- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад по английскому языку на тему Arctic animals
Содержание
- 1. Презентация по английскому языку на тему Arctic animals
- 2. There are many types of animals that
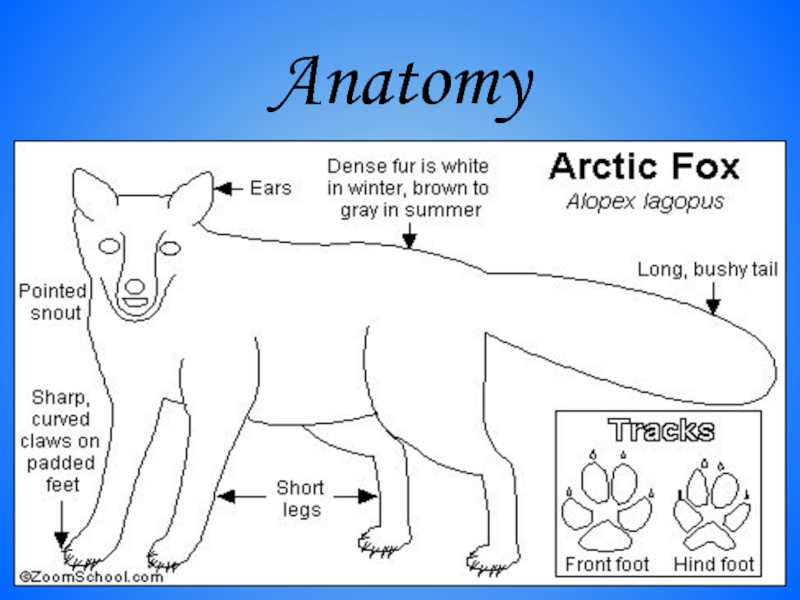
- 3. Arctic Fox (полярный песец)
- 4. The arctic foxes are well adapted for
- 5. Interesting FactsThe arctic fox has the warmest
- 6. Interesting Facts Arctic fox can be either
- 7. Interesting FactsHunting:Arctic fox walk along on top
- 8. Anatomy
- 9. Caribou (карибу) [ˈkærɪbu:]
- 10. The caribou is a member
- 11. Interesting FactsThey live throughout the arctic tundra
- 12. Interesting Facts
