Подготовил: учитель английского языка
Шабанова А.М.
МОУ Сергиевская СОШ
- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад по английскому языку на тему: Political system of Great Britain
Содержание
- 1. Презентация по английскому языку на тему: Political system of Great Britain
- 2. God save our gracious Queen,
- 3. ENGLANDIs the largest and
- 4. ENGLANDEngland became a unified state during
- 5. ENGLANDEngland is home to the Royal
- 6. Union JackBritish national flag is
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. The national floral emblem of England Tudor
- 9. Politics in BritainThe political system
- 10. ExecutiveLegislatureCourtBureaucraciesPolitical partiesInterest groupsDomestic economyDomestic cultureDomestic societyU.S.FranceGermanyRussia
- 11. Historical evolution: gradualismHistorical challenges to all industrialized
- 12. Monarch versus Parliament1215:
- 13. Britain is a constitutional monarchy The monarch
- 14. The official name of the British government
- 15. ConstitutionUnlike
- 16. The House of CommonsMP-S are elected by
- 17. The House of LordsMembers are not elected,
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. The Parties
- 20. Parliament
- 21. Government
- 22. Five last prime ministers since…1974-1976
- 23. The most important ministers…
- 24. English Politicians.
- 25. PMs Since 1945 (with
- 26. Margaret ThatcherEconomic stagflation in 1970sNeither party
- 27. Margaret ThatcherServed (1979 - 1990) longer
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Welfare stateEven under Thatcher and
- 30. Margaret Thatcher1979-1984 government spending actually rose from
- 31. Слайд 31
- 32. Tony Blair
- 33. political parties in the UK today:The Labour
- 34. Thank you for attention!
Слайд 1 Political system of
Слайд 2 God save our gracious Queen, Long live
Anthem of Great Britain
Слайд 3 ENGLAND
Is the largest and most populous constituent country
85% of the total population of the United Kingdom live there.
Population: 2006 - est.: 50,690,000
(2001 – census: 49,138,831)
Area: 130,395 km²
Слайд 4 ENGLAND
England became a unified state during the 10th century and
The capital city of England is London, which is the largest city in the British Isles and largest city in the European Union.
It was the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution and was the first country in the world to become industrialised.
Слайд 5 ENGLAND
England is home to the Royal Society, which laid the
England was the world's first parliamentary democracy.
The Kingdom of England was a separate state until 1 May 1707, when the Acts of Union resulted in a political union with the Kingdom of Scotland to create the Kingdom of Great Britain.
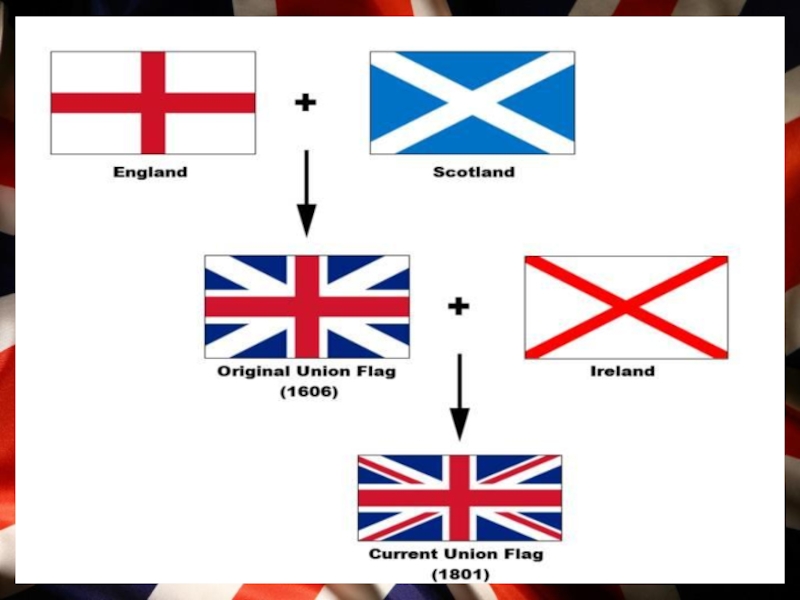
Слайд 6 Union Jack
British national flag is called "Union Jack".
