ОГСЭ.03. Иностранный язык.
Преподаватель Никольский Андрей Анатольевич.
Коломна 2018 г.
- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад на тему ОГСЭ.03 Английский язык Презентация по теме Пищеварительная система
Содержание
- 1. ОГСЭ.03 Английский язык Презентация по теме Пищеварительная система
- 2. Human digestive system, the system used in
- 3. Mouth.The mouth is the first part of the gastrointestinal tract and
- 4. The roof of the mouth is termed
- 5. Saliva moistens and softens food, and along with
- 6. Food enters the mouth where the first
- 7. Teeth are complex structures made of materials specific
- 8. The epiglottis is a flap of elastic cartilage attached to the
- 9. The pharynx is a part of the conducting zone of
- 10. At rest the esophagus is closed at
- 11. Once in the esophagus, the bolus travels
- 12. The diaphragm is an important part of the body's
- 13. The stomach is a major organ of the gastrointestinal
- 14. The liver is the second largest organ (after
- 15. The lower gastrointestinal tract (GI), includes the small
- 16. Blood supply.The digestive system is supplied by
- 17. Thank you for your attention!)
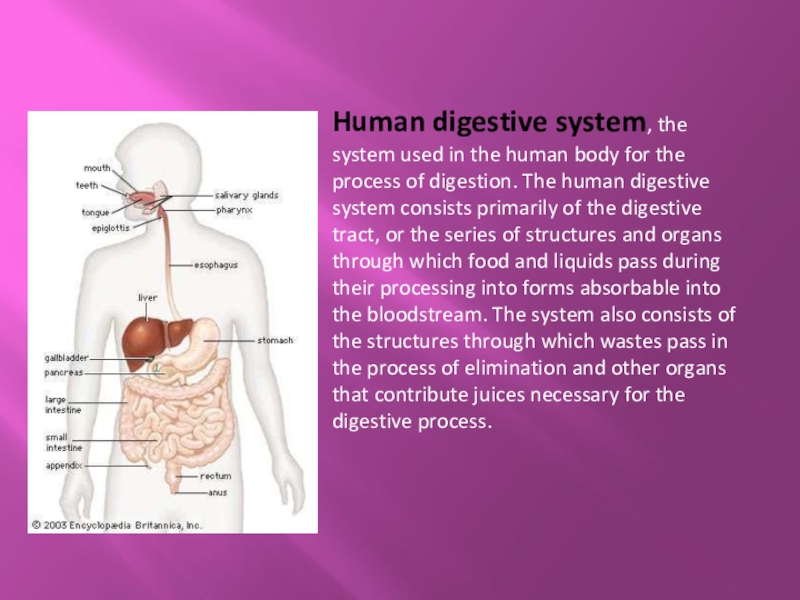
Human digestive system, the system used in the human body for the process of digestion. The human digestive system consists primarily of the digestive tract, or the series of structures and organs through which food and liquids pass during their processing into
Слайд 1Государственное бюджетное профессиональное образовательное учреждение
Московской области
«Московский областной медицинский колледж № 2»
(ГБПОУ МО «Московский областной медицинский колледж № 2»)
Коломенский филиал
Презентация на тему: «Пищеварительная система»
Слайд 2Human digestive system, the system used in the human body for the process
of digestion. The human digestive system consists primarily of the digestive tract, or the series of structures and organs through which food and liquids pass during their processing into forms absorbable into the bloodstream. The system also consists of the structures through which wastes pass in the process of elimination and other organs that contribute juices necessary for the digestive process.