- 13. Interesting FactsThe caribou has a very warm
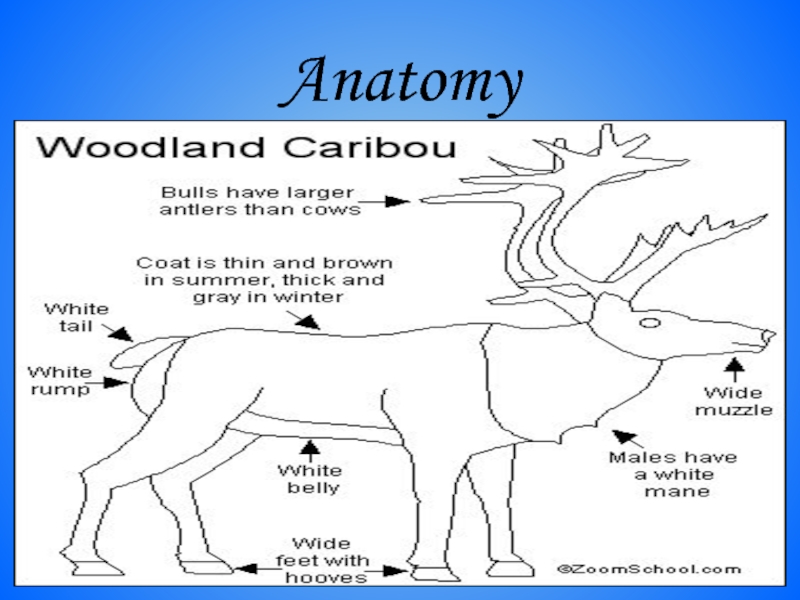
- 14. Anatomy
- 15. Lemming (лемминг)
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. Interesting FactsThe lemming has smaller ears and
- 18. Interesting FactsThey build their nests with dry
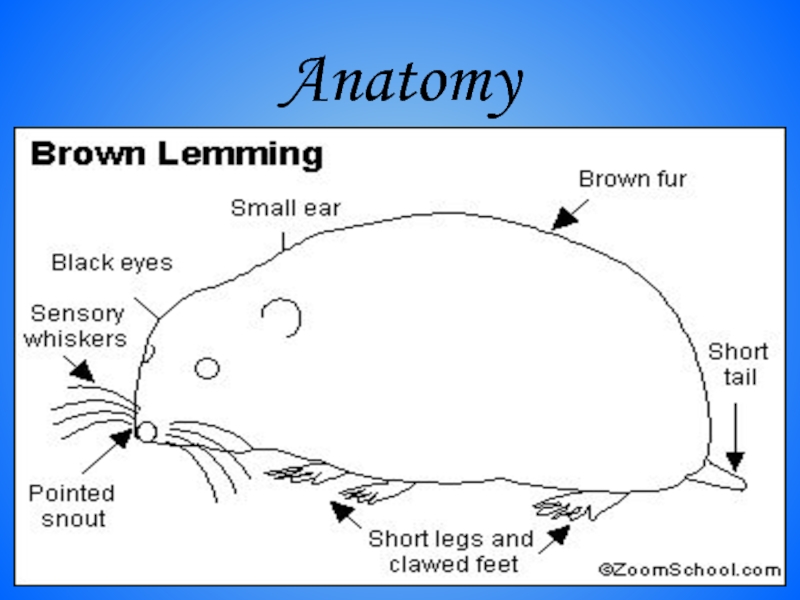
- 19. Anatomy
- 20. Polar Bear (белый медведь)
- 21. Polar bears live only in
- 22. Interesting FactsThe polar bear has many unique
- 23. Interesting Facts Eats mostly seals (тюлень). They
- 24. Interesting FactsPolar bear hide (шкура) is very
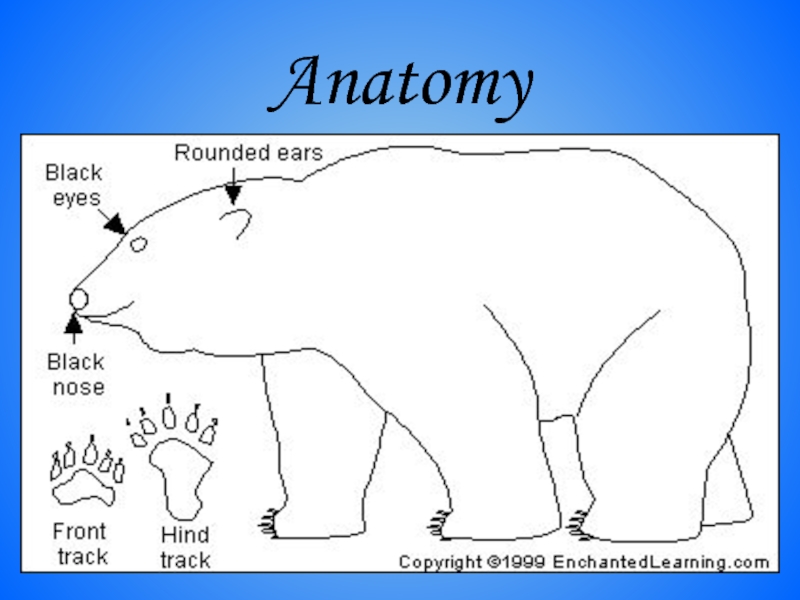
- 25. Anatomy
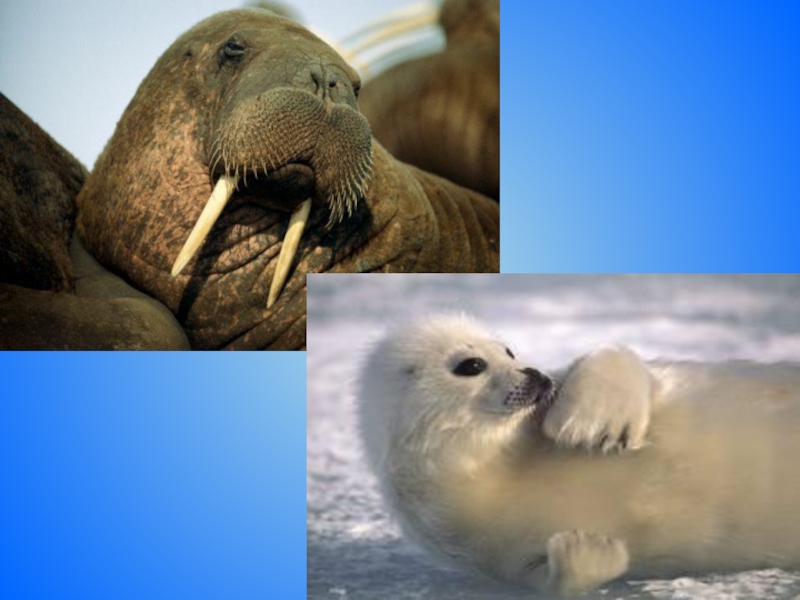
