by a fall in aggregate demand relative to potential GDP leading to a loss of real national output and employment
Real Wage Unemployment
Created when real wages are maintained above their market clearing level leading to an excess supply of labour at the prevailing wage rate
Occupational immobility of labour is a major cause of structural unemployment – labour market failure
Often involves long-term unemployment
Prevalent in regions where industries go into long-term decline
Cyclical (Keynesian)
There is a clear cyclical relationship between demand, output, employment and unemployment
Caused by a fall in aggregate demand relative to potential GDP leading to a loss of real national output and employment
Real Wage Unemployment
Created when real wages are maintained above their market clearing level leading to an excess supply of labour at the prevailing wage rate
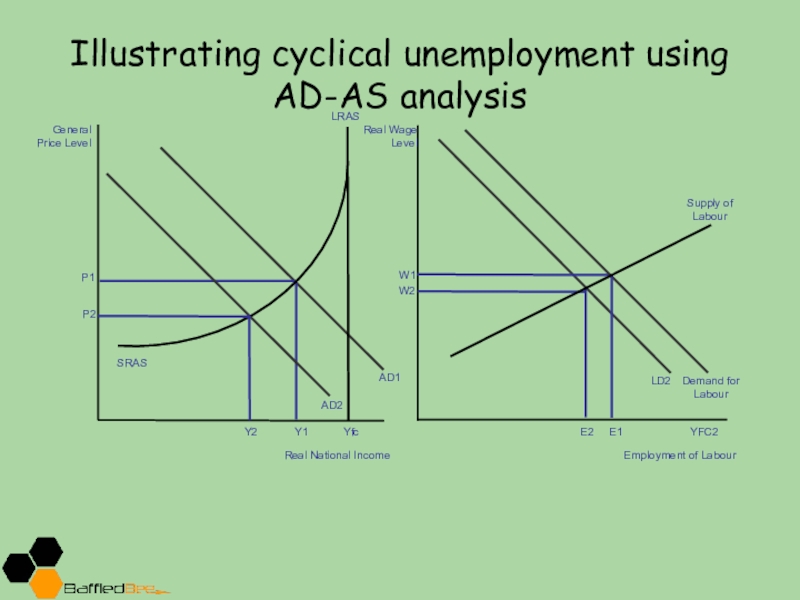
Слайд 14Illustrating cyclical unemployment using AD-AS analysis
General Price Level
Real National Income
AD1
SRAS
P1
Y1
LRAS
Yfc
AD2
Y2
P2
Real Wage
Level
LD2
W1
E2
YFC2
E1
Demand for Labour
W2
Employment of Labour
Supply of Labour
Слайд 16Economic and Social Costs of Unemployment
Private Costs for the Involuntary Unemployed
Loss
of income – but many households have major spending commitments (mortgage, credit agreements etc.)
Fall in real living standards
Increased Health risks (particularly for long term unemployed)
Stress
Reduction in quality of diet
Increased risk of marital break-up
Social exclusion because of loss of work and income
Loss of marketable skills (human capital) and motivation
The longer the duration of unemployment, the lower the chances of finding fresh employment - the unemployed become less attractive to potential employers (“outsiders in the labour market”)
Fall in real living standards
Increased Health risks (particularly for long term unemployed)
Stress
Reduction in quality of diet
Increased risk of marital break-up
Social exclusion because of loss of work and income
Loss of marketable skills (human capital) and motivation
The longer the duration of unemployment, the lower the chances of finding fresh employment - the unemployed become less attractive to potential employers (“outsiders in the labour market”)
Слайд 17Consequences of Unemployment (2)
Economic Consequences for Businesses
Negative consequences
Fall in demand for
goods and services
Fall in demand for businesses further down the supply chain
Consider the negative multiplier effects from the closure of a major employer in a town or city
Some positive consequences
Bigger pool of surplus labour is available – but still a problem if there is plenty of structural unemployment
Less pressure to pay higher wages
Less risk of industrial / strike action – fear of job losses – leading to reduced trade union power
Fall in demand for businesses further down the supply chain
Consider the negative multiplier effects from the closure of a major employer in a town or city
Some positive consequences
Bigger pool of surplus labour is available – but still a problem if there is plenty of structural unemployment
Less pressure to pay higher wages
Less risk of industrial / strike action – fear of job losses – leading to reduced trade union power
Слайд 18Consequences of Unemployment (3)
Consequences for the Government (Fiscal Policy)
Increased spending on
unemployment benefits and other income –related state welfare payments
Fall in revenue from income tax and taxes on consumer spending
Fall in profits – reduction in revenue from corporation tax
May lead to rise in government borrowing (i.e. a budget deficit)
Consequences for the Economy as a whole
Lost output (real GDP) from people being out of work – the economy will be operating well within its production frontier
Unemployment seen as an inefficient way of allocating resources – labour market failure?
Some of the long-term unemployed may leave the labour force permanently – fall in potential GDP
Increase in the inequality – rise in relative poverty
Fall in revenue from income tax and taxes on consumer spending
Fall in profits – reduction in revenue from corporation tax
May lead to rise in government borrowing (i.e. a budget deficit)
Consequences for the Economy as a whole
Lost output (real GDP) from people being out of work – the economy will be operating well within its production frontier
Unemployment seen as an inefficient way of allocating resources – labour market failure?
Some of the long-term unemployed may leave the labour force permanently – fall in potential GDP
Increase in the inequality – rise in relative poverty
Слайд 19Policies to Reduce Unemployment
Measures to boost labour demand (reduce cyclical unemployment)
Lower
interest rates (monetary stimulus)
Lower direct taxes (fiscal stimulus)
Government spending on major projects (e.g. improving the transport infrastructure)
Employment subsidies (including the New Deal programme)
Incentives to encourage flows of foreign investment in the UK
Measures to improve labour supply (reduce frictional and structural unemployment)
Increased spending on education & training including an emphasis on “lifetime-learning”)
Improved flows of information on job vacancies
Changes to income tax and benefits to improve incentives to find work
Lower direct taxes (fiscal stimulus)
Government spending on major projects (e.g. improving the transport infrastructure)
Employment subsidies (including the New Deal programme)
Incentives to encourage flows of foreign investment in the UK
Measures to improve labour supply (reduce frictional and structural unemployment)
Increased spending on education & training including an emphasis on “lifetime-learning”)
Improved flows of information on job vacancies
Changes to income tax and benefits to improve incentives to find work
Слайд 20Consequences of falling unemployment
The circular flow and the multiplier:
Incomes flowing into
households will grow
Falling unemployment adds to demand and creates a positive multiplier effect on incomes, demand and output.
The balance of payments:
When incomes and spending are growing, there is an increase in the demand for imports. Unless this is matched by a rise in export sales, the trade balance in goods and services will worsen
Government finances:
With more people in work paying income tax, national insurance and value added tax, the government can expect a large rise in tax revenues and a reduction in social security benefits
Inflationary effects
Falling unemployment can also create a rise in inflationary pressure – particularly when the economy moves close to operating at full capacity
Falling unemployment adds to demand and creates a positive multiplier effect on incomes, demand and output.
The balance of payments:
When incomes and spending are growing, there is an increase in the demand for imports. Unless this is matched by a rise in export sales, the trade balance in goods and services will worsen
Government finances:
With more people in work paying income tax, national insurance and value added tax, the government can expect a large rise in tax revenues and a reduction in social security benefits
Inflationary effects
Falling unemployment can also create a rise in inflationary pressure – particularly when the economy moves close to operating at full capacity