- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад по теме The Skeleton
Содержание
- 1. Презентация по теме The Skeleton
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. QUESTIONS TO THE CROSSWORDA German physic, who
- 4. R E N
- 5. The aims of the lesson:Learn various parts
- 6. Functions of the skeleton:Support: the skeleton is
- 7. Vocabularybone [boun] кость breastbone[ br’estbəʊːn] грудная кость
- 8. Vocabularyrib [rɪb] реброsacral [s’eɪːkrl] крестцовыйshoulder [ʃouldə] плечоskull
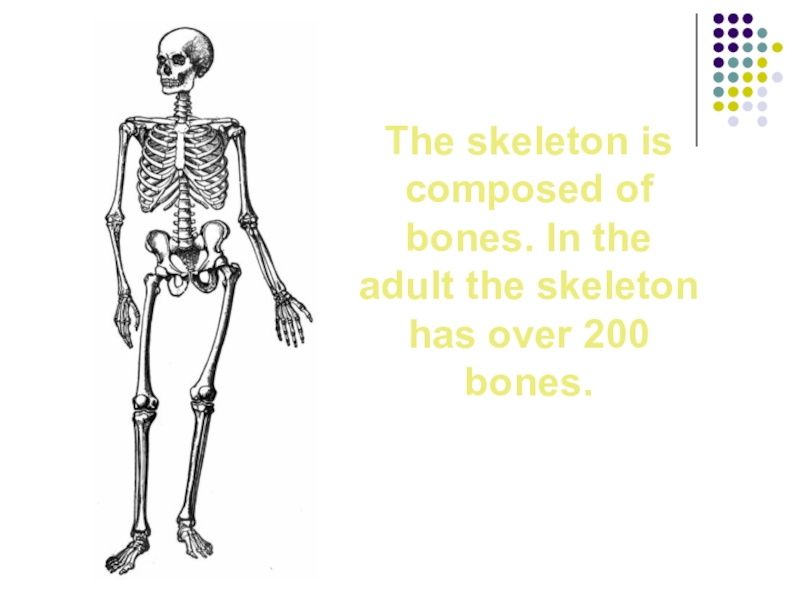
- 9. The skeleton is composed of bones. In the adult the skeleton has over 200 bones.
- 10. The bones of the skull consist of
- 11. The bones of the trunk are the
- 12. The cervical part of the
- 13. Chest The chest (thorax) is
- 14. On each side of
- 15. The upper extremity is formed by
- 16. The lower extremity consist of the
- 17. The bones of the skeleton are connected
- 18. The bones consist of organic and inorganic substance.
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. What are the largest vertebrae in the
- 21. The key1-c2-b3-c4-a5-c6-b7-a8-b9-c10-b
- 22. Think are these statements true or false?The
- 23. Слайд 23
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. The shell of the bonesTo be not
- 26. Слайд 26
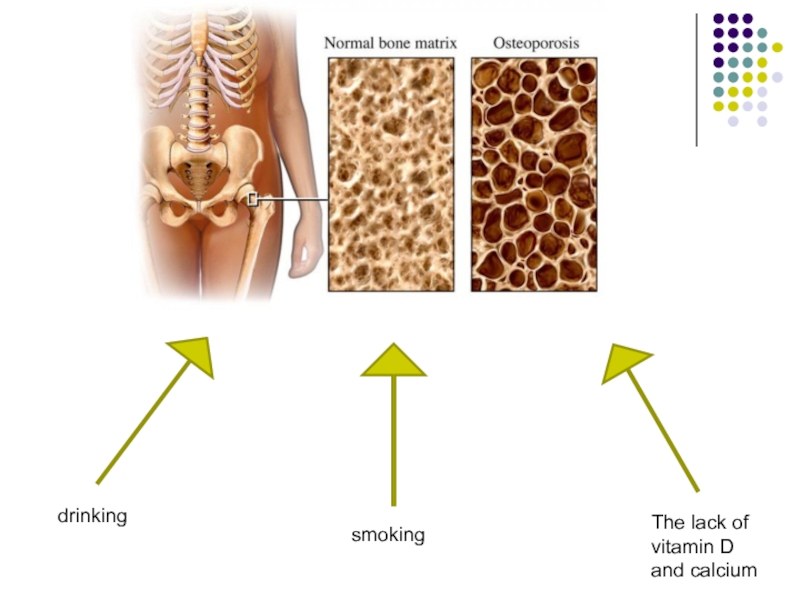
- 27. drinkingsmokingThe lack of vitamin D and calcium
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Answer the questions and make up dialogues