- 26. Walrus (морж) [ˈwɔ:lrəs]
- 27. Walruses are pinnipeds (ластоногие). Walruses are the
- 28. Interesting FactsDistinguishing Characteristics: Tusks (клыки), whiskers, and
- 29. Interesting FactsWalrus walk on all four fins.
- 30. Interesting FactsThe walrus have big whiskers. They
- 31. Wolverine (росомаха) [ˈwulvəri:n]
- 32. Despite it’s name, the wolverine is not
- 33. Interesting FactsThe wolverine doesn’t eat more
- 34. Interesting FactsThe wolverine has bad eyesight, is
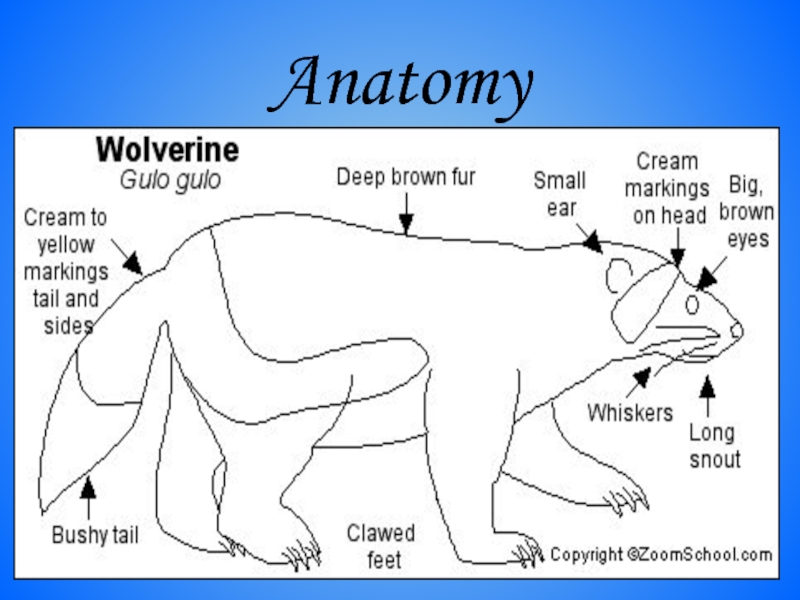
- 35. Anatomy
- 36. Seal (тюлень)
- 37. These mammals are well adapted
- 38. Interesting FactsEat shellfish (моллюски) and smaller fish.
