- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад на тему Байкальские заповедники
Содержание
- 1. Байкальские заповедники
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. Geographical positionBaikal Nature Reserve covers the central
- 4. ReliefRelief Baikal mountain region is a
- 5. СlimateThe climatic conditions of the reserve depends
- 6. Hydrology Within the
- 7. SoilReserve soil has good natural water-physical and site characteristics, ensuring the proper functioning of ecosystems.
- 8. Flora On the northern slopes of the
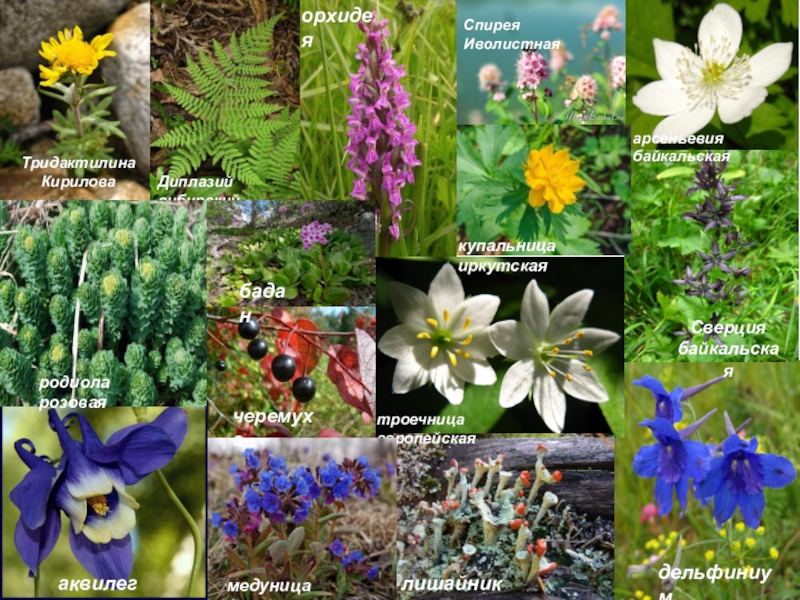
- 9. дельфиниумлишайникиСверция байкальскаяарсеньевия байкальскаятроечница европейскаямедуница дакийскаячеремухакупальница иркутскаяТридактилина КириловаДиплазий сибирскийаквилегияСпирея Иволистнаяродиола розоваяорхидеябадан
- 10. FaunaThe fauna of the reserve is very
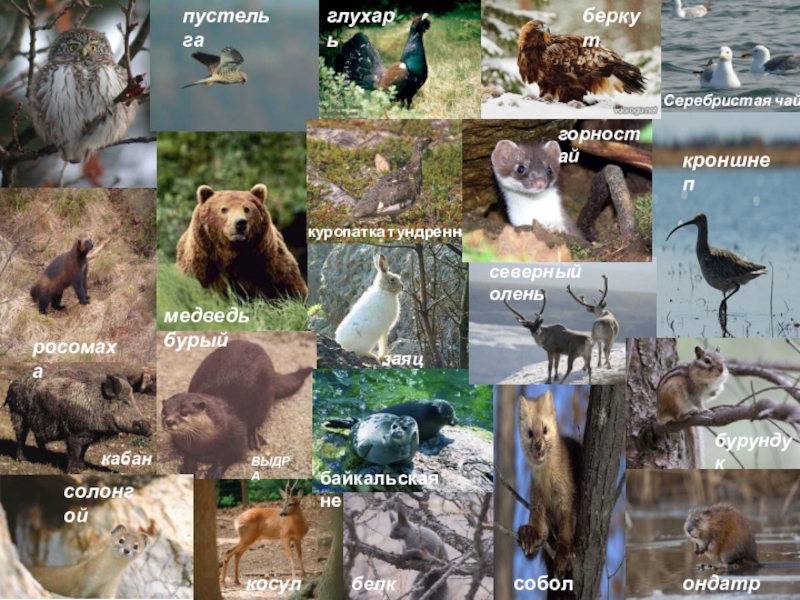
- 11. солонгойпустельгавыдракабан косулясобольмедведь бурыйглухарькуропатка тундренная заяц белякбайкальская нерпаберкутсеверный оленьгорностайондатрабелкабурундукСеребристая чайкаросомахакроншнеп
- 12. The main threats to natural complexes and
About reserves Reserve - one of the categories of protected natural areas of federal significance, completely withdrawn from economic use for the conservation of natural processes
Слайд 2 About reserves Reserve
- one of the categories of protected natural areas of federal significance, completely withdrawn from economic use for the conservation of natural processes and phenomena, and rare species of plants and animals
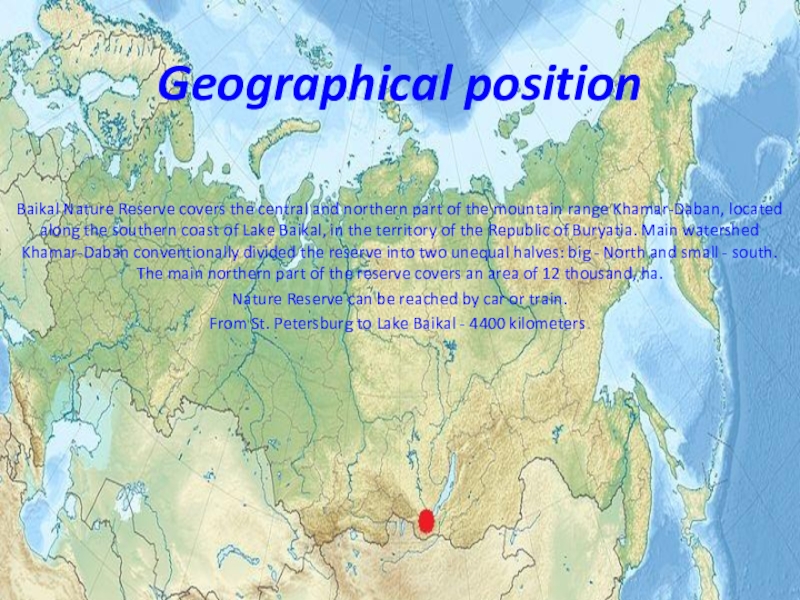
