- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад к уроку английского языка Операционные системы
Содержание
- 1. Презентация к уроку английского языка Операционные системы
- 2. What is Operating systems?An operating system is
- 3. WindowsWhen referring to an operating system, Windows or win is an
- 4. Microsoft Windows was first introduced with version
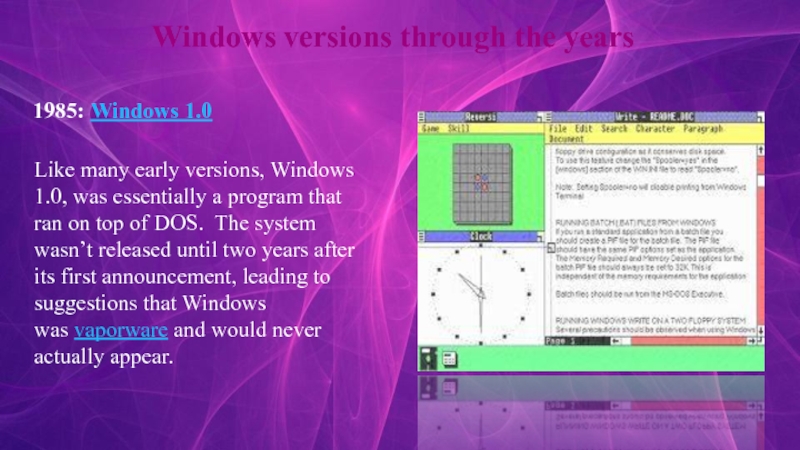
- 5. Windows versions through the years 1985: Windows 1.0Like
- 6. 1987: Windows 2.0-2.11The system introduced the control panel
- 7. 1990: Windows 3.0Windows 3.0 was highly successful upon
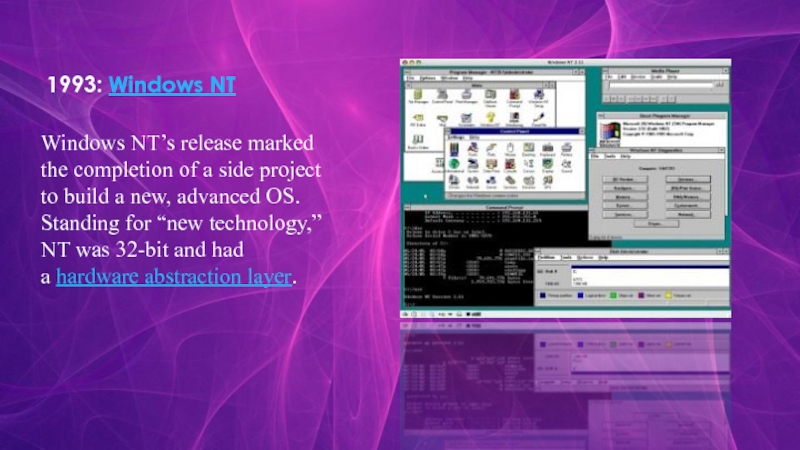
- 8. 1993: Windows NTWindows NT’s release marked the completion
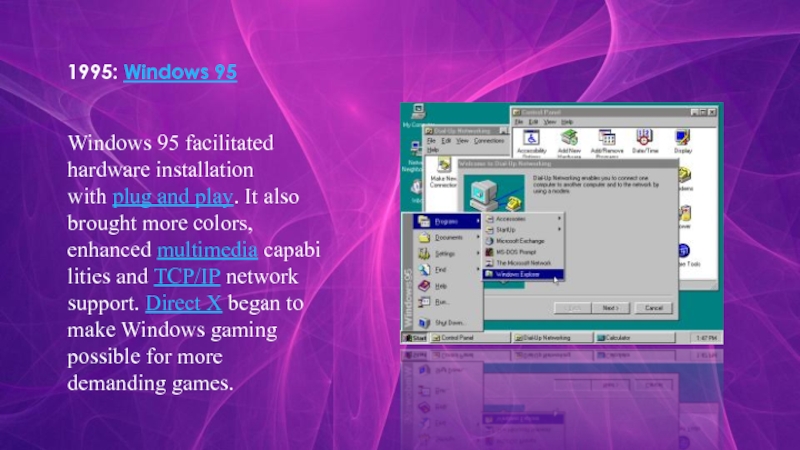
- 9. 1995: Windows 95Windows 95 facilitated hardware installation with plug
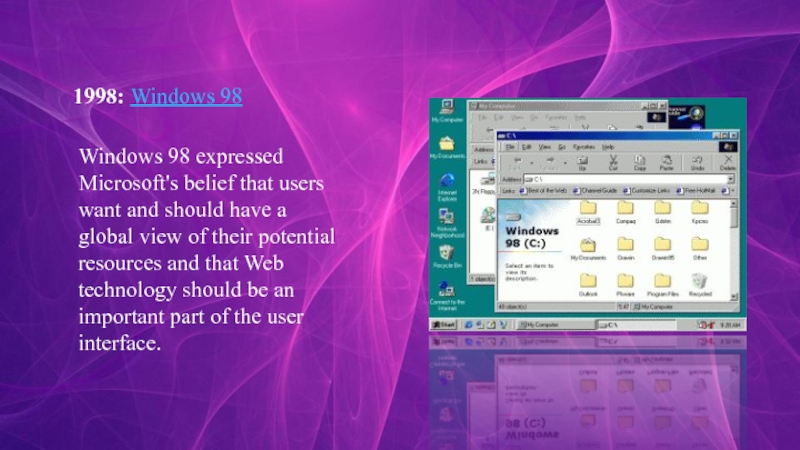
- 10. 1998: Windows 98Windows 98 expressed Microsoft's belief that
- 11. 2001: Windows ХРWindows XP was released as the
- 12. 2006: ОS Windows Vista СWindows Vista was a
- 13. 2009: Windows 7Windows 7 is built on the Vista kernel.