- 39. Interesting FactsHarp, ribbon, ringed, leopard and
- 40. Interesting FactsSeals are different from sea lions
- 41. Слайд 41
- 42. Слайд 42
- 43. Слайд 43
There are many types of animals that have their own habitat and it isn't all frozen. The animals vary in size and characteristics
Слайд 2There are many types of animals that have their own habitat
and it isn't all frozen. The animals vary in size and characteristics
Слайд 4The arctic foxes are well adapted for the cold harsh weather
of the Arctic. The arctic fox can hunt lemming but if the arctic fox can't kill enough to eat, it will settle for leftovers (объедки) from other animals. Live in
Northern and
western Alaska,
Russia,
and Greenland;
a few records
indicate presence
farther south.
Northern and
western Alaska,
Russia,
and Greenland;
a few records
indicate presence
farther south.
Слайд 5Interesting Facts
The arctic fox has the warmest
fur, even warmer than
the polar
bear and arctic wolf.
Arctic fox feed primarily on small mammals (млекопитающиеся), including lemmings and tundra voles (полевка), also seabirds such as puffins (буревестники), and murres (кайры).
bear and arctic wolf.
Arctic fox feed primarily on small mammals (млекопитающиеся), including lemmings and tundra voles (полевка), also seabirds such as puffins (буревестники), and murres (кайры).
Слайд 6Interesting Facts
Arctic fox can be either gray-blue or white.
As summer begins, the arctic fox sheds its white coat for a brown one. Foxes of the blue coloring remain dark colored all year but become a little lighter in winter.
Слайд 7Interesting Facts
Hunting:
Arctic fox walk along on top of the snow listening
for
the small creatures under the snow. When they
hear one they jump up and down to break through
the snow with their
front paws. Once
the snow is broken
they can grab their
prey (добыча).
hear one they jump up and down to break through
the snow with their
front paws. Once
the snow is broken
they can grab their
prey (добыча).
Слайд 10 The caribou is a member of the deer family.
Although the caribou looks like a deer, they are different from other members of their family in many ways. They are capable of sleeping in water, and are herd (стадо) animals that are always on the move. This tamable (укротимый) animal likes to eat moss (мох) and lay in the shade.
Слайд 11Interesting Facts
They live throughout the arctic tundra of Russia, Alaska, Canada
and Greenland.
Eat moss and lichen (лишайники).
Caribous are wild, if they are domesticated they are called reindeer
[ˈreɪndɪə].
Eurasians do not use
the name caribou at all,
they use the terms wild
and domestic reindeer.
Eat moss and lichen (лишайники).
Caribous are wild, if they are domesticated they are called reindeer
[ˈreɪndɪə].
Eurasians do not use
the name caribou at all,
they use the terms wild
and domestic reindeer.
Слайд 12Interesting Facts
When the caribou eats,
the food goes down to
the caribou’s first
stomach, where it is
mashed into small balls
called cud and stored to
eat at the caribou’s next meal.
the food goes down to
the caribou’s first
stomach, where it is
mashed into small balls
called cud and stored to
eat at the caribou’s next meal.
Слайд 13Interesting Facts
The caribou has a very warm very soft fur that
sheds (сбрасывать, избавляться) water and snow. The caribou population kept dropping because of overhunting until laws were passed to protect it.
The caribou is color blind
Caribou eat large quantities of food to increase their internal heat production.
The caribou is color blind
Caribou eat large quantities of food to increase their internal heat production.
Слайд 16
The lemming is one
of
the most interesting
Arctic animals
because of how it
has adapted to the cold Arctic temperatures. It is a small rodent (грызун) that burrows under the snow or ground making extensive runways. The lemming grows enlarged claws on the third and fourth 'fingers' of its front feet.
of
the most interesting
Arctic animals
because of how it
has adapted to the cold Arctic temperatures. It is a small rodent (грызун) that burrows under the snow or ground making extensive runways. The lemming grows enlarged claws on the third and fourth 'fingers' of its front feet.
Слайд 17Interesting Facts
The lemming has smaller ears and tails than other rodents.
The lemming is the only true rodent that turns white in the winter.
Live only in the Arctic tundra.
In summer their main foods are shoots (побеги)
of grasses and shrubs (кусты).
During the winter they eat bark
and twigs (ветки) off willow
(ива) and birch (береза).
Live only in the Arctic tundra.
