- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад по английскому языку Фразовые глаголыАнглийский в мире и в науке
Содержание
- 1. Презентация по английскому языку Фразовые глаголыАнглийский в мире и в науке
- 2. Einstein Albert14 March 1879 - 18 April
- 3. MendeleevDmitry 27 January [8 February] 1834 - 20
- 4. Исмаил-заде Милена 8 «Б»Project " Global warming"
- 5. " Global warming"The Kyoto Protocol implements the
- 6. Renewable energyTo contain global warming within 2
- 7. BiofuelsThe fact is that Cirrus clouds, like
- 8. Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions The risks
- 9. Acid rainSince carbon dioxide is the most
- 10. Исмаил-заде Милена 8 «Б»Project "The European Union"
- 11. Spain
- 12. Government of Philip VI jhfghsigi
- 13. EconomyAccording to the world Tourism Organization, Spain
- 14. GeographyA sovereign state in southwestern Europe and
- 15. HistoryIn 1492, Christopher Columbus under the Spanish
- 16. CultureBullfighting
- 17. CultureFlamenco
- 18. CultureFootball
Einstein Albert14 March 1879 - 18 April 1955 Jew- ЕврейThe scientist developed the General theory of relativity. Figuratively, he imagined a beam of light that permeates the falling Elevator. Reaching the far wall as the Elevator descends,
Слайд 2Einstein
Albert
14 March 1879 - 18 April 1955
Jew- Еврей
The scientist
developed the General theory of relativity. Figuratively, he imagined a beam of light that permeates the falling Elevator. Reaching the far wall as the Elevator descends, it crosses it and the beam begins to bend upwards. Einstein suggested that the beam does not actually bend, everything only seems, because time and space are distorted by the force pulling the Elevator down.
Formula E=mc2
Formula E=mc2
Слайд 3Mendeleev
Dmitry
27 January [8 February] 1834 - 20 January [2 February] 1907
Russian
scientist-Jew
The periodic law is one of the fundamental laws of nature. It lies in the fact that the properties of chemical elements depend on their atomic weight. Mendeleev discovered the periodic law in 1869. His scientific revolution was not immediately realized by chemists.
The periodic law is one of the fundamental laws of nature. It lies in the fact that the properties of chemical elements depend on their atomic weight. Mendeleev discovered the periodic law in 1869. His scientific revolution was not immediately realized by chemists.
Слайд 5" Global warming"
The Kyoto Protocol implements the UNFCCC goal of combating
global warming by reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere to "a level that will prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system"(article 2). The Kyoto Protocol is an international Treaty that extends the United Nations framework Convention on climate change, which obliges States to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Слайд 6Renewable energy
To contain global warming within 2 degrees, the use of
coal should cease by 2050. The solution in the short term could be to replace it with shale gas, which has a CO2 emission factor of half.
Слайд 7Biofuels
The fact is that Cirrus clouds, like other forms of clouds
together with greenhouse gases, absorb thermal or infrared radiation of the Earth directed into space. Part of it they radiate back to the earth's surface. Meteorologists call this stream of infrared radiation anti-radiation, or counter-radiation of the atmosphere. The higher the humidity and the denser the clouds, the less night cooling of the earth's surface.
Liquid biofuels, Solid biofuels, Gaseous biofuels.
Liquid biofuels, Solid biofuels, Gaseous biofuels.
Слайд 8Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions
The risks of complete or partial loss
of ecosystems and species due to climate change are now increasing. This is confirmed both by the increase in the number and strength of dangerous hydro meteorological phenomena (in Russia — 2 times over the past 15-20 years), and by scientific work on the physics of the atmosphere and ocean, linking this effect with greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, primarily CO2 from fossil fuel combustion. Russia is the world's fourth emitter of greenhouse gases, after China, the US and India, so reducing its emissions is important from a global point of view.
Слайд 9Acid rain
Since carbon dioxide is the most important greenhouse gas, planting
trees and other plants will help slow or stop global warming. Plants take carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
Слайд 13Economy
According to the world Tourism Organization, Spain ranks second in the
world in the number of foreign tourists, second only to France. Spain receives 7% of the world's tourist flow, ahead of the US and Italy. Tourism in Spain brings the Spanish economy more than 50 million euro's per year. The heyday of Spanish winemaking can be considered the middle of the XIX century, when Europe was struck by the phylloxera epidemic, mainly affecting France. A few years later, the Spanish vines were also infected, but by the time the world has become familiar with the works of local winemakers, besides has already been found salvation: grafting to regional varieties of American vines that are immune to the disease.
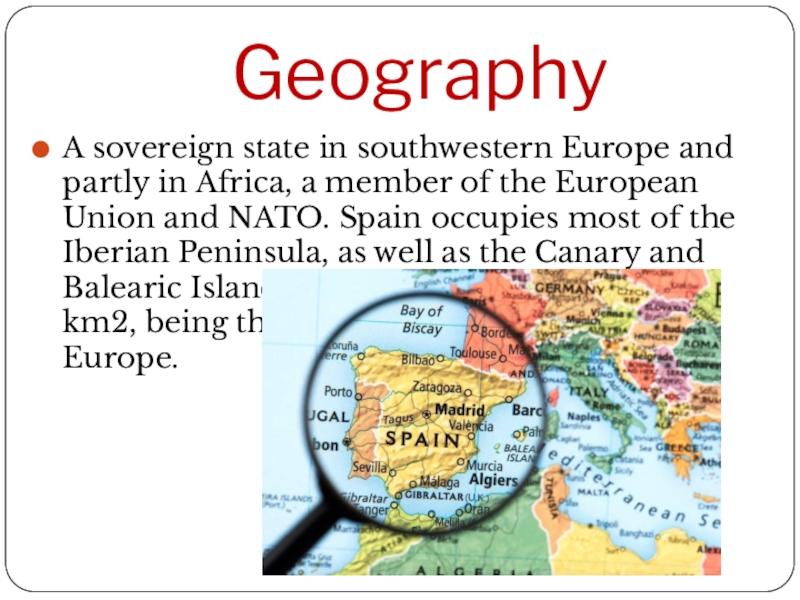
Слайд 14Geography
A sovereign state in southwestern Europe and partly in Africa, a
member of the European Union and NATO. Spain occupies most of the Iberian Peninsula, as well as the Canary and Balearic Islands, has a total area of 504782 km2, being the fourth largest country in Europe.
Слайд 15History
In 1492, Christopher Columbus under the Spanish flag opened a New
World – and a new market for the export of Spanish wine, especially since the country's relations with England began to gradually deteriorate.


![Презентация по английскому языку Фразовые глаголыАнглийский в мире и в науке MendeleevDmitry 27 January [8 February] 1834 - 20 January [2 February] 1907Russian MendeleevDmitry 27 January [8 February] 1834 - 20 January [2 February] 1907Russian scientist-JewThe periodic law is one of](/img/thumbs/fd2e35661ae3b52db67d7e189b5248f9-800x.jpg)