- 14. 2012: Windows 8Windows 8 was released with a
- 15. 2015: Windows 10Microsoft announced Windows 10 in
- 16. UnixUnix -- often spelled UNIX, especially as an
- 17. Prior to 1973, Unix was written in
- 18. Unix has a set of concepts that
- 19. Popular basic Unix commands
- 20. Uses and the future of UnixRecently, Unix
- 21. LinuxLinux is a Unix-like, open source and community-developed operating
- 22. History of LinuxLinus Torvalds started working on Linux
- 23. How is Linux operating system usedEvery version
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. What are the advantages and disadvantages of
- 26. Disadvantages:Understanding: To become familiar with Linux you need
- 27. Windows Operating System:Advantages:Ease: Microsoft Windows has made much
- 28. Disadvantage:Price: Microsoft windows is costly compared to Linux as
- 29. Unix Operating System:Advantages:Full multitasking with protected memory.
- 30. Disadvantage:The traditional command line shell interface is
- 31. Both Windows, Unix and Linux Hosting have
- 32. List of sources used:https://www.quora.com/http://searchdatacenter.techtarget.com/definition/Unix
- 33. Presentation endedThank you for your attention!
Слайд 1Operating systems
Teacher : Popova E.P.
Nizhny Novgorod
2016
Nizhny Novgorod Automotive Technical School
Слайд 2What is Operating systems?
An operating system is the program that manages all the application programs
Operating systems evolved as the solution to the problems that were evident in early computer systems, and coincide with the changing computer systems
Слайд 3Windows
When referring to an operating system, Windows or win is an operating environment created by Microsoft that
Слайд 4Microsoft Windows was first introduced with version 1.0 on November 10, 1983.
Слайд 5Windows versions through the years
1985: Windows 1.0
Like many early versions, Windows 1.0,
Слайд 61987: Windows 2.0-2.11
The system introduced the control panel and ran the first
Слайд 71990: Windows 3.0
Windows 3.0 was highly successful upon initial release. The system
Слайд 81993: Windows NT
Windows NT’s release marked the completion of a side project
Слайд 91995: Windows 95
Windows 95 facilitated hardware installation with plug and play. It also
Слайд 101998: Windows 98
Windows 98 expressed Microsoft's belief that users want and should
Слайд 112001: Windows ХР
Windows XP was released as the first NT-based system with
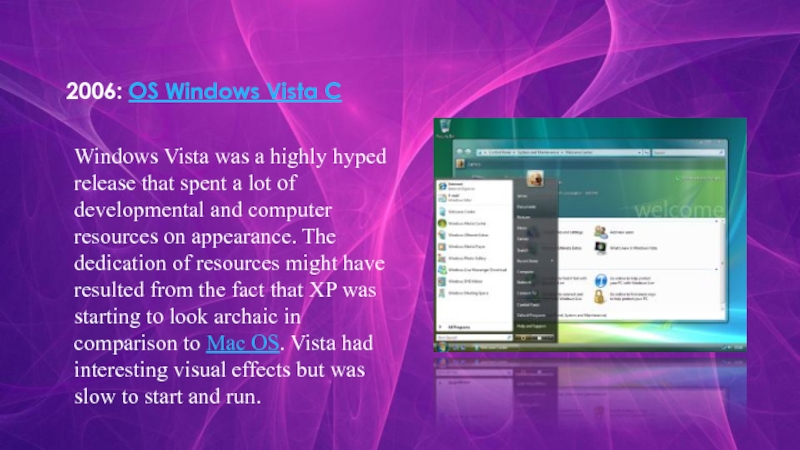
Слайд 122006: ОS Windows Vista С
Windows Vista was a highly hyped release that
Слайд 132009: Windows 7
Windows 7 is built on the Vista kernel. Windows 7 had the
Слайд 142012: Windows 8
Windows 8 was released with a number of enhancements and
Слайд 152015: Windows 10
Microsoft announced Windows 10 in September 2014, skipping Windows
Слайд 16Unix
Unix -- often spelled UNIX, especially as an official trademark -- is
Слайд 17Prior to 1973, Unix was written in assembler language, but the
In the late 1970s and early 80s, Unix had a strong influence in academia that led commercial startups, such as Solaris Technologies and Sequent, to adopt it on a larger scale. In the late 1990s, a network of programmers collaboratively developed Linux and Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) distributions, which led Unix-like systems to grow in popularity. Today, a variety of modern servers, workstations and mobile devices use Unix operating systems.