In summer their main foods are shoots (побеги)
of grasses and shrubs (кусты).
During the winter they eat bark
and twigs (ветки) off willow
(ива) and birch (береза).
Слайд 18Interesting Facts
They build their nests with dry grasses, feathers, and fur.
The number of lemmings reduces and grows depending on how much food (plants) is available.
The collared lemming is so important as a food source in the Arctic.
Слайд 21 Polar bears live only in the northern Arctic where
they spend most of their time on ice floes (ледники). They are the largest land meat-eater in the world and the largest of the bear family. They are well suited to the cold Arctic ice and snow.
Слайд 22Interesting Facts
The polar bear has many unique adaptations for dealing with
the Arctic cold. The polar bear's skin is actually black, which allows it to soak up as much heat as possible from
the sun. They are
also great swimmers.
They have been seen
swimming 50 miles
away from any ice or
land.
the sun. They are
also great swimmers.
They have been seen
swimming 50 miles
away from any ice or
land.
Слайд 23Interesting Facts
Eats mostly seals (тюлень). They will occasionally eat other
mammals, eggs, vegetation and carrion (падаль). Polar bears don't drink water. They get all the liquids that they need from the animals that they eat.
Polar bears find a seal air hole and sneak up on (красться) it slowly and sit there until a seal comes up to breathe and then they scoop (копать, вычерпывать) him right out of the hole.
Polar bears are usually solitary (одинокий)
Polar bears find a seal air hole and sneak up on (красться) it slowly and sit there until a seal comes up to breathe and then they scoop (копать, вычерпывать) him right out of the hole.
Polar bears are usually solitary (одинокий)
Слайд 24Interesting Facts
Polar bear hide (шкура) is very useful it can be
used as clothing, rugs, and blankets (одеяла). Polar bear meat can also be eaten.
Слайд 27Walruses are pinnipeds (ластоногие). Walruses are the largest pinnipeds in the
Arctic and Subarctic areas. They like to live in shallow water by ice floes or land. There are two types of walrus - the Pacific and the Atlantic.
The walrus migrate in the spring and fall following the food.
The walrus migrate in the spring and fall following the food.
Слайд 28Interesting Facts
Distinguishing Characteristics: Tusks (клыки), whiskers, and sounds they make.
Eat clams
(моллюски), snails, crabs, shrimp and worms.
You can tell how old a walrus is by the number of rings you can find in a cross-section of its
teeth. Most walrus don't
die from old age but from
hunting. The longer the
walrus tusk is the more
important their rank in
their group.
You can tell how old a walrus is by the number of rings you can find in a cross-section of its
teeth. Most walrus don't
die from old age but from
hunting. The longer the
walrus tusk is the more
important their rank in
their group.
Слайд 29Interesting Facts
Walrus walk on all four fins. He can even move
on land as fast as a man can run.
The walrus' skin is very wrinkly (морщинистый). These wrinkles are like armor and protect the walrus.
Living in the Arctic is not hard for the walrus to do because they have blubber under their skin. Blubber is their body fat.
The walrus' skin is very wrinkly (морщинистый). These wrinkles are like armor and protect the walrus.
Living in the Arctic is not hard for the walrus to do because they have blubber under their skin. Blubber is their body fat.
Слайд 30Interesting Facts
The walrus have big whiskers. They use their whiskers to
feel around until they find food.
The arctic people use the walrus for many things. The meat is eaten by the villagers and fed to the dogs.They use the ivory tusks and carve (вырезать) beautiful pictures on them and make a lot of different
objects with them like
necklaces (ожерелья).
The arctic people use the walrus for many things. The meat is eaten by the villagers and fed to the dogs.They use the ivory tusks and carve (вырезать) beautiful pictures on them and make a lot of different
objects with them like
necklaces (ожерелья).
Слайд 32Despite it’s name, the wolverine is not related to the wolf.
