- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад по английскому языку The Structure of the United States Government
Содержание
- 1. Презентация по английскому языку The Structure of the United States Government
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. Federal GovernmentLegislative branchExecutivebranchJudicialbranchthe Senatethe House of Representativesthe
- 4. QuestionsI Fill the gaps in the following
- 5. II Fill in the chart Federal GovernmentIII
- 6. The Legislative branchVested in the CongressThe Congress:
- 7. The House of Representatives has its special
- 8. II House Standing Committees:
- 9. How a bill is made a law
- 10. QuestionsI Fill in the tableThe CongressThe number
- 11. II Matching
- 12. The Executive branchVested in the President, Vice-President
- 13. The Cabinet includes the secretaries of the
- 14. QuestionsI Fill the gaps The
- 15. The Judicial branchDual court system: Federal judiciary
- 16. QuestionsI Complete the chart The Judicial branchFederal
the US Flag “the stars and stripes & old glory” (1777)
Слайд 2
the US Flag
“the stars and stripes & old glory” (1777)
13 horizontal stripes = 13 original states
50 stars = 50 modern states
Red stripes – courage, white – liberty, a field of blue – loyalty.
the US Coat-of-Arms
an eagle with a bundle of rods in the left claw,
the olive twig – in the right.
the Motto: E pluribus unium (“Out of many”)
the US nickname – “Uncle Sam”
“the stars and stripes & old glory” (1777)
13 horizontal stripes = 13 original states
50 stars = 50 modern states
Red stripes – courage, white – liberty, a field of blue – loyalty.
the US Coat-of-Arms
an eagle with a bundle of rods in the left claw,
the olive twig – in the right.
the Motto: E pluribus unium (“Out of many”)
the US nickname – “Uncle Sam”
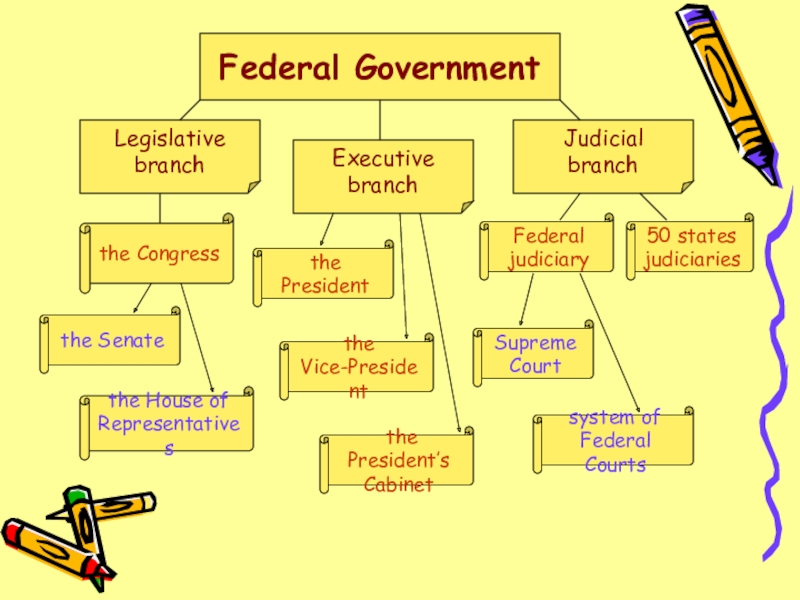
Слайд 3Federal Government
Legislative
branch
Executive
branch
Judicial
branch
the Senate
the House of
Representatives
the Congress
the President
the President’s
Cabinet
the
Vice-President
Federal
judiciary
50 states
judiciaries
Supreme
Court
system of
Federal Courts
Слайд 4Questions
I Fill the gaps in the following sentences:
The flag of the
US called … was adopted in …
The flag of the US consists of … … stripes equal to the number of … …, with a blue union marked with … white stars equal to the number of …
The red stripes proclaim …, the white … and a field of blue …
The Coat-of-arms represents an eagle, holding … of … in the left claw and … … in the right claw.