It
The flag is made up of the crosses of the patron saints of:
England (St George's red cross on a white field)
Ireland (St Patrick's red diagonals on a white field)
Scotland (St Andrew's white diagonals on a blue field)
Wales is not represented because when the flag first appeared it was already united with England.
Слайд 8The national floral emblem of England
Tudor Rose was adopted
The rose is used in a variety of contexts in its use for England's representation.
the British Twenty Pence coin
the Royal Coat of Arms
Tudor Rose
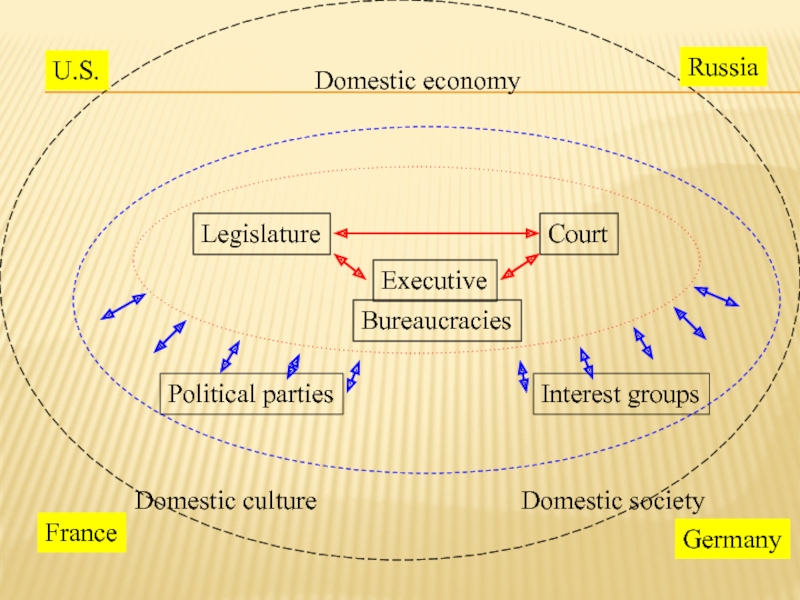
Слайд 10Executive
Legislature
Court
Bureaucracies
Political parties
Interest groups
Domestic economy
Domestic culture
Domestic society
U.S.
France
Germany
Russia
Слайд 11Historical evolution: gradualism
Historical challenges to all industrialized democracies:
Building the nation-state
Defining the
Establishing liberal democracy
Dealing with the impact of the industrial revolution
Слайд 12 Monarch versus Parliament
1215: Magna Carta
1500s: the Church
1642-60: Civil War and Restoration
1688: Glorious Revolution
1701: Act of Settlement
royal succession
Early 1700s: emergence of prime minister
Слайд 13Britain is a constitutional monarchy
The monarch is the Head of
The current monarch is Queen Elizabeth the Second
But the Monarch has no real powers - the role of the monarch is primarily ceremonial
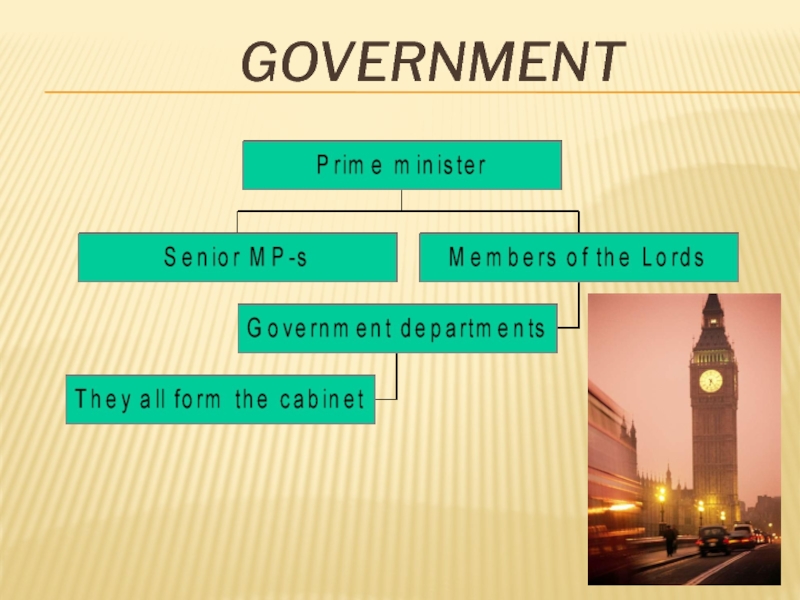
Слайд 14The official name of the British government is Her Majesty’s Government
The
While the Prime Minister is NOT the Head of State he has many of the powers that a Head of State would have, i.e. declaring war