- 30. Слайд 30
- 31. Слайд 31
- 32. Слайд 32
- 33. Слайд 33
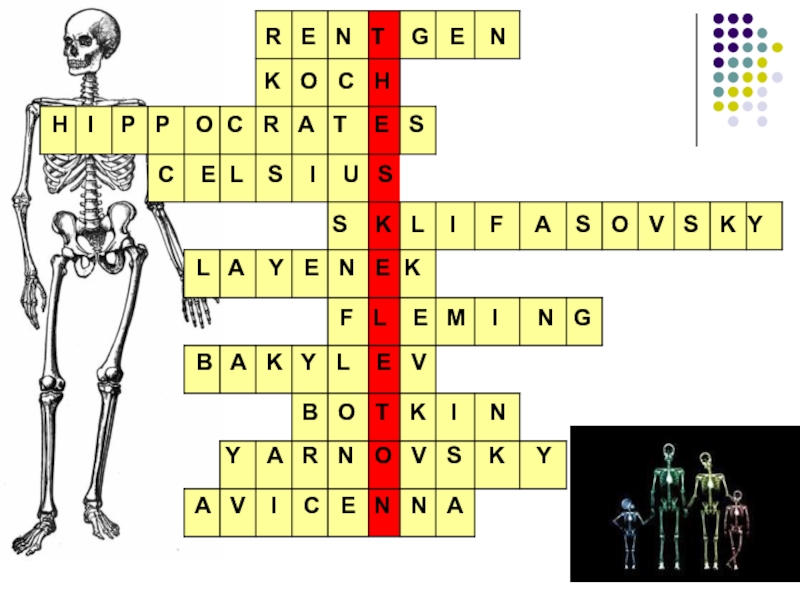
Слайд 3QUESTIONS TO THE CROSSWORD
A German physic, who produced and detected electromagnetic
A prominent German physician, who discovered the tuberculosis bacillus ( a small comma-shaped bacterium)
“The father of medicine”
A Swedish astronomer, who developed a similar temperature scale
A Russian surgeon and physiologist. The Moscow Institute of Emergency First Aid has beard his name since 1923
A Poland physician, who resorted to auscultation as a new method of diagnoses
A Scottish biologist, pharmacologist and botanist, who discovered the antibiotic substance “penicillin”
A prominent Soviet surgeon, one of the founders of cardiovascular surgery in the USSR
A Russian professor of the St. Petersburg academy, the founder of the physiological approach in the Russian medical science
A Russian doctor, made a great contribution to the treatment of venereal diseases
A famous eastern (Persian) medical man, who played an important role in the history of medicine and wrote “The Book of Healing” and “The Canon of Medicine”
Слайд 4
R E N T G
K O C H
H I P P O C R A T E S
S K L I F A S O V S K Y
L A Y E N E K
F L E M I N G
B A K Y L E V
B O T K I N
Y A R N O V S K Y
A V I C E N N A
C E L S I U S
Слайд 5The aims of the lesson:
Learn various parts of the human skeleton.
Review
Pay attention on the process of strengthening of our skeleton.
