near a small Ukrainian town of Chernobyl was affected by the largest-scale radiation-related manmade catastrophe in the history of humankind. The devastating tragedy left around five million suffering who lived in the area encompassing five thousand towns and villages of today’s Belarus, Russia and Ukraine… Radioactive cesium and strontium with half-life of 28 and 30 years contaminated around 150,000 square kilometers across the territories of the three countries. A total of 17 European countries were affected by the radioactive fall-outs.
- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад Environmental problems
Содержание
- 1. Презентация Environmental problems
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. Слайд 3
- 4. At night between 25 and 26 April
- 5. Currently, a new National Programme is drafted for
- 6. Not only Chernobyl but many of our
- 7. Global warming Global warming process of the gradual
- 8. The hole in the ozone layerOzone absorbs
- 9. Land degradationWater and wind erosion are now
- 10. During the 17th and 18th centuries, Easter
- 11. The loss of soil fertility due to
- 12. Prevention and remediationThe most effective known method
- 13. ResultsAs many as 159 countries — members
At night between 25 and 26 April 1986, a nuclear station near a small Ukrainian town of Chernobyl was affected by the largest-scale radiation-related manmade catastrophe in the history of humankind. The devastating tragedy left around
Слайд 5 Currently, a new National Programme is drafted for the mitigation of Chernobyl
after-effects for the years 2011-2015. Its major goal will be to rehabilitate and develop the affected areas socially and economically, maintain the required level of safety for the suffering citizens and radiation safety. The principal task of the current programme is to move away from the rehabilitation efforts in most critical directions of the mitigation towards social and economic revival and sustainable development of the affected areas.
Слайд 6Not only Chernobyl but many of our «peaceful» factories and towns
cause a great damage to the environment. Dangerous dust and blow-outs of the enterprises are being carried out by winds for long distances destroying the life around. People all over the world are worried about what is happening to the environment. They understand that the earth is their home, a big green home. The environment protection should be our universal concern.
Слайд 7 Global warming
Global warming process of the gradual increase fair-annual temperature of
the atmosphere of the Land and World ocean.
The Scientist were defined: uncontrolled surges in atmosphere and other thoughtless behaviour of the person was a reason of the steady change the climate, capable completely to change the planet. The Danger of the global catastrophe has acknowledged the government and folk of the developed countries of the world.
The Scientist were defined: uncontrolled surges in atmosphere and other thoughtless behaviour of the person was a reason of the steady change the climate, capable completely to change the planet. The Danger of the global catastrophe has acknowledged the government and folk of the developed countries of the world.
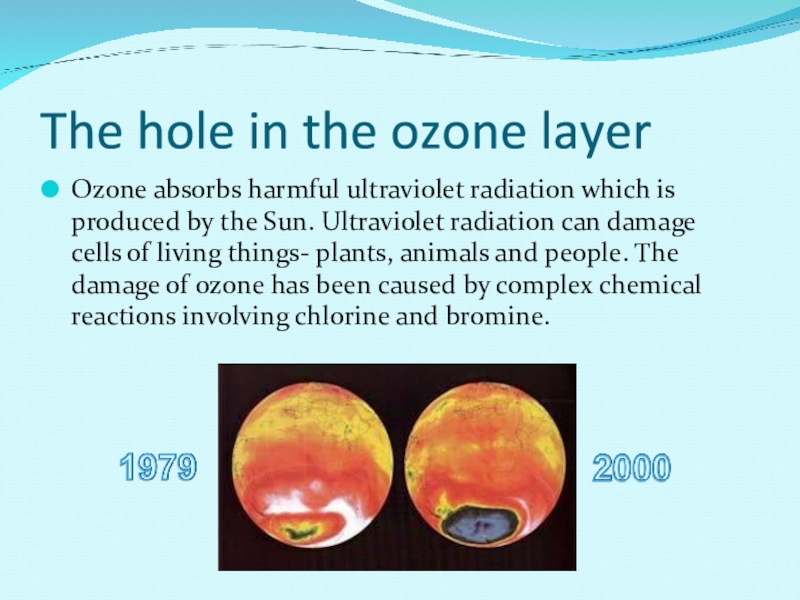
Слайд 8The hole in the ozone layer
Ozone absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation which
is produced by the Sun. Ultraviolet radiation can damage cells of living things- plants, animals and people. The damage of ozone has been caused by complex chemical reactions involving chlorine and bromine.
Слайд 9Land degradation
Water and wind erosion are now the two primary causes
of land degradation; combined, they are responsible for 84% of degraded acreage. Each year, about 75 billion tons of soil is eroded from the land—a rate that is about 13-40 times as fast as the natural rate of erosion. Approximately 40% of the world's agricultural land is seriously degraded. According to the United Nations , an area of fertile soil the size of Ukraine is lost every year because of drought, deforestation and climate change. In Africa, if current trends of soil degradation continue, the continent might be able to feed just 25% of its population by 2025, according to UNU's Ghana-based Institute for Natural Resources in Africa.
Слайд 10During the 17th and 18th centuries, Easter Island experienced severe erosion
due to deforestation and unsustainable agricultural practices. The resulting loss of topsoil ultimately led to ecological collapse, causing mass starvation and the complete disintegration of the Easter Island civilization.
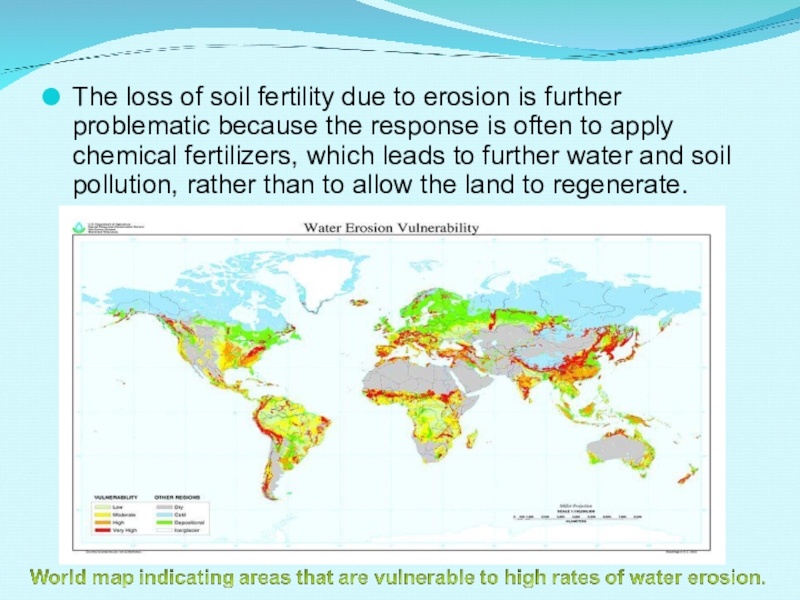
Слайд 11The loss of soil fertility due to erosion is further problematic
because the response is often to apply chemical fertilizers, which leads to further water and soil pollution, rather than to allow the land to regenerate.
Слайд 12Prevention and remediation
The most effective known method for erosion prevention is
to increase vegetative cover on the land, which helps prevent both wind and water erosion. Terracing is an extremely effective means of erosion control, which has been practiced for thousands of years by people all over the world.
Слайд 13Results
As many as 159 countries — members of the UNO have
set up environmental protection agencies. Numerous conferences have been held to discuss questions of ecologically poor regions including the Aral Sea, the South Urals, Kuzbass, Donbass, Semipalatsinsk and Chernobyl.