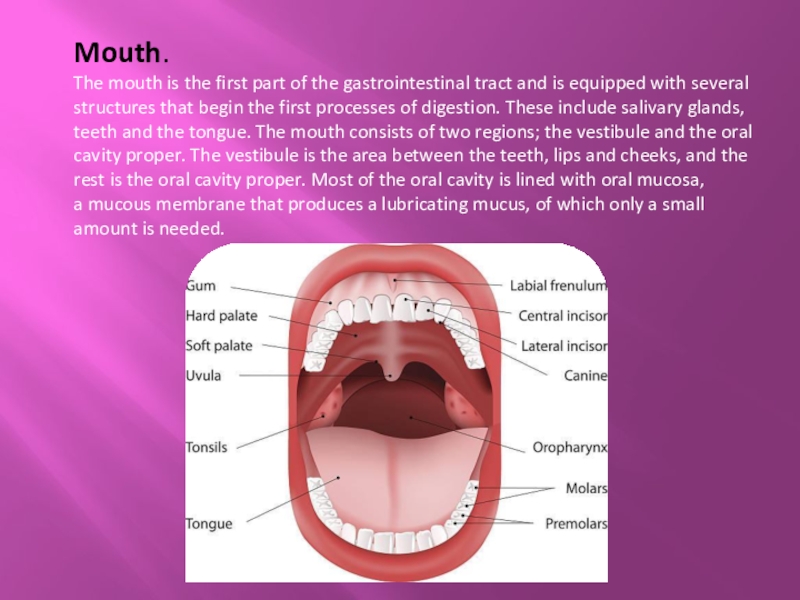
Слайд 3Mouth.
The mouth is the first part of the gastrointestinal tract and is equipped with several
structures that begin the first processes of digestion. These include salivary glands, teeth and the tongue. The mouth consists of two regions; the vestibule and the oral cavity proper. The vestibule is the area between the teeth, lips and cheeks, and the rest is the oral cavity proper. Most of the oral cavity is lined with oral mucosa, a mucous membrane that produces a lubricating mucus, of which only a small amount is needed.
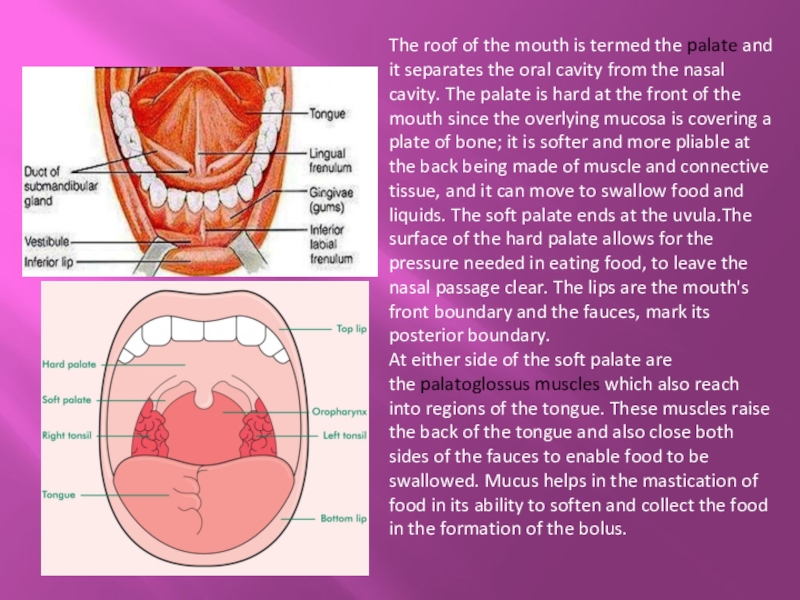
Слайд 4The roof of the mouth is termed the palate and it separates the
oral cavity from the nasal cavity. The palate is hard at the front of the mouth since the overlying mucosa is covering a plate of bone; it is softer and more pliable at the back being made of muscle and connective tissue, and it can move to swallow food and liquids. The soft palate ends at the uvula.The surface of the hard palate allows for the pressure needed in eating food, to leave the nasal passage clear. The lips are the mouth's front boundary and the fauces, mark its posterior boundary.
At either side of the soft palate are the palatoglossus muscles which also reach into regions of the tongue. These muscles raise the back of the tongue and also close both sides of the fauces to enable food to be swallowed. Mucus helps in the mastication of food in its ability to soften and collect the food in the formation of the bolus.
At either side of the soft palate are the palatoglossus muscles which also reach into regions of the tongue. These muscles raise the back of the tongue and also close both sides of the fauces to enable food to be swallowed. Mucus helps in the mastication of food in its ability to soften and collect the food in the formation of the bolus.
Слайд 5Saliva moistens and softens food, and along with the chewing action of
the teeth, transforms the food into a smooth bolus. The bolus is further helped by the lubrication provided by the saliva in its passage from the mouth into the esophagus. Also of importance is the presence in saliva of the digestive enzymes amylase and lipase. Amylase starts to work on the starch in carbohydrates, breaking it down into the simple sugars of maltose and dextrose that can be further broken down in the small intestine. Saliva in the mouth can account for 30% of this initial starch digestion. Lipase starts to work on breaking down fats. Lipase is further produced in the pancreas where it is released to continue this digestion of fats. The presence of salivary lipase is of prime importance in young babies whose pancreatic lipase has yet to be developed.
