- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
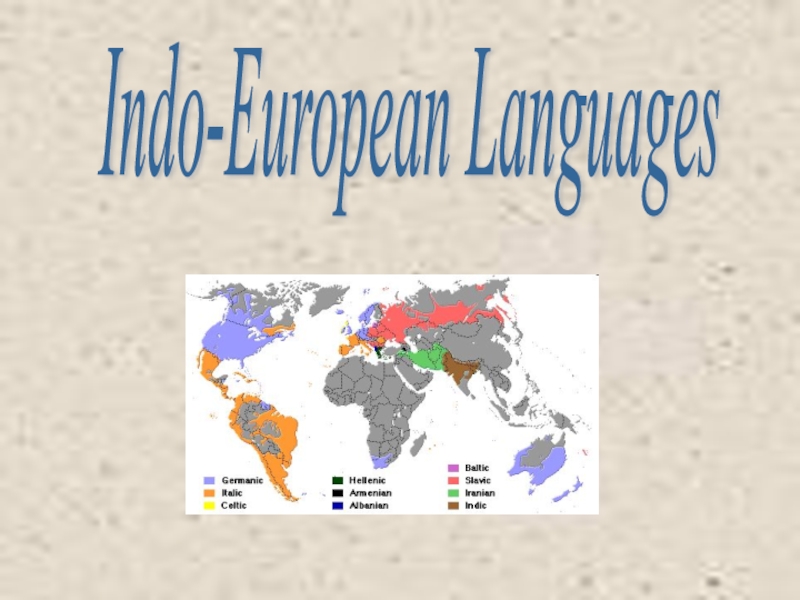
Презентация, доклад к уроку на тему: Индо-европейские языки
Содержание
- 1. Презентация к уроку на тему: Индо-европейские языки
- 2. The Top Ten Language FamiliesIndo-European languagesIndo-European languages 46%
- 3. The Indo-European languages are a family of
- 4. When first Europeans came to India, they
- 5. Indo-European languages are spoken by almost three
- 6. Worldwide Distribution of Indo-European Languages The
- 7. The Germanic Branch English :
- 8. The Slavic Branch Russian :
- 9. The Celtic Branch Welsh :
Слайд 2The Top Ten Language Families
Indo-European languagesIndo-European languages 46%
Sino-Tibetan languagesSino-Tibetan languages 21% (East
Niger-Congo languagesNiger-Congo languages 6.4% (Sub-Saharan Africa(Sub-Saharan Africa)
Afro-Asiatic languagesAfro-Asiatic languages 6.0% (North Africa6.0% (North Africa to Horn of Africa, Southwest Asia)
Austronesian languagesAustronesian languages 5.9% (Oceania5.9% (Oceania, Madagascar5.9% (Oceania, Madagascar, maritime Southeast Asia5.9% (Oceania5.9% (Oceania, Madagascar5.9% (Oceania, Madagascar, maritime Southeast Asia)
Dravidian languagesDravidian languages 3.7% (South AsiaDravidian languagesDravidian languages 3.7% (South Asia)
Altaic languagesAltaic languages 2.3% (Central AsiaAltaic languages 2.3% (Central Asia, Northern Asia, AnatoliaAltaic languages 2.3% (Central Asia, Northern Asia, Anatolia, SiberiaAltaic languagesAltaic languages 2.3% (Central AsiaAltaic languages 2.3% (Central Asia, Northern Asia, AnatoliaAltaic languages 2.3% (Central Asia, Northern Asia, Anatolia, Siberia)
Japonic languagesJaponic languages 2.1% (JapanJaponic languagesJaponic languages 2.1% (Japan)
Austro-Asiatic languagesAustro-Asiatic languages 1.7% (mainland Southeast Asia)
Tai-Kadai languagesTai-Kadai languages 1.3% (Southeast AsiaTai-Kadai languagesTai-Kadai languages 1.3% (Southeast Asia)
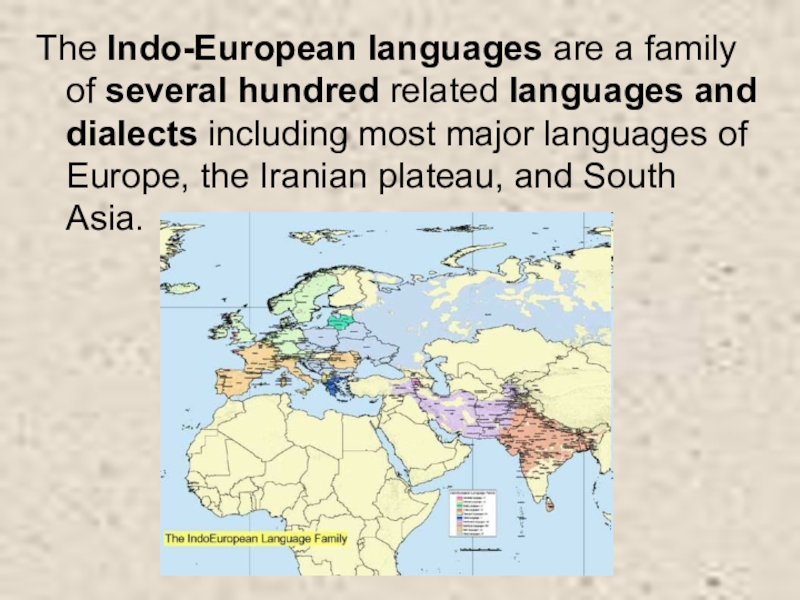
Слайд 3The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages
Слайд 4When first Europeans came to India, they found that Indian speeches
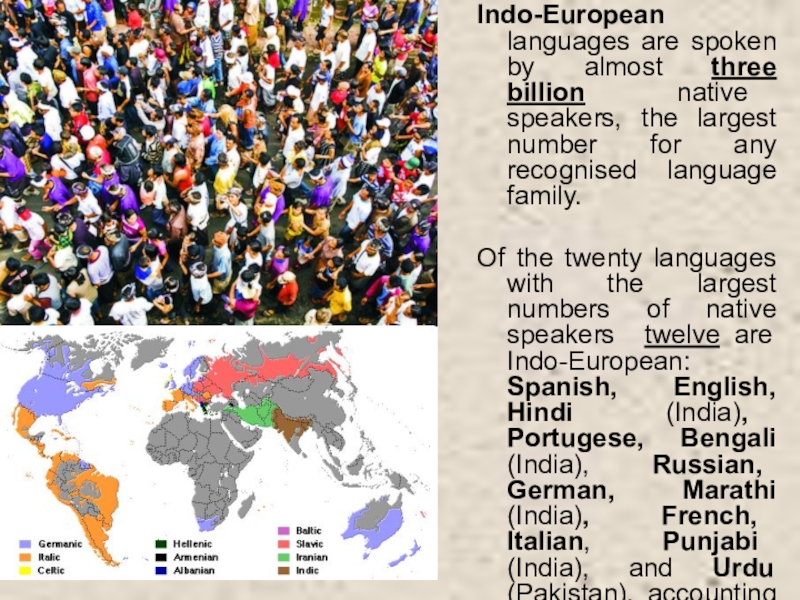
Слайд 5Indo-European languages are spoken by almost three billion native speakers, the
Of the twenty languages with the largest numbers of native speakers twelve are Indo-European: Spanish, English, Hindi (India), Portugese, Bengali (India), Russian, German, Marathi (India), French, Italian, Punjabi (India), and Urdu (Pakistan), accounting for over 1.7 billion native speakers.
Слайд 6Worldwide Distribution of
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European Family is divided into
Слайд 7 The Germanic Branch English : Dutch : Flemish : Frisian : Afrikaans:
The languages of the Germanic Branch originate from Old Norse and Saxon. They use the Latin Alphabet.
They include English, Dutch and German and Frisian.
Flemish and Afrikaans are varieties of Dutch while Yiddish is a variety of German.
Three of the four (mainland) Scandinavian languages belong to this branch: (Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish). Icelandic is the least changed of the Germanic Languages - being close to Old Norse. Another old language is Faroese.
Seven languages are extinct from this branch.
Слайд 8 The Slavic Branch Russian : Belorussian : Ukrainian : Polish : Sorbian
These languages are confined to Eastern Europe.In general, the Catholic peoples use the Latin alphabet while the Orthodox use the Cyrillic alphabet which is derived from the Greek. Indeed some of the languages are very similar differing only in the script used (Croatian and Serbian are virtually the same language).
One of the oldest of these languages is Bulgarian. The most important is Russian. Others include Polish, Kashubian (spoken in parts of Poland), Sorbian (spoken in parts of eastern Germany), Czech, Slovak, Slovene, Macedonian, Bosnian, Ukrainian and Byelorussian.
Слайд 9 The Celtic Branch Welsh : Irish Gaelic : Scottish Gaelic : Breton Cornish
The Celtic Branch is now the smallest branch. The languages originated in Central Europe and once dominated Western Europe (around 400BC). The people migrated across to the British Isles over 2000 years ago.
Later, when the Germanic speaking Anglo Saxons arrived, the Celtic speakers were pushed into Wales (Welsh), Ireland (Irish Gaelic) and Scotland (Scottish Gaelic).One group of Celts moved back to France. Their language became Breton spoken in the Brittany region of France. Breton is closer to Welsh than to French.
Other Celtic languages have became extinct.