ОГСЭ.03. Иностранный язык
Преподаватель Никольский Андрей Анатольевич
- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад на тему ОГСЭ.03 Английский язык Презентация по теме Легкие
Содержание
- 1. ОГСЭ.03 Английский язык Презентация по теме Легкие
- 2. Lightweight (pulmones) are paired organ, which occupies
- 3. Each lung has a truncated cone shape,
- 4. The right lung wider and shorter. In nizhneperednem
- 5. Lungs are composed of light fraction (lobi
- 6. The upper interlobar fissure of the right
- 7. Lungs 1 - the larynx; 2 -
- 8. The right lung 1 - top of
- 9. The left lung 1 - the root
- 10. A kind of skeletal framework constitute the
- 11. The branches of the bronchi supply air
- 12. On the walls of alveolar sacs and
- 13. Slice of Light 1 - bronchiole; 2
- 14. Light is also divided into bronchopulmonary segments
- 15. Outside, each lung is surrounded by the
- 16. Between pleural sacs formed space, which is
- 17. Thank you for your attention!)
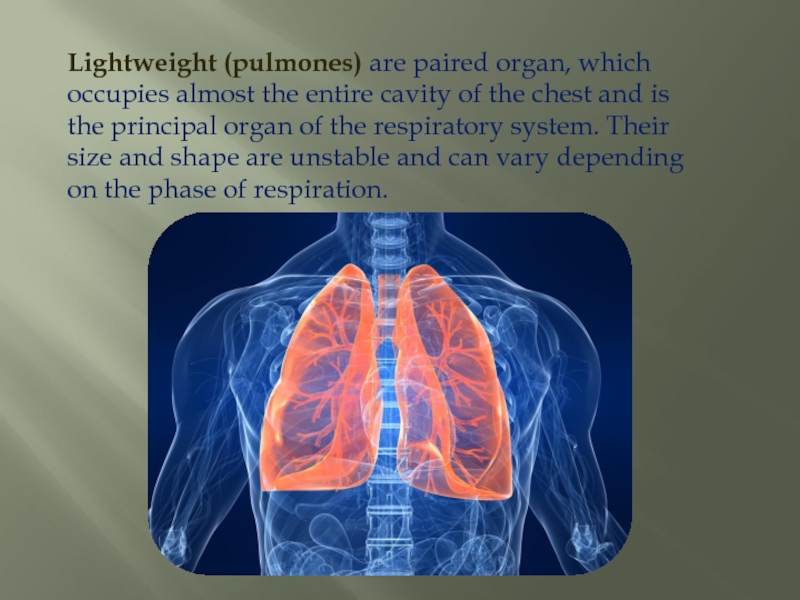
Lightweight (pulmones) are paired organ, which occupies almost the entire cavity of the chest and is the principal organ of the respiratory system. Their size and shape are unstable and can vary depending on the phase of
Слайд 1Государственное бюджетное профессиональное образовательное учреждение
Московской области
«Московский областной медицинский колледж № 2»
(ГБПОУ МО «Московский областной медицинский колледж № 2»)
Коломенский филиал
Презентация на тему: «лёгкие»
Слайд 2Lightweight (pulmones) are paired organ, which occupies almost the entire cavity
of the chest and is the principal organ of the respiratory system. Their size and shape are unstable and can vary depending on the phase of respiration.
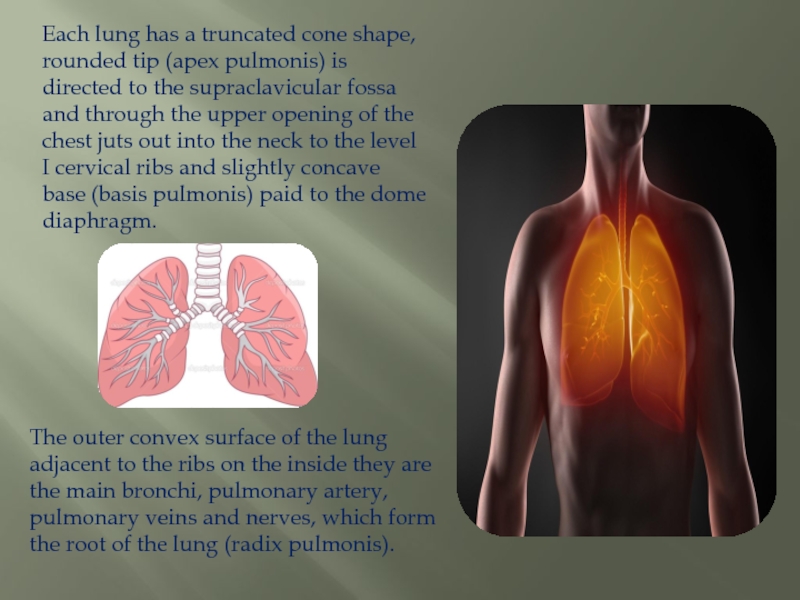
Слайд 3Each lung has a truncated cone shape, rounded tip (apex pulmonis)
is directed to the supraclavicular fossa and through the upper opening of the chest juts out into the neck to the level I cervical ribs and slightly concave base (basis pulmonis) paid to the dome diaphragm.