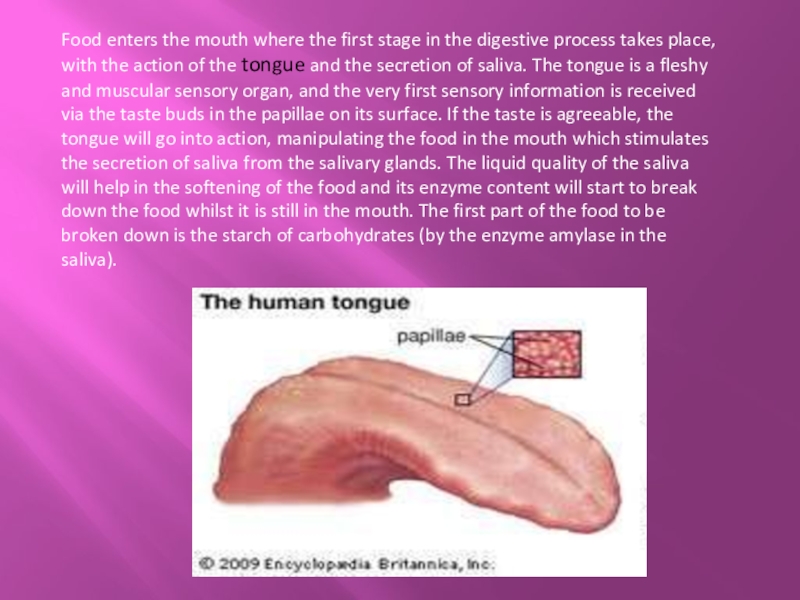
Слайд 6Food enters the mouth where the first stage in the digestive
process takes place, with the action of the tongue and the secretion of saliva. The tongue is a fleshy and muscular sensory organ, and the very first sensory information is received via the taste buds in the papillae on its surface. If the taste is agreeable, the tongue will go into action, manipulating the food in the mouth which stimulates the secretion of saliva from the salivary glands. The liquid quality of the saliva will help in the softening of the food and its enzyme content will start to break down the food whilst it is still in the mouth. The first part of the food to be broken down is the starch of carbohydrates (by the enzyme amylase in the saliva).
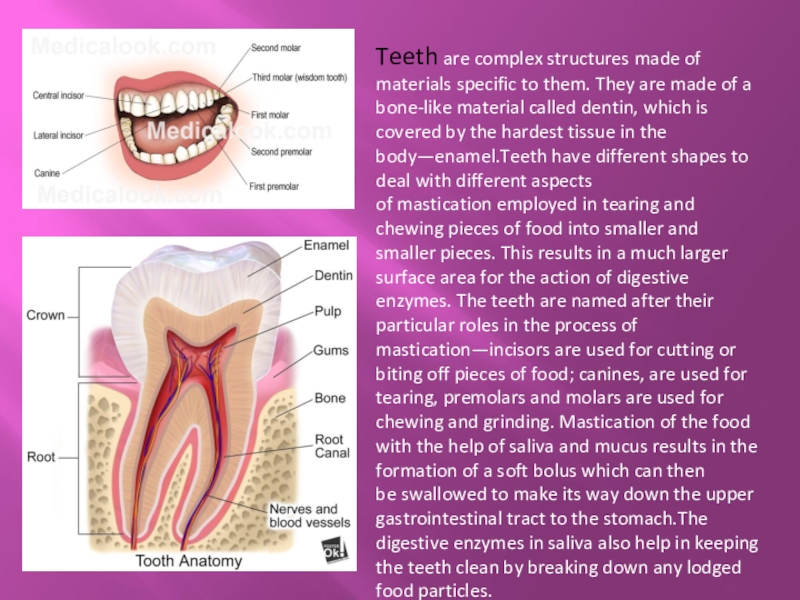
Слайд 7Teeth are complex structures made of materials specific to them. They are
made of a bone-like material called dentin, which is covered by the hardest tissue in the body—enamel.Teeth have different shapes to deal with different aspects of mastication employed in tearing and chewing pieces of food into smaller and smaller pieces. This results in a much larger surface area for the action of digestive enzymes. The teeth are named after their particular roles in the process of mastication—incisors are used for cutting or biting off pieces of food; canines, are used for tearing, premolars and molars are used for chewing and grinding. Mastication of the food with the help of saliva and mucus results in the formation of a soft bolus which can then be swallowed to make its way down the upper gastrointestinal tract to the stomach.The digestive enzymes in saliva also help in keeping the teeth clean by breaking down any lodged food particles.