The motto on the Coat-of-arms is …
The nickname of the US is … …
The flag of the US consists of … … stripes equal to the number of … …, with a blue union marked with … white stars equal to the number of …
The red stripes proclaim …, the white … and a field of blue …
The Coat-of-arms represents an eagle, holding … of … in the left claw and … … in the right claw.
The motto on the Coat-of-arms is …
The nickname of the US is … …
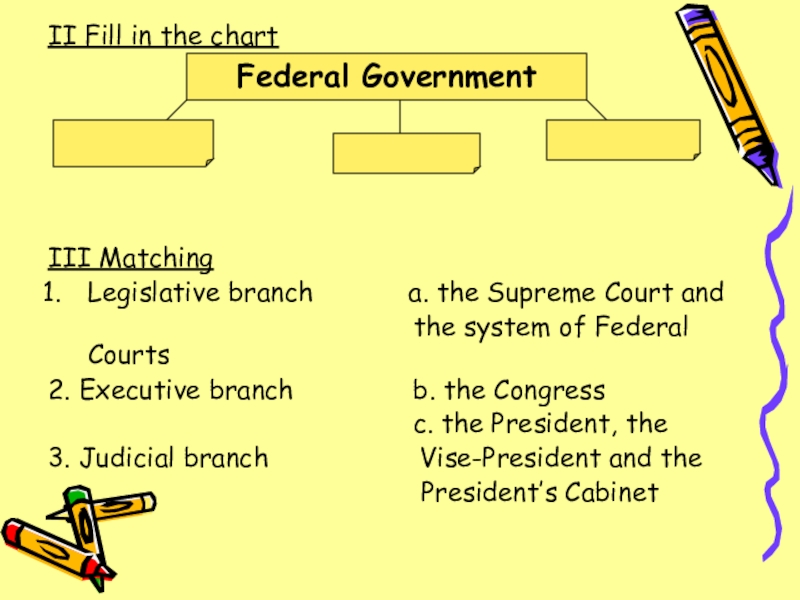
Слайд 5II Fill in the chart
Federal Government
III Matching
Legislative branch
a. the Supreme Court and
the system of Federal Courts
2. Executive branch b. the Congress
c. the President, the
3. Judicial branch Vise-President and the
President’s Cabinet
the system of Federal Courts
2. Executive branch b. the Congress
c. the President, the
3. Judicial branch Vise-President and the
President’s Cabinet
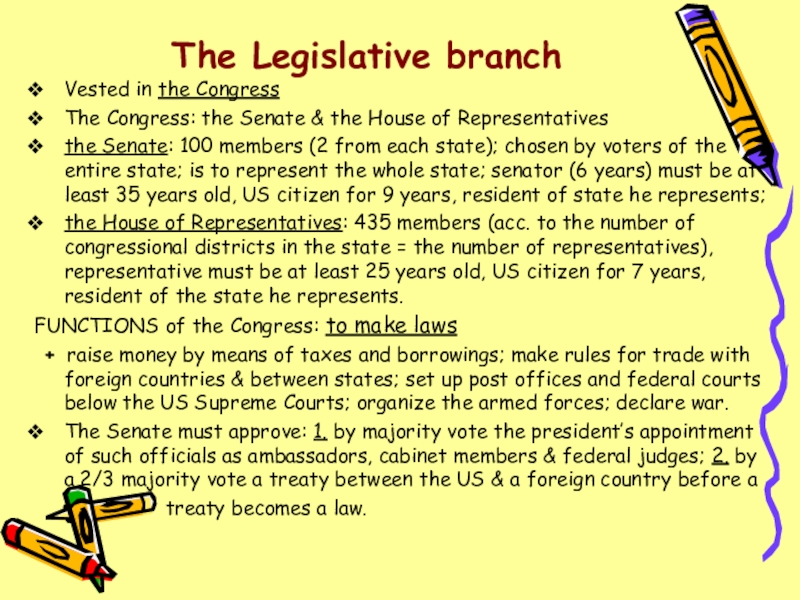
Слайд 6The Legislative branch
Vested in the Congress
The Congress: the Senate & the
House of Representatives
the Senate: 100 members (2 from each state); chosen by voters of the entire state; is to represent the whole state; senator (6 years) must be at least 35 years old, US citizen for 9 years, resident of state he represents;
the House of Representatives: 435 members (acc. to the number of congressional districts in the state = the number of representatives), representative must be at least 25 years old, US citizen for 7 years, resident of the state he represents.