Слайд 3Geographical position
Baikal Nature Reserve covers the central and northern part of
the mountain range Khamar-Daban, located along the southern coast of Lake Baikal, in the territory of the Republic of Buryatia. Main watershed Khamar-Daban conventionally divided the reserve into two unequal halves: big - North and small - south. The main northern part of the reserve covers an area of 12 thousand, ha.
Nature Reserve can be reached by car or train.
From St. Petersburg to Lake Baikal - 4400 kilometers.
Nature Reserve can be reached by car or train.
From St. Petersburg to Lake Baikal - 4400 kilometers.
Слайд 4 Relief
Relief Baikal mountain region is a complex construction system and
middle mountainous ridges and deep intermountain basins. Characteristic features of the terrain - an arcuate shape and direction echelon ridges and intermontane basins.
Chief Khamar-Daban, reaches a height of 2000-2300 m above sea level. m. The top of his largely aligned, with gentle slopes. Spurs ridge, sloping down to the north and south, are cut by narrow river valleys. Often rocky slopes, a lot of rock slides. To the north slope is characterized by sharp alpine landforms with circuses and canyons south has a smoother relief.
Chief Khamar-Daban, reaches a height of 2000-2300 m above sea level. m. The top of his largely aligned, with gentle slopes. Spurs ridge, sloping down to the north and south, are cut by narrow river valleys. Often rocky slopes, a lot of rock slides. To the north slope is characterized by sharp alpine landforms with circuses and canyons south has a smoother relief.
Слайд 5Сlimate
The climatic conditions of the reserve depends on the geographical location,
its orography, the dominant atmospheric flows, but the most significant is the impact of a huge water mass of Baikal.
Forming a kind of climate on the northern macro-slope largely contribute to north-westerly winds, which cause heavy precipitation and continental climate mitigation. The average temperature in January is -17,9 ° C, in July - 14, HS.
The climate of the southern macro Khamar-Daban is very different from the north. Winter is little snow, summers are hot and dry. The average temperature in July - + 18-19 ° C, in January + 26-27 ° C. The annual rainfall is less than 400 mm.
Forming a kind of climate on the northern macro-slope largely contribute to north-westerly winds, which cause heavy precipitation and continental climate mitigation. The average temperature in January is -17,9 ° C, in July - 14, HS.
The climate of the southern macro Khamar-Daban is very different from the north. Winter is little snow, summers are hot and dry. The average temperature in July - + 18-19 ° C, in January + 26-27 ° C. The annual rainfall is less than 400 mm.
Слайд 6Hydrology
Within the reserve is more
than 160 small and large lakes:
- The depth of the lakes varies from 1 to 50 meters;
- Surface area from 0.1 to 25 m.
The most abundant river Temnyk has a width of 10 to 40 and a depth of 0.8 to 2.5 meters, considerably exceeding the specified value during floods.
- The depth of the lakes varies from 1 to 50 meters;
- Surface area from 0.1 to 25 m.
The most abundant river Temnyk has a width of 10 to 40 and a depth of 0.8 to 2.5 meters, considerably exceeding the specified value during floods.
Слайд 7Soil
Reserve soil has good natural water-physical and site characteristics, ensuring the
proper functioning of ecosystems.
Слайд 8Flora
On the northern slopes of the Khamar-Daban prevails dark coniferous
taiga fir and cedar. In some places there birch, somewhere common spruce. In the valleys of the common birch and poplar plantations with dense undergrowth of wild cherry, rowan, alder. In deciduous forests and meadows abundant developing grasses and ferns; large areas are covered berries.
On the southern slopes of the Khamar-Daban more common light coniferous larch, pine and cedar-larch taiga. In river valleys - birch and aspen forests, and their headwaters are found pure cedar. All in the flora of the reserve of about 800 species of vascular plants.
On the southern slopes of the Khamar-Daban more common light coniferous larch, pine and cedar-larch taiga. In river valleys - birch and aspen forests, and their headwaters are found pure cedar. All in the flora of the reserve of about 800 species of vascular plants.
Слайд 9дельфиниум
лишайники
Сверция байкальская
арсеньевия байкальская
троечница европейская
медуница дакийская
черемуха
купальница иркутская
Тридактилина Кирилова
Диплазий сибирский
аквилегия
Спирея Иволистная
родиола розовая
орхидея
бадан
Слайд 10Fauna
The fauna of the reserve is very typical for the mountains
of southern Siberia. A peculiarity of the fauna is that it contains species of animals, especially birds, originating in the deep areas of Central Asia. ? Ichthyofauna reserve includes 17 species. The main ones are grayling, goldilocks and trout. All these species enter rivers for spawning and feeding period, at the end of the summer, they migrate into the lake and spend the winter in the lake. An exception is the river Temnik where grayling, goldilocks, burbot, and perhaps trout are able to live and winter.
Слайд 11солонгой
пустельга
выдра
кабан
косуля
соболь
медведь бурый
глухарь
куропатка тундренная
заяц беляк
байкальская нерпа
беркут
северный олень
горностай
ондатра
белка
бурундук
Серебристая чайка
росомаха
кроншнеп
Слайд 12The main threats to natural complexes and objects of the reserve
illegal hunting
Illegal fishing
Unlawful presence of citizens and
vehicles on the reserve
forest fires
Illegal fishing
Unlawful presence of citizens and
vehicles on the reserve
forest fires