Слайд 8The epiglottis is a flap of elastic cartilage attached to the entrance of the larynx. It
is covered with a mucous membrane and there are taste buds on its lingual surface which faces into the mouth.Its laryngeal surface faces into the larynx. The epiglottis functions to guard the entrance of the glottis, the opening between the vocal folds. It is normally pointed upward during breathing with its underside functioning as part of the pharynx, but during swallowing, the epiglottis folds down to a more horizontal position, with its upper side functioning as part of the pharynx. In this manner it prevents food from going into the trachea and instead directs it to the esophagus, which is behind. During swallowing, the backward motion of the tongue forces the epiglottis over the glottis' opening to prevent any food that is being swallowed from entering the larynx which leads to the lungs; the larynx is also pulled upwards to assist this process. Stimulation of the larynx by ingested matter produces a strong cough reflex in order to protect the lungs.
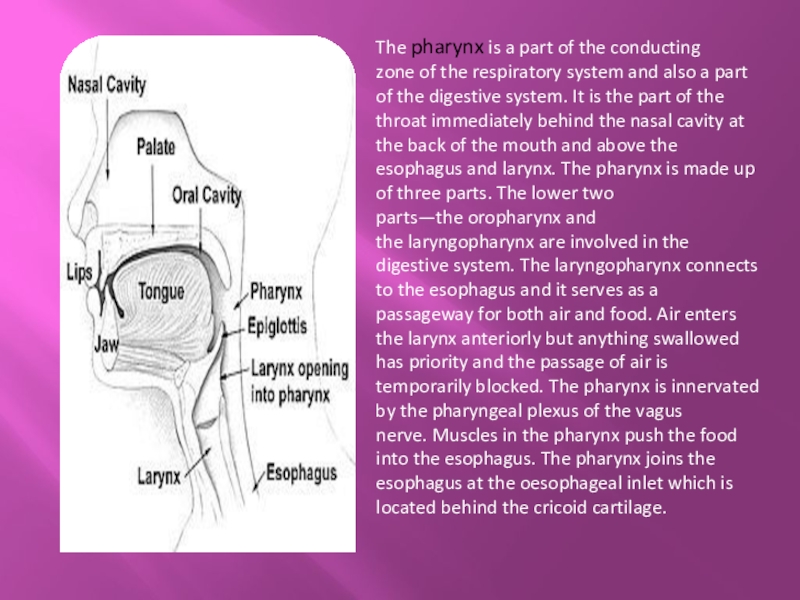
Слайд 9The pharynx is a part of the conducting zone of the respiratory system and also a
part of the digestive system. It is the part of the throat immediately behind the nasal cavity at the back of the mouth and above the esophagus and larynx. The pharynx is made up of three parts. The lower two parts—the oropharynx and the laryngopharynx are involved in the digestive system. The laryngopharynx connects to the esophagus and it serves as a passageway for both air and food. Air enters the larynx anteriorly but anything swallowed has priority and the passage of air is temporarily blocked. The pharynx is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus of the vagus nerve. Muscles in the pharynx push the food into the esophagus. The pharynx joins the esophagus at the oesophageal inlet which is located behind the cricoid cartilage.
Слайд 10At rest the esophagus is closed at both ends, by the
upper and lower esophageal sphincters. The opening of the upper sphincter is triggered by the swallowing reflex so that food is allowed through. The sphincter also serves to prevent back flow from the esophagus into the pharynx. The esophagus has a mucous membrane and the epithelium which has a protective function is continuously replaced due to the volume of food that passes inside the esophagus. During swallowing, food passes from the mouth through the pharynx into the esophagus. The epiglottis folds down to a more horizontal position so as to prevent food from going into the trachea, instead directing it to the esophagus.