The history of Unix
Слайд 18Unix has a set of concepts that make it unique. For
How Unix works and why it's important
Слайд 20Uses and the future of Unix
Recently, Unix has seen a decline
However, Unix is still the preferred system for many use cases, such as vertical-specific software, vertical scaling applications and security features. Future Unix server sales are expected to drop, but applications in financial, government and telecommunications will continue to drive Unix use.
Eventually, Unix may be abandoned completely, but it will likely be a long, slow decline before that happens.
Слайд 21Linux
Linux is a Unix-like, open source and community-developed operating system for computers, servers, mainframes,
Слайд 22History of Linux
Linus Torvalds started working on Linux as a replacement to
Torvalds released the Linux kernel in September 1991. A community of developers worked to integrate GNU components with Torvalds' kernel to create a complete, free operating system known collectively as Linux. Torvalds continues to develop the Linux kernel, currently at version 4.9, and a vast developer community continues to create and integrate a wide range of components.
Слайд 23How is Linux operating system used
Every version of the Linux operating
For example, Linux has emerged as a popular operating system for web servers such as Apache, as well as for network operations, scientific computing tasks that require huge compute clusters, running databases, desktop/endpoint computing and running mobile devices with OS versions like Android.
Слайд 25What are the advantages and disadvantages of Windows, Unix and Linux?
Linux
Performance: Linux provides high performance on workstations and on networks. It also helps in making old computers sufficient and usable again and also can handle many users at a time.
Stability: You don’t have to reboot periodically to maintain performance. It can handle large number of users and does not hang up or slow down due to memory issues. Continuous up time upto a year or so is common.
Flexibility: It is used for high performance applications, desktop applications and embedded applications. You can save disk space by installing components required for a particular use. You can restrict specific computers instead of all computers.
Security: The security aspect of the linux is very strong as it is very secure and it is less prominent to viruses, even if there is an attack there would be immediate step taken by the developers all over the world to resolve it.
Choice: Choice is one of the greatest advantage of Linux. It gives the power to control every aspect of the operating system. Main features that you have control is look and feel of desktop by Windows Manager and kernel.
Advantages:
Слайд 26Disadvantages:
Understanding: To become familiar with Linux you need to have a lot
Software: Linux has a limited selection of available softwares.
Ease: Even though Linux has improved a lot in ease of use but windows is much easier.
Hardware: Linux doesnot support many hardware devices.
Слайд 27Windows Operating System:
Advantages:
Ease: Microsoft Windows has made much advancement and changes which
Software: Since there are more number of Microsoft users there are more software programs, games and utilities for windows. All most all games are compatible to windows, some CPU intensive and graphic intensive games are also supported.
Hardware: All hardware manufacturers will support Microsoft windows. Due to large number of Microsoft users and broader driver, all the hardware devices are supported.
Front Page Extension: When using a popular web design program having windows hosting makes it lot more easier. You don’t have to worry if it supported or not.
Development: If you plan to develop windows based applications then windows platform is most suggested as linux does not support windows applications.
Слайд 28Disadvantage:
Price: Microsoft windows is costly compared to Linux as each license costs between
Security: When compared to linux it is much more prone to viruses and other attacks.
Reliability: It needs to be rebooted periodically else there is a possibility of hang up of the system.
Software Cost: Even though the windows have softwares,games for free most of the programs will cost more than $200.
Слайд 29Unix Operating System:
Advantages:
Full multitasking with protected memory. Multiple users can run
A rich set of small commands and utilities that do specific tasks well -- not cluttered up with lots of special options. Unix is a well-stocked toolbox, not a giant do-it-all Swiss Army Knife.
Ability to string commands and utilities together in unlimited ways to accomplish more complicated tasks -- not limited to preconfigured combinations or menus, as in personal computer systems.
A powerfully unified file system. Everything is a file: data, programs, and all physical devices. Entire file system appears as a single large tree of nested directories, regardless of how many different physical devices (disks) are included.
A lean kernel that does the basics for you but doesn't get in the way when you try to do the unusual.
Available on a wide variety of machines - the most truly portable operating system.
Optimized for program development, and thus for the unusual circumstances that are the rule in research.
Слайд 30Disadvantage:
The traditional command line shell interface is user hostile -- designed
Commands often have cryptic names and give very little response to tell the user what they are doing. Much use of special keyboard characters - little typos have unexpected results.
To use Unix well, you need to understand some of the main design features. Its power comes from knowing how to make commands and programs interact with each other, not just from treating each as a fixed black box.
Richness of utilities (over 400 standard ones) often overwhelms novices. Documentation is short on examples and tutorials to help you figure out how to use the many tools provided to accomplish various kinds of tasks.
Слайд 31 Both Windows, Unix and Linux Hosting have advantages and disadvantages. Based
Conclusion: