- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад К УРОКУ АНГЛИЙСКОГО ЯЗЫКА C ИСПОЛЬЗОВАНИЕМ ИНТЕРАКТИВНЫХ ТЕХНОЛОГИЙ НА ТЕМУ THE CONSTITUTION OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION ДЛЯ СТУДЕНТОВ 2-ОГО КУРСА СПЕЦИАЛЬНОСТИ 40.02.01 ПРАВО И ОРГАНИЗАЦИЯ СОЦИАЛЬНОГО ОБЕСПЕЧЕНИЯ
Содержание
- 1. ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ К УРОКУ АНГЛИЙСКОГО ЯЗЫКА C ИСПОЛЬЗОВАНИЕМ ИНТЕРАКТИВНЫХ ТЕХНОЛОГИЙ НА ТЕМУ THE CONSTITUTION OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION ДЛЯ СТУДЕНТОВ 2-ОГО КУРСА СПЕЦИАЛЬНОСТИ 40.02.01 ПРАВО И ОРГАНИЗАЦИЯ СОЦИАЛЬНОГО ОБЕСПЕЧЕНИЯ
- 2. AIMS:To learn more about the Constitution of
- 3. Слайд 3
- 4. What chambers does it consist of?The State
- 5. What are the most important special powers
- 6. What route must a bill pass to
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. Слайд 8
- 9. It contains the basic principles of the
- 10. The Constitution of the Russian Federationdefines the
- 11. Separate articles are devoted to the bodies
- 12. Under the Constitution adopted on December 12,
- 13. The President of the Russian Federation isthe
- 14. The Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation (the Federation Council and the State Duma) representsthe legislature
- 15. The Government of the Russian Federation isthe executive branch
- 16. Constitutional, civil, administrative, and criminal legal proceedings representjudicial power
- 17. The system of courts of the Russian
- 18. Separate articles are devoted to the Russian
- 19. Exersises:Translate into Russian:1) to establish the principles
- 20. Find the English equivalents:1) установить принцип суверенитета2)
- 21. Find the synonyms:1) fundamental
- 22. Find the anthonyms:1) separation
- 23. Try to retell about the Constitution of
- 24. Grammar Revision.(The System of Tenses. Passive Voice)
- 25. Change the verbs from Active into Passive
- 26. The rights and freedoms of a human
- 27. 5. The Constitution established the principles of
- 28. Hometask.Exercises 10, 11, p.67.
- 29. Thanks for attention and your good work!
Слайд 2AIMS:
To learn more about the Constitution of the Russian Federation;
To learn
To improve our reading skills;
To work on our Grammar;
To enjoy working in pairs and groups;
To do a little test on the topic;
And to speak our favourite English
using new vocabulary!
Слайд 3
What is legislation?
It is one of the three main functions of government.
Who are legislators?
Those who have the formal power to create legislation.
What purposes can legislation have?
To regulate, to authorize, to proscribe, to provide funds, to sanction, to grant, to declare or to restrict.
What is the lawmaking body of the Russian Federation?
The Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation.
Слайд 4What chambers does it consist of?
The State Duma, which is the
and the Federation Council, which is the upper house.
What special powers does the State Duma have?
consent to the appointment of the Prime minister of Russia;
hearing annual reports from the Government of the Russian Federation on the results of its work, including issues raised by the State Duma;
deciding the issue of confidence in the Government of the Russian Federation;
appointment and dismissal of the Chairman of the Central Bank of Russia, the Chairman and half of the auditors of the Accounting Chamber;
announcement of amnesty;
bringing charges against the President of the Russian Federation for his impeachment.
Слайд 5What are the most important special powers of the Federation Council?
Approval
Approval of a decree of the President of the Russian Federation on the introduction of martial law;
Approval of a decree of the President of the Russian Federation on the introduction of a state of emergency;
Deciding on the possibility of using the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation outside the territory of the Russian Federation;
Declaring elections of the President of the Russian Federation;
Impeachment of the President of the Russian Federation;
Approving the President’s nomination of judges of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, the Higher Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation; Approving the President’s nomination of the Attorney General of the Russian Federation.
Слайд 6What route must a bill pass to become a law?
All bills
After this a draft law is considered by the Federation Council, which has fourteen days to place the bill on its calendar.
If the Federation Council rejects a bill passed by the State Duma, the two chambers may form a conciliation commission to work out a compromise version of the legislation.
If the two chambers cannot reach a compromise, or the Duma insists on passing the bill as it is, the veto of the Federation Council can be overridden if two thirds of the Duma’s constitutional composition vote in favour of the bill.
Then the President signs it into the law.
Слайд 7
Dr. Johnson and Mr. Johnson
After great consideration
Came to the conclusion
That the Indian nation
Beyond the Indian ocean
Is back in education
Because the chief occupation
Is cultivation.
Слайд 8
1. separation of powers— разделение властей
2. Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces— Верховнокомандующий ВС
3. oath— присяга
4. to take office— вступать в должность
5. irremovability— несменяемость
6. impartiality— беспристрастность
7. promulgation—обнародование
Слайд 9It contains the basic principles of the Russian
constitutional system.
The Constitution of
Russia’s supreme law
passed through a national vote.
The Constitution :
1) defines the federative structure of the Russian Federation;
2) establishes the principles of sovereignty and independence of the Russian Federation;
3) defines the principle of separation of powers between legislative, executive and judicial branches;
4) establishes equality of ideologies and re
ligions;.
5) defines the Russian Federation as a secular state.
Слайд 10The Constitution of the Russian Federation
defines the rights and
freedoms of a
sets their priority when deciding any
issues, and proclaims the principle of equality before law and court
contains the list of component units of the Russian Federation, covers the issues that are within the
jurisdiction of the Russian Federation and those that are within the joint jurisdiction of federal and local authorities
Слайд 11Separate articles are devoted to the bodies of federal power:
the President
of
the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation
the Government of the Russian Federation
the judicial power
of the Russian Federation
and to the order and the terms of appointed and elected officials and the limits of their competence
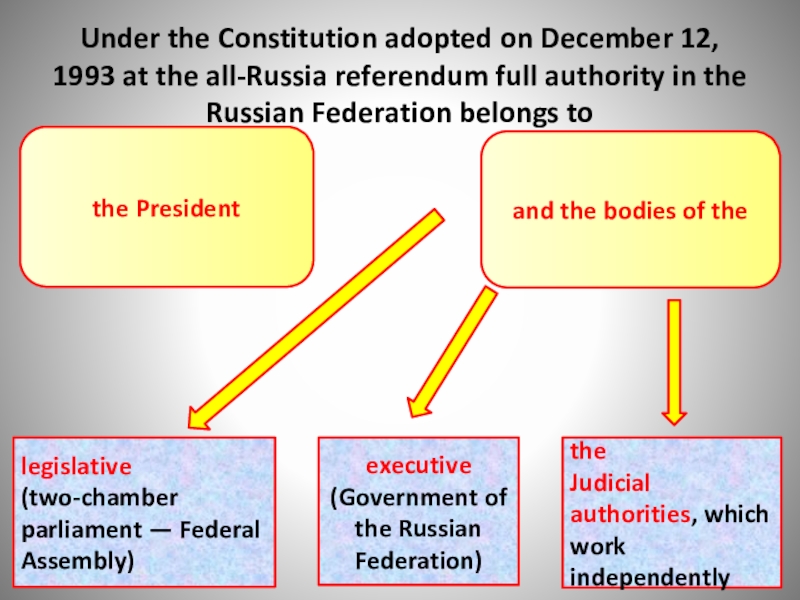
Слайд 12Under the Constitution adopted on December 12, 1993 at the all-Russia
the President
and the bodies of the
legislative (two-chamber parliament — Federal
Assembly)
executive (Government of the Russian Federation)
the
Judicial authorities, which work independently
Слайд 13The President of the Russian Federation is
the Head of the State,
has
Commander
of the Armed Forces
of the Russian Federation
Слайд 14The Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation (the Federation Council and the
the legislature
Слайд 16Constitutional, civil,
administrative, and criminal legal proceedings represent
judicial power
Слайд 17The system of courts of the Russian Federation consists of:
the Constitutional
the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation
the Higher Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation
Слайд 18Separate articles are devoted to the Russian Federation Procurator’s Office with
The Constitution regulates the issues of local self- government, including its authority and sphere of activity.
Transitional and Final provisions regulating the promulgation of the Constitution and its enforcement are contained in Part 2 of the Constitution.
Слайд 19Exersises:
Translate into Russian:
1) to establish the principles of sovereignty and independence
2)
3) to be devoted to the bodies of federal power
4) to define the federative structure
5) legislative authority
6) executive authority
7) judicial authority
8) to list duties
9) the Armed Forces
10) to represent the legislature
11) to determine the extent of the jurisdiction
12) immunity of judges
13) impartiality of the court
14) supervision and control
15) promulgation of the Constitution
Слайд 20Find the English equivalents:
1) установить принцип суверенитета
2) принцип разделения властей
3) установить
4) светское государство
5) провозглашать принцип равенства перед законом
6) Федеральное Собрание
7) рамки полномочий
8) судебная власть
9) глава государства
10) порядок избрания представителей
11) установить принцип несменяемости судей
12) Прокуратура Российской Федерации
13) беспристрастность суда
14) процедура принятия поправок к Конституции
Слайд 21Find the synonyms:
1) fundamental
2) power b) period of time
3) independently c) be vested in
4) establish d) choose
5) duty e) obligation
6) solemn promise f) basic
7) term g) separately
8) elect h) oath
9) objective i) set up
10) belong to j) authority
Слайд 22Find the anthonyms:
1) separation
2) within b) reject
3) sovereignty c) unity
4) adopt d) beyond
5) secular e) religious
Слайд 23Try to retell about the Constitution of the Russian Federation using
1. What does the Constitution of the Russian Federation define and establish?
2. What provisions does the Constitution contain regarding the federative structure?
3. What are the bodies of federal power?
4. Who does the full authority in the Russian Federation belong to under the current Constitution?
5. What provisions concerning the legislature are provided by the Constitution?
6. What is the executive branch of power in the Russian Federation?
7. How is judicial power implemented in the Russian Federation?
8. What principles of judicial power does the Constitution establish?
9. What does the system of courts consist of?
10. Does the Constitution regulate the activities of local self-government?
Слайд 25Change the verbs from Active into Passive as in the examples:
Examples:
MODEL
The federative structure of the Russian Federation is defined in the Constitution.
MODEL 2 The constitution defined the federative structure of the Russian Federation.
The federative structure of the Russian Federation was defined in the Constitution (several years ago, yesterday, two days ago, the day before yesterday).
MODEL 3 The constitution will define the federative structure of the Russian Federation.
The federative structure of the Russian Federation will be defined in the Constitution (one of these days, tomorrow, in a week, in several months).
Слайд 26The rights and freedoms of a human and a citizen are
the Constitution of the Russian Federation defines the rights and
freedoms of a human and a citizen.
4. The Constitution determines the extent of the jurisdiction of the
Russian Government.
2. The Constitution defined the Russian Federation as a secular state
in 1993.
3. The Constitution contains the text of the oath taken by the
President of the Russian Federation.
1.The Constitution of the Russian Federation defines the rights and
freedoms of a human and a citizen.
The text of the oath is taken by the President of the Russian Federation.
The Russian Federation is defined as a secular state in 1993.
Слайд 275. The Constitution established the principles of independence,
irremovability and immunity of
The principles of independence irremovability and immunity were
established by the Constitution.
The issuses of local self-government will be regulated by the
Constitution in a year.
The extent of the jurisdiction is determined by the Constitution.
6. The Constitution will regulate the issues of local self-government in
a year.