FUNCTIONS of the Congress: to make laws
+ raise money by means of taxes and borrowings; make rules for trade with foreign countries & between states; set up post offices and federal courts below the US Supreme Courts; organize the armed forces; declare war.
The Senate must approve: 1. by majority vote the president’s appointment of such officials as ambassadors, cabinet members & federal judges; 2. by a 2/3 majority vote a treaty between the US & a foreign country before a
treaty becomes a law.
the Senate: 100 members (2 from each state); chosen by voters of the entire state; is to represent the whole state; senator (6 years) must be at least 35 years old, US citizen for 9 years, resident of state he represents;
the House of Representatives: 435 members (acc. to the number of congressional districts in the state = the number of representatives), representative must be at least 25 years old, US citizen for 7 years, resident of the state he represents.
FUNCTIONS of the Congress: to make laws
+ raise money by means of taxes and borrowings; make rules for trade with foreign countries & between states; set up post offices and federal courts below the US Supreme Courts; organize the armed forces; declare war.
The Senate must approve: 1. by majority vote the president’s appointment of such officials as ambassadors, cabinet members & federal judges; 2. by a 2/3 majority vote a treaty between the US & a foreign country before a
treaty becomes a law.
Слайд 7The House of Representatives has its special power. Only a
member
of the House can introduce a bill to raise money but the money raising
bill must be passed by the Senate before it becomes a law.
Most of congressmen work is done in committee meeting where bills are studied, experts are heard & recommendations are made.
During 2-year term 20 000 bills may be introduced 16 standing committees in the Senate & 20 in the House of R. (sift & sort the bills)
The chairman – who has served longest on the committee.
The committees in the Congress are: I Senate Standing Committee:
1) aeronautical space science 8) finance
2) agriculture & forestry 9) foreign relations
3) appropriations 10) government operations
4) armed services 11) interior & insular affair
5) banking & currency 12) judiciary
6) commerce 13) labour & public welfare
7) district of Columbia 14) post office & civil service
15) public works
16) rules & administration
of the House can introduce a bill to raise money but the money raising
bill must be passed by the Senate before it becomes a law.
Most of congressmen work is done in committee meeting where bills are studied, experts are heard & recommendations are made.
During 2-year term 20 000 bills may be introduced 16 standing committees in the Senate & 20 in the House of R. (sift & sort the bills)
The chairman – who has served longest on the committee.
The committees in the Congress are: I Senate Standing Committee:
1) aeronautical space science 8) finance
2) agriculture & forestry 9) foreign relations
3) appropriations 10) government operations
4) armed services 11) interior & insular affair
5) banking & currency 12) judiciary
6) commerce 13) labour & public welfare
7) district of Columbia 14) post office & civil service
15) public works
16) rules & administration
Слайд 8II House Standing Committees:
1) agriculture
11) interstate & foreign commerce
2) appropriations 12) judiciary
3) armed services 13) merchant marine
4) banking & currency 14) post office & civil service
5) district of Columbia 15) public works
6) education & labour 16) rules
7) foreign affair 17) science & aeronautics
8) government operations 18) internal security
9) house administration 19) veterans affairs
10) interior & insular affairs 20) ways & means
2) appropriations 12) judiciary
3) armed services 13) merchant marine
4) banking & currency 14) post office & civil service
5) district of Columbia 15) public works
6) education & labour 16) rules
7) foreign affair 17) science & aeronautics
8) government operations 18) internal security
9) house administration 19) veterans affairs
10) interior & insular affairs 20) ways & means
Слайд 9How a bill is made a law
A Senator/a
Representative introduces a bill → to the clerk of its house, clerk – a number & title – first reading → to the proper committee. May decide unwise/unnecessary – tumble the bill, thus killing it or if it worthwhile & hold hearings. → a vote (if favourable – sent back to the House). Clerk reads to the House – second reading → debates. Third reading – by title only. → a vote → to the other house of Congress (defeated or passed with/ without amendmence) – if defeated – dies, if passed with amendments – Joined Congressional Committee must be appointed to iron the differences → to the President – signs and bill becomes a LAW/ vetoes & sends back.