The present Prime Minister is David Cameron
Слайд 15 Constitution
Unlike most countries, Britain does
Britain’s constitution is uncodefied, which means it cannot be found in any single document
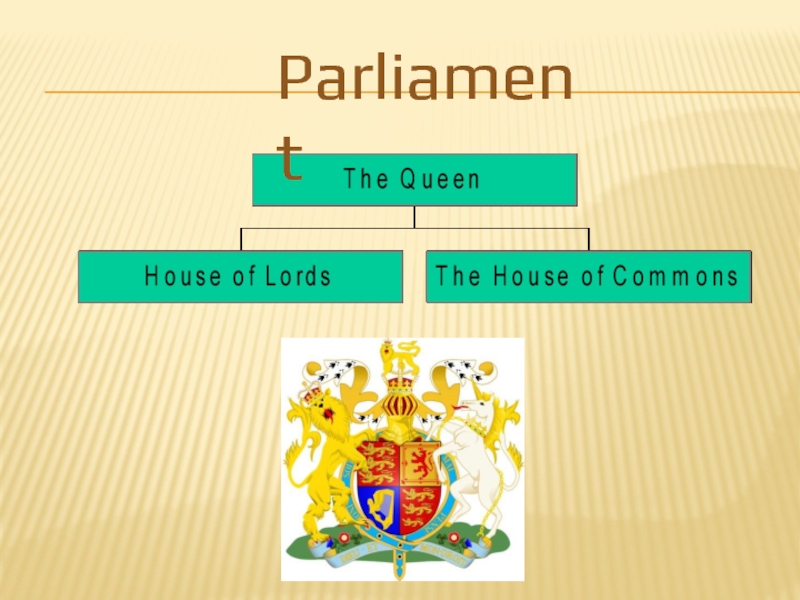
Слайд 16The House of Commons
MP-S are elected by the British public
The House
The chairman is called speaker
Слайд 17The House of Lords
Members are not elected, they inherit their seats
Members are called life peers
Слайд 18 Political
You do not have to belong to a political party to be an MP but most MPs belong to one of the main political parties
Currently the three biggest parties in Britain in terms of MPs:
1) Labour
2) Conservatives
3) Liberal Democrats
Слайд 22 Five last prime ministers since…
1974-1976
1976-1979 James Callaghan Labour
1979-1990 Margaret Thatcher Conservative
1990-1997 John Major Conservative
1997 Tony Blair Labour
Слайд 23 The most important ministers…
Chancellor of the Exchequer
Responsibility
Government spending
Presents the Budget annually in March
Lives at 11 Downing street
Слайд 25 PMs Since 1945 (with ratings
Winston Churchill (1940 – 1945) (C) #1
Clement Attlee (1945 – 1951 (L) #3
Winston Churchill (1951 – 1955) (C) #1
Sir Anthony Eden (1955 (C) #19
Harold Macmillan 1957 – 1963 (C) #6
Sir Alec Douglas – Home 1963 – 1964 (C) #15
Harold Wilson (1964 – 1970) (L) #10
Edward Heath (1970 – 1974 (C) #11
Harold Wilson (1974 – 1976) (L) #10
James Callaghan (1976 – 1979) (L) #12
Margaret Thatcher ( 1979 – 1990) (C) #5
John Major (1990 – 1997) (C) #17