The outer convex surface of the lung adjacent to the ribs on the inside they are the main bronchi, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins and nerves, which form the root of the lung (radix pulmonis).
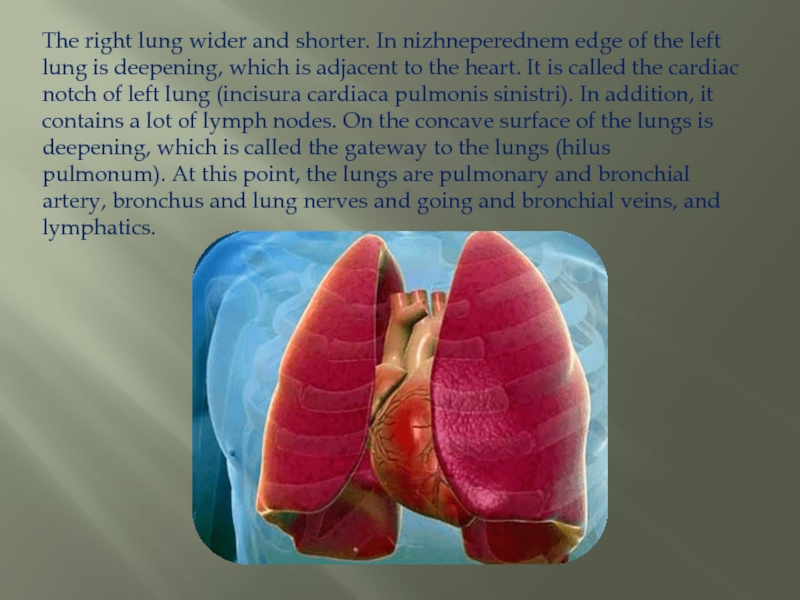
Слайд 4The right lung wider and shorter. In nizhneperednem edge of the left
lung is deepening, which is adjacent to the heart. It is called the cardiac notch of left lung (incisura cardiaca pulmonis sinistri). In addition, it contains a lot of lymph nodes. On the concave surface of the lungs is deepening, which is called the gateway to the lungs (hilus pulmonum). At this point, the lungs are pulmonary and bronchial artery, bronchus and lung nerves and going and bronchial veins, and lymphatics.
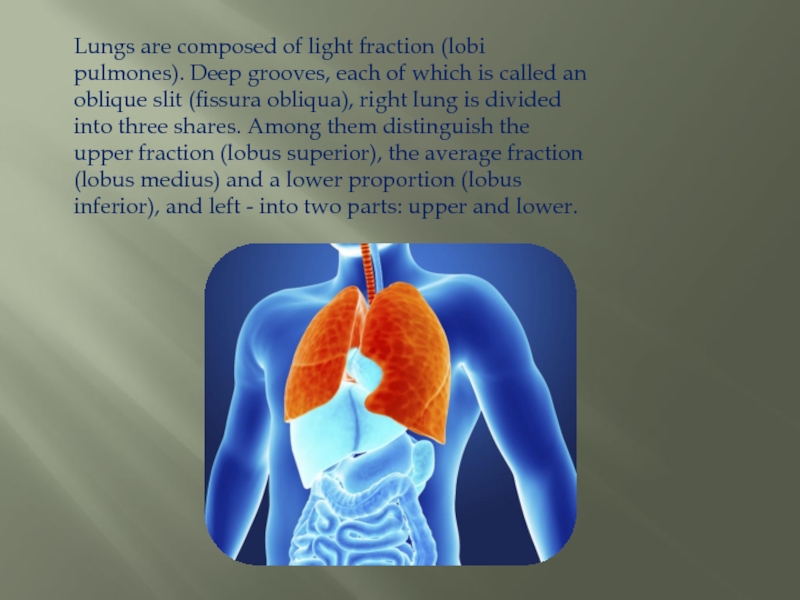
Слайд 5Lungs are composed of light fraction (lobi pulmones). Deep grooves, each of
which is called an oblique slit (fissura obliqua), right lung is divided into three shares. Among them distinguish the upper fraction (lobus superior), the average fraction (lobus medius) and a lower proportion (lobus inferior), and left - into two parts: upper and lower.