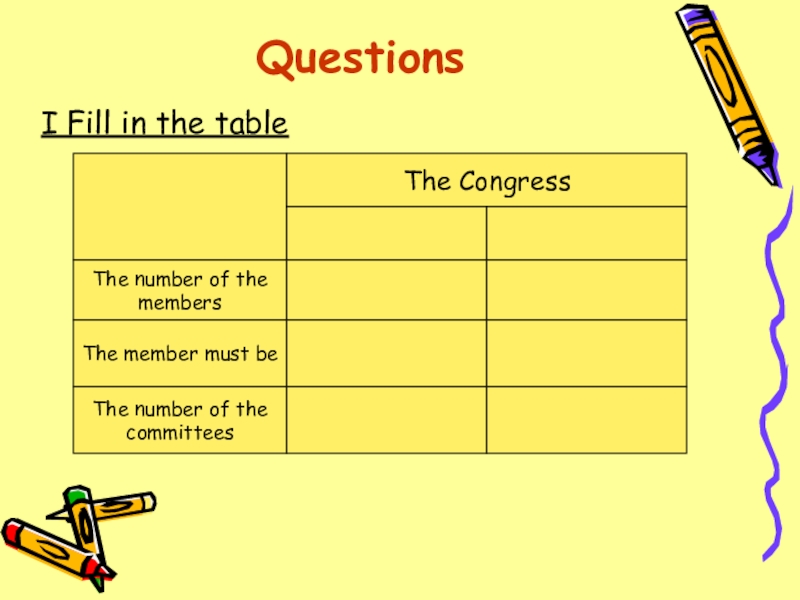
Слайд 10Questions
I Fill in the table
The Congress
The number of the
members
The member
must be
The number of the
committees
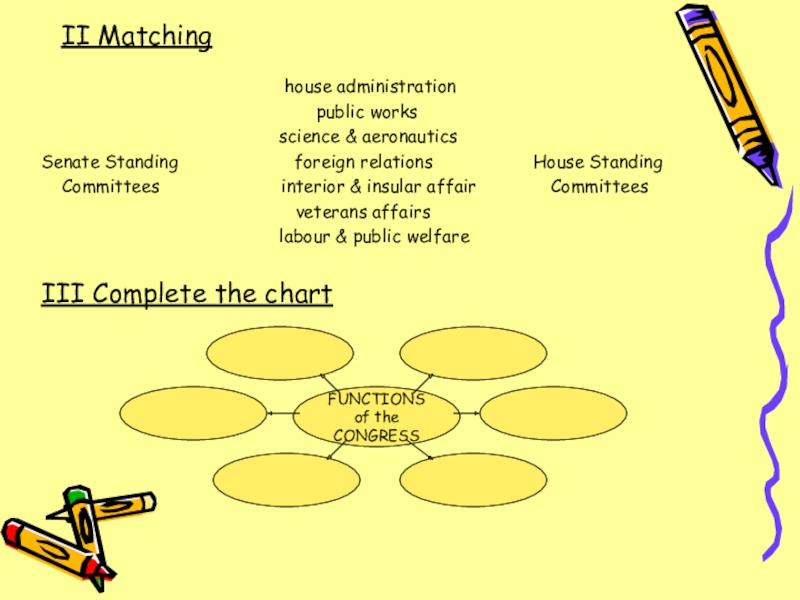
Слайд 11II Matching
house administration
public works
science & aeronautics
Senate Standing foreign relations House Standing
Committees interior & insular affair Committees
veterans affairs
labour & public welfare
III Complete the chart
FUNCTIONS
of the CONGRESS
Слайд 12The Executive branch
Vested in the President, Vice-President & the President’s Cabinet.
responsible for administrating & executing the laws
President – 4 years (begins at noon on January,20). Must be natural born citizen, at least 35, at least 15 years – a resident of the US. Elections are held in 2 stages: 1 – voters choose electors, 2 – voters elect the President. P. administers National Government through instructions to Heads of departments & agencies (appointed & removed by him); appoints higher officers (Cabinet Ministers, ambassadors, federal judges); has initiative in foreign affairs; can’t be forced to make a treaty.
= Commander-in-Chief; can involve the country in a state of war; can reject legislation.
the Vice-President, elected with President for 4 years; presides the Senate; may be used to as a contact man among Senators,
may sit at Cabinet Meetings as an understudy to the
President, takes his place if he’s unable to finish his term.
President – 4 years (begins at noon on January,20). Must be natural born citizen, at least 35, at least 15 years – a resident of the US. Elections are held in 2 stages: 1 – voters choose electors, 2 – voters elect the President. P. administers National Government through instructions to Heads of departments & agencies (appointed & removed by him); appoints higher officers (Cabinet Ministers, ambassadors, federal judges); has initiative in foreign affairs; can’t be forced to make a treaty.
= Commander-in-Chief; can involve the country in a state of war; can reject legislation.
the Vice-President, elected with President for 4 years; presides the Senate; may be used to as a contact man among Senators,
may sit at Cabinet Meetings as an understudy to the
President, takes his place if he’s unable to finish his term.
Слайд 13The Cabinet includes the secretaries of the major 11 executive departments,
who are directly/fully responsible to the President’s Cabinet members meet frequently with the President in the Cabinet Room of the executive officers in the White House as a council of advisers. 11 secretaries are Heads of 11 executive departments:
1. secretary of state 7. secretary of commerce
2. secretary of the treasury 8. secretary of labour
3. secretary of defence 9. secretary of health, education
4. attorney general and welfare
5. secretary of the interior 10. secretary of housing & urban
6. secretary of agriculture development
11. secretary of transportation
There are many independent agencies in the Federal
Government.
1. secretary of state 7. secretary of commerce
2. secretary of the treasury 8. secretary of labour
3. secretary of defence 9. secretary of health, education
4. attorney general and welfare
5. secretary of the interior 10. secretary of housing & urban
6. secretary of agriculture development
11. secretary of transportation
There are many independent agencies in the Federal
Government.