Tony Blair (1997 -- ) (L)
Слайд 26 Margaret Thatcher
Economic stagflation in 1970s
Neither party was able to manage
1978-79 “winter of discontent” strikes
Thatcher’s alternative vision
cut taxes, reduce social services
stimulate the private sector
market and “businesslike” methods
Слайд 27 Margaret Thatcher
Served (1979 - 1990) longer without interruption than any
Слайд 29 Welfare state
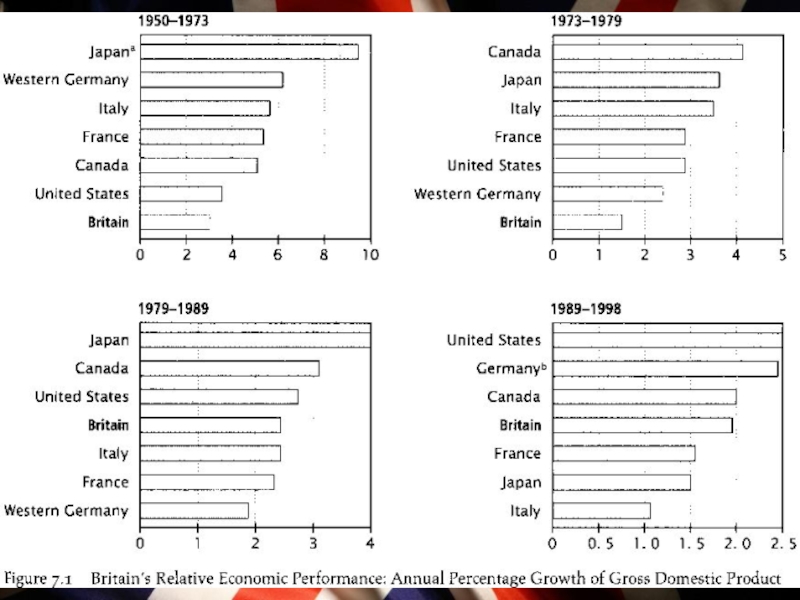
Even under Thatcher and Major, Britain experienced real
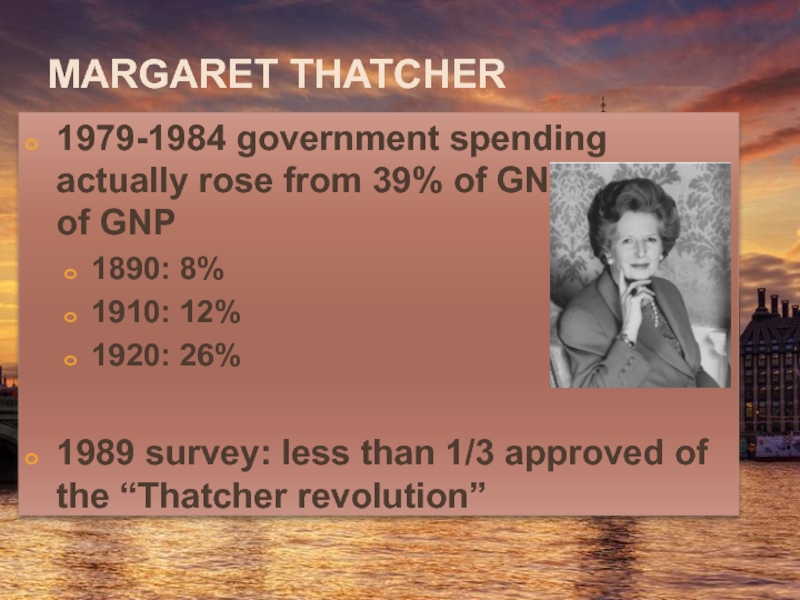
Слайд 30Margaret Thatcher
1979-1984 government spending actually rose from 39% of GNP to
1890: 8%
1910: 12%
1920: 26%
1989 survey: less than 1/3 approved of the “Thatcher revolution”
Слайд 31
1997 electoral victory
the largest majority in parliament (419/659) that the Labour Party has ever held
Conservative vote fell to its lowest share since 1832
Tony Blair: “New Labour is a party of ideas and ideals, but not of outdated ideology. What counts is what works.”
Слайд 32 Tony Blair & “Third Way”
“Third way”
rejected the historic ties between Labour governments and the trade union movement
reversed the tendency to provide centralized statist solutions to economic and social problem
A vague philosophy to draw support from across the social-economic spectrum.
Слайд 33political parties in the UK today:
The Labour Party - left wing,
The Conservative Party – right wing, they put more emphasis in private enterprise
The Liberals
Social and Liberal Democrats - left of centre
Scottish National Party (SNP)
Sinn Féin - the oldest political movement in Ireland