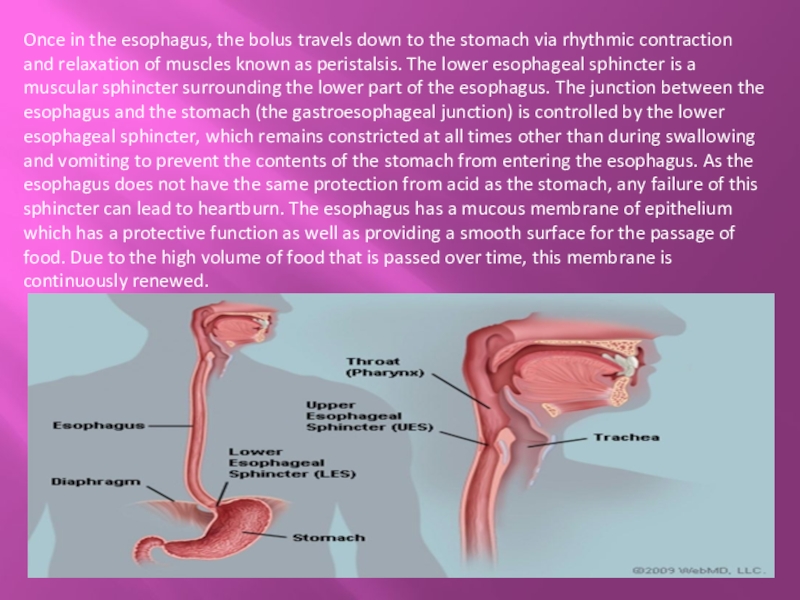
Слайд 11Once in the esophagus, the bolus travels down to the stomach
via rhythmic contraction and relaxation of muscles known as peristalsis. The lower esophageal sphincter is a muscular sphincter surrounding the lower part of the esophagus. The junction between the esophagus and the stomach (the gastroesophageal junction) is controlled by the lower esophageal sphincter, which remains constricted at all times other than during swallowing and vomiting to prevent the contents of the stomach from entering the esophagus. As the esophagus does not have the same protection from acid as the stomach, any failure of this sphincter can lead to heartburn. The esophagus has a mucous membrane of epithelium which has a protective function as well as providing a smooth surface for the passage of food. Due to the high volume of food that is passed over time, this membrane is continuously renewed.
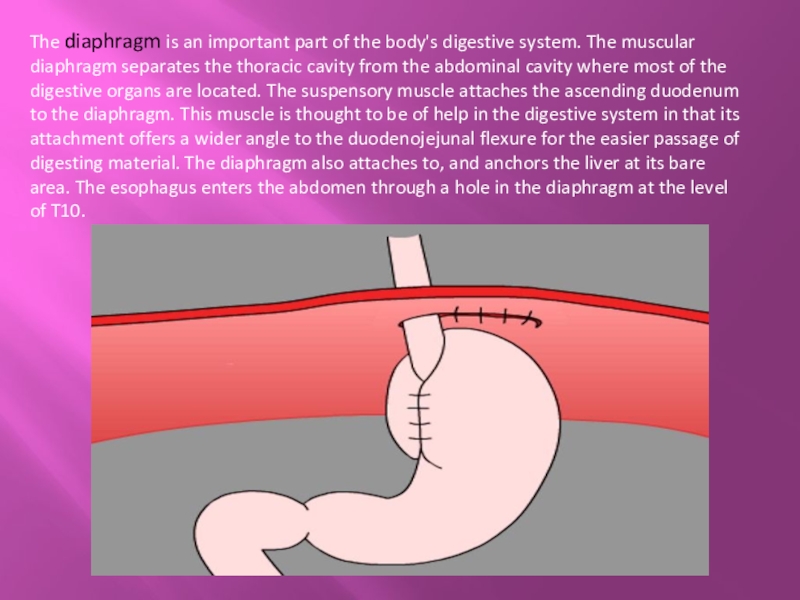
Слайд 12The diaphragm is an important part of the body's digestive system. The muscular
diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity where most of the digestive organs are located. The suspensory muscle attaches the ascending duodenum to the diaphragm. This muscle is thought to be of help in the digestive system in that its attachment offers a wider angle to the duodenojejunal flexure for the easier passage of digesting material. The diaphragm also attaches to, and anchors the liver at its bare area. The esophagus enters the abdomen through a hole in the diaphragm at the level of T10.