Summarize and systematize our knowledge on the topic: “The Skeleton”
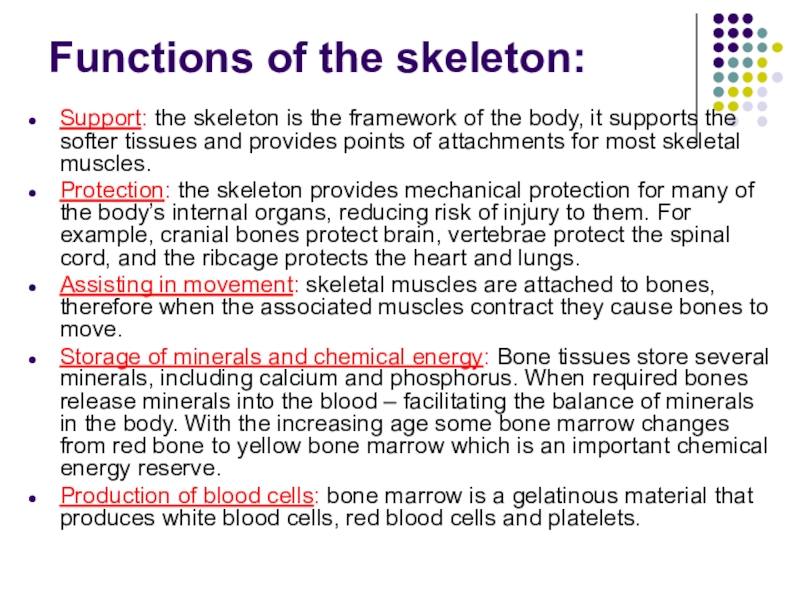
Слайд 6Functions of the skeleton:
Support: the skeleton is the framework of the
Protection: the skeleton provides mechanical protection for many of the body’s internal organs, reducing risk of injury to them. For example, cranial bones protect brain, vertebrae protect the spinal cord, and the ribcage protects the heart and lungs.
Assisting in movement: skeletal muscles are attached to bones, therefore when the associated muscles contract they cause bones to move.
Storage of minerals and chemical energy: Bone tissues store several minerals, including calcium and phosphorus. When required bones release minerals into the blood – facilitating the balance of minerals in the body. With the increasing age some bone marrow changes from red bone to yellow bone marrow which is an important chemical energy reserve.
Production of blood cells: bone marrow is a gelatinous material that produces white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets.
Слайд 7Vocabulary
bone [boun] кость
breastbone[ br’estbəʊːn] грудная кость
cartilage [k’ɑːtɪlɪdʒ] хрящ
cervical
chest [tʃˈest] грудная клетка
coccyx [k’ɒksɪks] копчик
cranial [kr’eɪːnɪəl] черепной
facial [f’eɪːʃl] лицевой
forearm [f’ɔːrɑːm] предплечье
joint [dʒ’ɔɪːnt] сустав
ligament [l’ɪgəmənt] анат. cвязка
lower extremity [louə rɪkstr’emɪti] нижняя конечность
lumbar [l’ʌmbə] поясничный
pelvis [p’elvɪs] таз
Слайд 8Vocabulary
rib [rɪb] ребро
sacral [s’eɪːkrl] крестцовый
shoulder [ʃouldə] плечо
skull [sk’ʌl] череп
spinal column [sp’aɪnl
spine [sp’aɪn] позвоночник
the skeleton [ðə sk’elɪtn̩] скелет
thigh[θ’aɪ] бедро
thoracic [θh’ɔːræsɪk] грудной
thorax [θ’ɔːræks] грудная клетка
trunk [tr’ʌŋk] торс
upper extremity [‘ʌpə rɪkstr’emɪti] верхняя конечность
vertebra [v’ɜːtɪbrə] позвонок
verterbrae [v’ɜːəbrɛɪː] позвонки
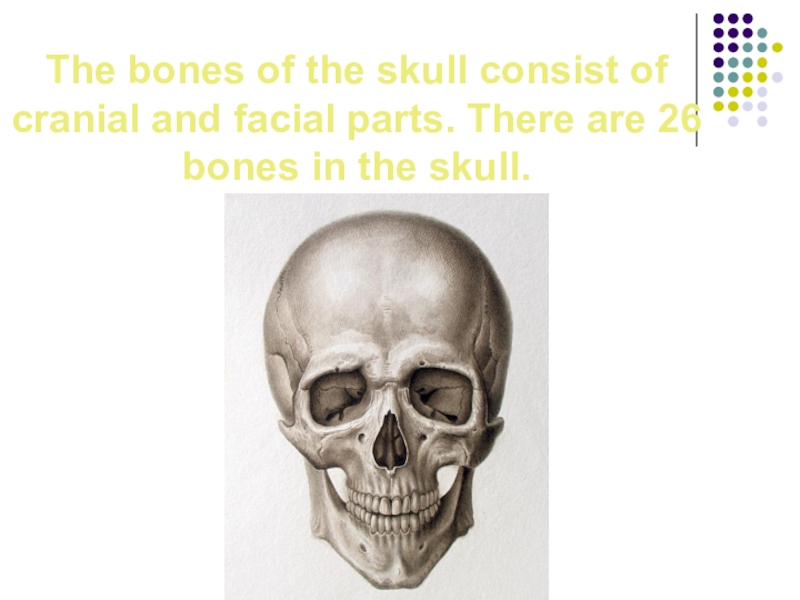
Слайд 10The bones of the skull consist of cranial and facial parts.
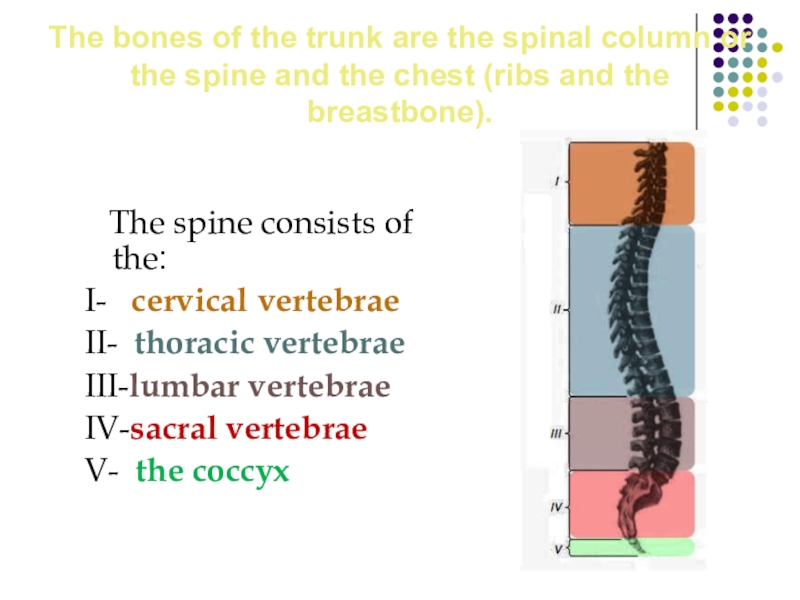
Слайд 11The bones of the trunk are the spinal column or the
The spine consists of the:
I- cervical vertebrae
II- thoracic vertebrae
III-lumbar vertebrae
IV-sacral vertebrae
V- the coccyx
Слайд 12 The cervical part of the spine is formed by
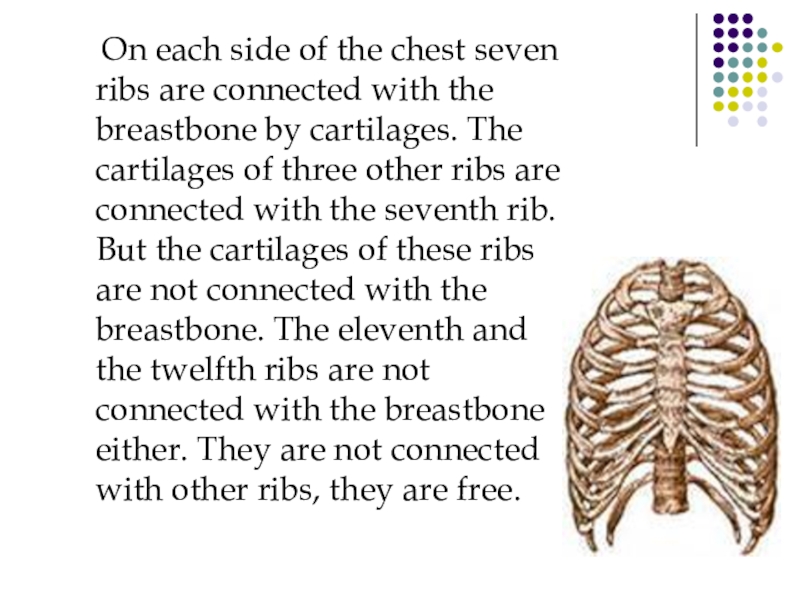
Слайд 13Chest
The chest (thorax) is composed of 12 thoracic
Слайд 14 On each side of the chest seven ribs
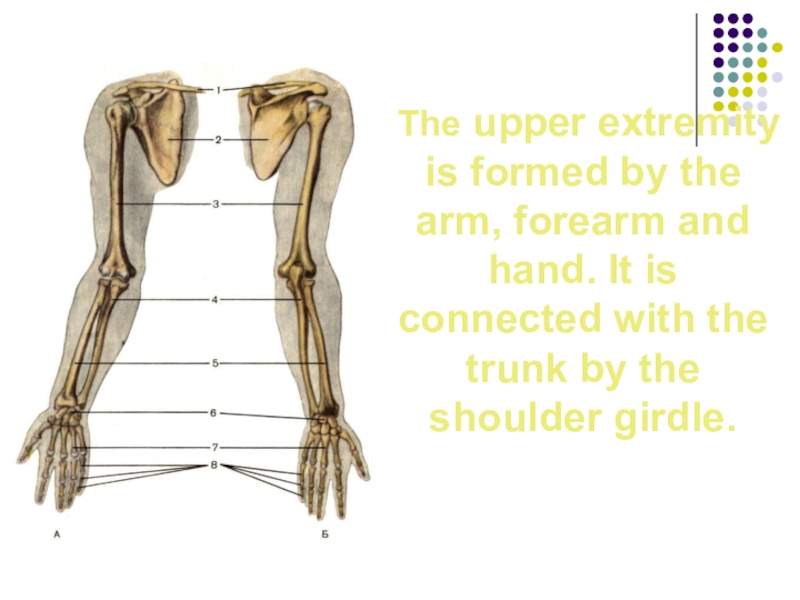
Слайд 15 The upper extremity is formed by the arm, forearm and
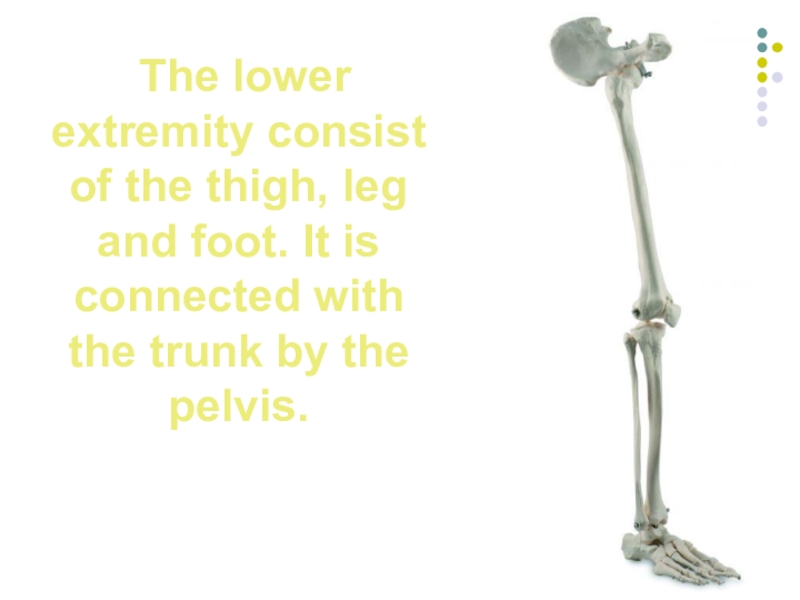
Слайд 16 The lower extremity consist of the thigh, leg and foot.
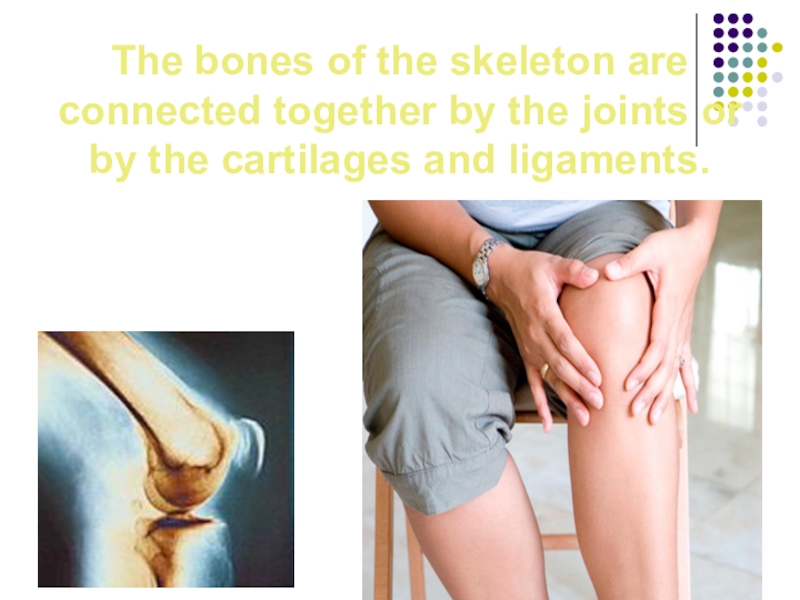
Слайд 17The bones of the skeleton are connected together by the joints
Слайд 19
The skeleton of the adult has over:
250 bones
205 bones
200 bones
All the vertebrae compose
the breastbone
the spine
the pelvis
There are:
10 pairs of rib
2 pairs of ribs
12 pairs of ribs
What ribs are free?
the eleventh and the twelfth
the seventh and the sixth ribs
all the ribs
The bones of the skull consist of:
cranial part
facial part
cranial and facial parts
Слайд 20What are the largest vertebrae in the spinal column?
cervical
lumbar
thoracic
In which way
by pelvis
by shoulder girdle
by ribs
In which way is the upper extremity connected the trunk
by pelvis
by shoulder girdle
by ribs
The basic part of the chest is formed by…
cranial and facial parts
the vertebrae
the ribs
The breastbone is…
a long bone in the middle of the spinal column
a long bone in the middle of the chest
a long bone in the middle of the pelvis.
Слайд 22Think are these statements true or false?
The bones of the skull
The spine consists of the thoracic, cervical lumbar and sacral vertebrae and the coccyx .
The vertebra is a small bone, which is formed by the body and the arches.
The lumbar vertebrae are the smallest vertebrae in the spinal column.
The cartilages of the eleventh and the twelfth ribs are not connected with the breastbone .
Each rib isn’t composed of a head, neck and body.
The bones of the human skeleton are living things.
The lower extremity is connected with the trunk by the shoulder girdle.
The lower extremity is not connected with the trunk the by the shoulder girdle.
The bones consists of organic and inorganic substance .
Слайд 25The shell of the bones
To be not solid enough
To suffer from
To prevent
Measuring the mineral density of a person's bones
The strength of the bones
To advise several steps towards the goal of healthy bones
Слайд 29Answer the questions and make up dialogues
What kind of bones is
Is the spinal column the most important part of the body?
What does the skull include?
The bones of the trunk include the spinal column, the ribs and the breastbone, don’t’ they?
What role do the ribs play?
Is the spinal column formed by the vertebrae?
What is a vertebra?
What does the lower extremity consist of?
By what is the upper extremity connected with the trunk?
In which way are the bones of the skeleton connected together?
What are the functions of the skeleton?
What diseases of bones do you know?
How can a human strengthen the skeleton?
Слайд 32 Home work
To
To make up dialogues about the skeleton; the functions of the skeleton; the diseases of bones and how to strengthen our skeleton.
To explain the meaning of the English proverb: “Every family has a skeleton in the cupboard.”



![Презентация по теме The Skeleton Vocabularybone [boun] кость breastbone[ br’estbəʊːn] грудная кость cartilage [k’ɑːtɪlɪdʒ] хрящ cervical Vocabularybone [boun] кость breastbone[ br’estbəʊːn] грудная кость cartilage [k’ɑːtɪlɪdʒ] хрящ cervical [sɜːv’aɪkl] шейный chest [tʃˈest] грудная клетка](/img/thumbs/7101a93efc5e7d1126ad4351dd86143b-800x.jpg)
![Презентация по теме The Skeleton Vocabularyrib [rɪb] реброsacral [s’eɪːkrl] крестцовыйshoulder [ʃouldə] плечоskull [sk’ʌl] черепspinal column [sp’aɪnl Vocabularyrib [rɪb] реброsacral [s’eɪːkrl] крестцовыйshoulder [ʃouldə] плечоskull [sk’ʌl] черепspinal column [sp’aɪnl k’ɒləm] позвоночный столбspine [sp’aɪn] позвоночникthe skeleton](/img/tmb/5/480858/8d39087e7083ca97fbc8d14137903a0a-800x.jpg)