The wolverine is related to the weasel (ласка) and like most weasels the wolverine is scarcely seen. There are people who have spent years in the Alaskan wild and never seen one. Although you may not see them, you can smell them because like
most weasels the
wolverine has glands
that it often uses to
mark territory. The
wolverine is very fierce,
fearless and protective
of it’s young.
most weasels the
wolverine has glands
that it often uses to
mark territory. The
wolverine is very fierce,
fearless and protective
of it’s young.
Слайд 33Interesting Facts
The wolverine
doesn’t eat more
than
he needs. If he
kills a caribou or bear
he will bury it. Later
he will come back and
finish it.
Although the Alaska natives don’t let any part of the wolverine go to waste, they prize the soft warm fur to keep them warm in subzero temperatures.
kills a caribou or bear
he will bury it. Later
he will come back and
finish it.
Although the Alaska natives don’t let any part of the wolverine go to waste, they prize the soft warm fur to keep them warm in subzero temperatures.
Слайд 34Interesting Facts
The wolverine has bad eyesight, is slow, and clumsy (неуклюжий).
The wolverines bad eyesight and slow pace requires it to hunt in an ambush (засада) type way.
Going as fast as possible helps the wolverine stay on top
of the snow. This
MUST be done or it
can’t cover the
distance it has to for
finding food.
Going as fast as possible helps the wolverine stay on top
of the snow. This
MUST be done or it
can’t cover the
distance it has to for
finding food.
Слайд 37 These mammals are well adapted to live in the
water for a good portion of their lives, but they are capable of moving about on land. Seals are much more vulnerable (уязвимый) to predators (хищники) when not in the water.
There are many species of seals living in the tundra biome,
including harp,
gray, Weddell,
elephant and ribbon
seals.
There are many species of seals living in the tundra biome,
including harp,
gray, Weddell,
elephant and ribbon
seals.
Слайд 38Interesting Facts
Eat shellfish (моллюски) and smaller fish.
Arctic seals have thick
layers of fat called blubber that protects their internal organs from coldThe fur is thick but short.
Seals can hold their breath for a long time underwater and dive very deep by letting air out of their lungs.
Seals can hold their breath for a long time underwater and dive very deep by letting air out of their lungs.
Слайд 39Interesting Facts
Harp, ribbon, ringed, leopard
and spotted seals are
named for the different
markings they have on their coats. After molting (линька), harp seals usually have a distinctive black harp (вееробразный) pattern. Ribbon seals and ringed seals have lighter marks on their dark coats. Leopard seals have dark spots on their tan (жёлто-коричневый) or brown coats, and spotted seals have light gray or white spots on dark gray or black coats.
markings they have on their coats. After molting (линька), harp seals usually have a distinctive black harp (вееробразный) pattern. Ribbon seals and ringed seals have lighter marks on their dark coats. Leopard seals have dark spots on their tan (жёлто-коричневый) or brown coats, and spotted seals have light gray or white spots on dark gray or black coats.
Слайд 40Interesting Facts
Seals are different from sea lions in specific ways. Sea
lions can walk on their back flippers, but seals pull themselves over land using only their front flippers. Sea lions also have flaps (заслонка) that cover their ears, but seals' ears are flat (плотно прилегающий) to their head without flaps. Having flat ears enables seals to swim faster.







![Презентация по английскому языку на тему Arctic animals Caribou (карибу) [ˈkærɪbu:] Caribou (карибу) [ˈkærɪbu:]](/img/thumbs/3da08eabb0a864bafd7ffb7de1045f42-800x.jpg)













![Презентация по английскому языку на тему Arctic animals Walrus (морж) [ˈwɔ:lrəs] Walrus (морж) [ˈwɔ:lrəs]](/img/thumbs/a078cfcd9d1aaf355a7adef071cc5d53-800x.jpg)




![Презентация по английскому языку на тему Arctic animals Wolverine (росомаха) [ˈwulvəri:n] Wolverine (росомаха) [ˈwulvəri:n]](/img/thumbs/2bc822a0c90a24868e3edfd3c52666bf-800x.jpg)