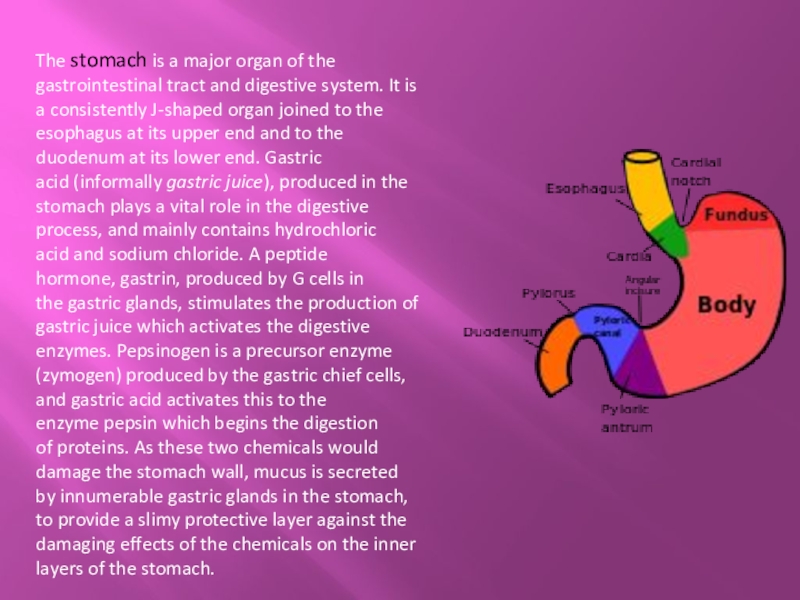
Слайд 13The stomach is a major organ of the gastrointestinal tract and digestive system.
It is a consistently J-shaped organ joined to the esophagus at its upper end and to the duodenum at its lower end. Gastric acid (informally gastric juice), produced in the stomach plays a vital role in the digestive process, and mainly contains hydrochloric acid and sodium chloride. A peptide hormone, gastrin, produced by G cells in the gastric glands, stimulates the production of gastric juice which activates the digestive enzymes. Pepsinogen is a precursor enzyme (zymogen) produced by the gastric chief cells, and gastric acid activates this to the enzyme pepsin which begins the digestion of proteins. As these two chemicals would damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by innumerable gastric glands in the stomach, to provide a slimy protective layer against the damaging effects of the chemicals on the inner layers of the stomach.
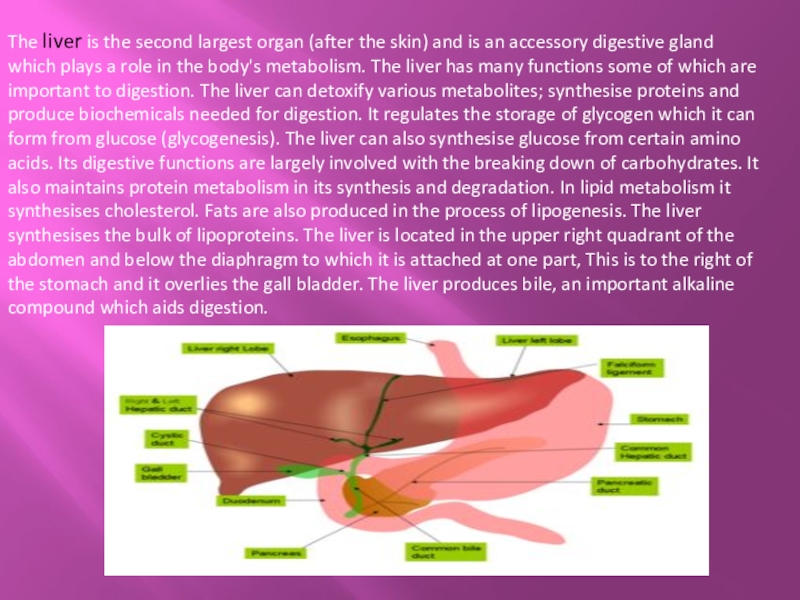
Слайд 14The liver is the second largest organ (after the skin) and is an
accessory digestive gland which plays a role in the body's metabolism. The liver has many functions some of which are important to digestion. The liver can detoxify various metabolites; synthesise proteins and produce biochemicals needed for digestion. It regulates the storage of glycogen which it can form from glucose (glycogenesis). The liver can also synthesise glucose from certain amino acids. Its digestive functions are largely involved with the breaking down of carbohydrates. It also maintains protein metabolism in its synthesis and degradation. In lipid metabolism it synthesises cholesterol. Fats are also produced in the process of lipogenesis. The liver synthesises the bulk of lipoproteins. The liver is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen and below the diaphragm to which it is attached at one part, This is to the right of the stomach and it overlies the gall bladder. The liver produces bile, an important alkaline compound which aids digestion.