Слайд 14Questions
I Fill the gaps
The executive branch is
vested in …, … and … It is responsible for ... and … the laws. The President is elected for … years. He must be … citizen, at least … years old and for at least … years a resident of the US. Elections are held in 2 stages:
…
…
The … is elected with the President for … years. He presides over …
II Complete the list of the secretaries
*Secretary of state *
* *Secretary of commerce
*Secretary of the treasury *
* *Secretary of labour
*Secretary of defence *
* Secretary of the interior
…
…
The … is elected with the President for … years. He presides over …
II Complete the list of the secretaries
*Secretary of state *
* *Secretary of commerce
*Secretary of the treasury *
* *Secretary of labour
*Secretary of defence *
* Secretary of the interior
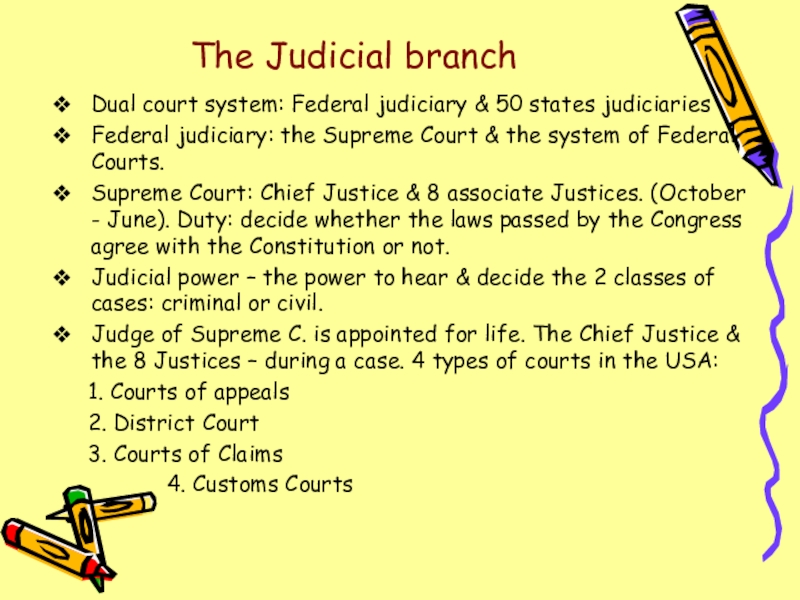
Слайд 15The Judicial branch
Dual court system: Federal judiciary & 50 states judiciaries
Federal
judiciary: the Supreme Court & the system of Federal Courts.
Supreme Court: Chief Justice & 8 associate Justices. (October - June). Duty: decide whether the laws passed by the Congress agree with the Constitution or not.
Judicial power – the power to hear & decide the 2 classes of cases: criminal or civil.
Judge of Supreme C. is appointed for life. The Chief Justice & the 8 Justices – during a case. 4 types of courts in the USA:
1. Courts of appeals
2. District Court
3. Courts of Claims
4. Customs Courts
Supreme Court: Chief Justice & 8 associate Justices. (October - June). Duty: decide whether the laws passed by the Congress agree with the Constitution or not.
Judicial power – the power to hear & decide the 2 classes of cases: criminal or civil.
Judge of Supreme C. is appointed for life. The Chief Justice & the 8 Justices – during a case. 4 types of courts in the USA:
1. Courts of appeals
2. District Court
3. Courts of Claims
4. Customs Courts
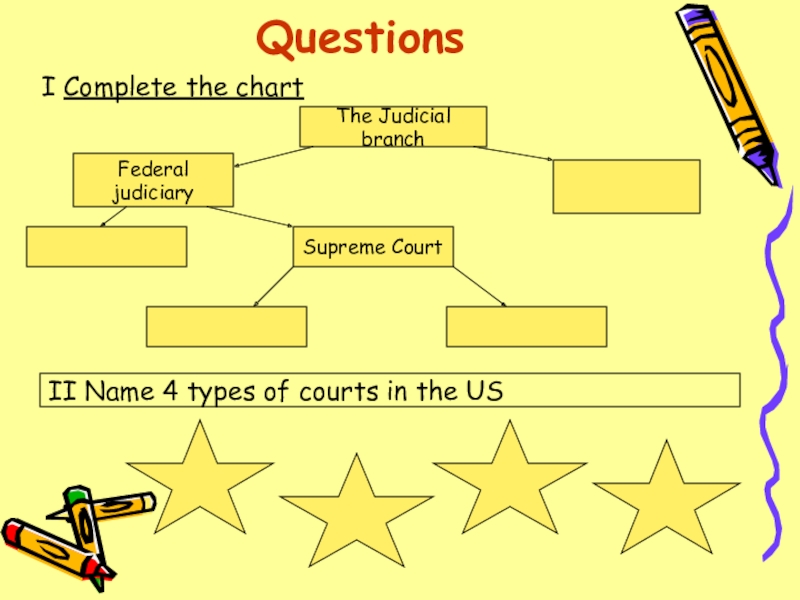
Слайд 16Questions
I Complete the chart
The Judicial branch
Federal
judiciary
Supreme Court
II Name
4 types of courts in the US