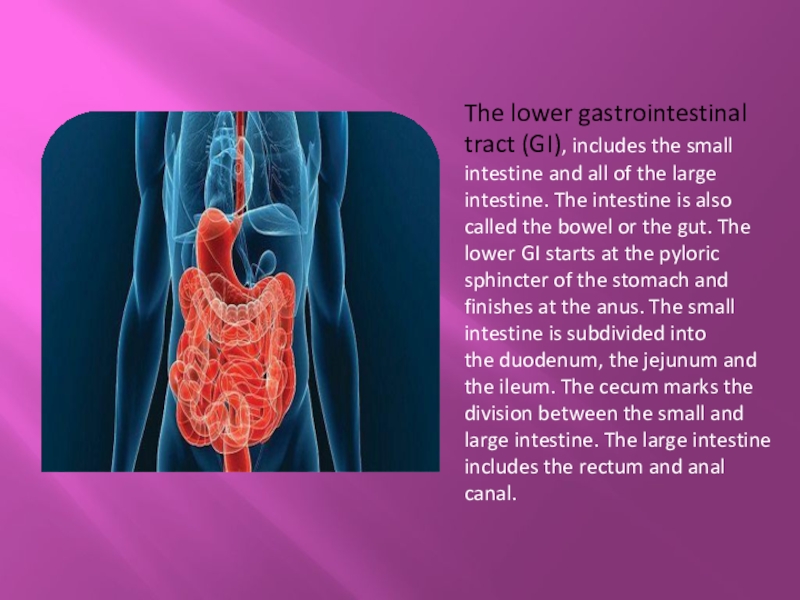
Слайд 15The lower gastrointestinal tract (GI), includes the small intestine and all of the large
intestine. The intestine is also called the bowel or the gut. The lower GI starts at the pyloric sphincter of the stomach and finishes at the anus. The small intestine is subdivided into the duodenum, the jejunum and the ileum. The cecum marks the division between the small and large intestine. The large intestine includes the rectum and anal canal.
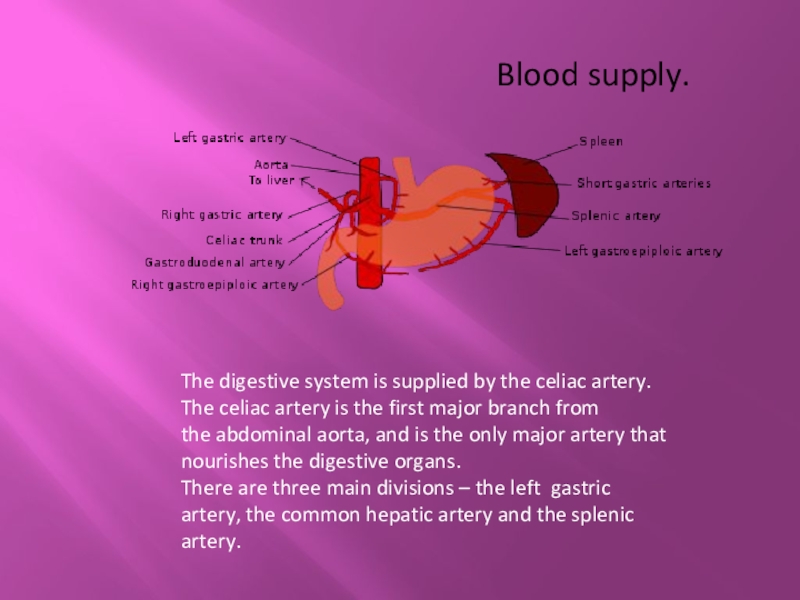
Слайд 16Blood supply.
The digestive system is supplied by the celiac artery. The celiac
artery is the first major branch from the abdominal aorta, and is the only major artery that nourishes the digestive organs.
There are three main divisions – the left gastric artery, the common hepatic artery and the splenic artery.
There are three main divisions – the left gastric artery, the common hepatic artery and the splenic artery.