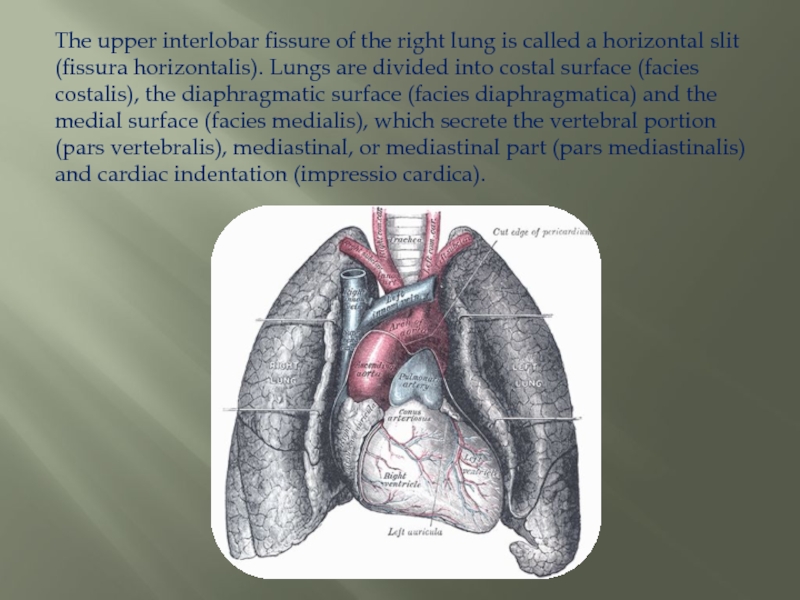
Слайд 6The upper interlobar fissure of the right lung is called a
horizontal slit (fissura horizontalis). Lungs are divided into costal surface (facies costalis), the diaphragmatic surface (facies diaphragmatica) and the medial surface (facies medialis), which secrete the vertebral portion (pars vertebralis), mediastinal, or mediastinal part (pars mediastinalis) and cardiac indentation (impressio cardica).
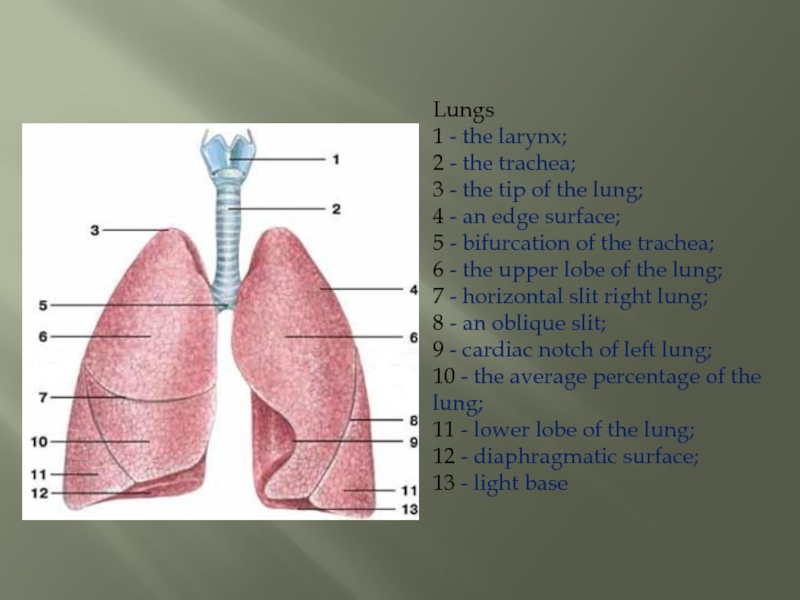
Слайд 7Lungs 1 - the larynx; 2 - the trachea; 3 - the tip of
the lung;
4 - an edge surface;
5 - bifurcation of the trachea;
6 - the upper lobe of the lung;
7 - horizontal slit right lung;
8 - an oblique slit;
9 - cardiac notch of left lung;
10 - the average percentage of the lung;
11 - lower lobe of the lung;
12 - diaphragmatic surface;
13 - light base
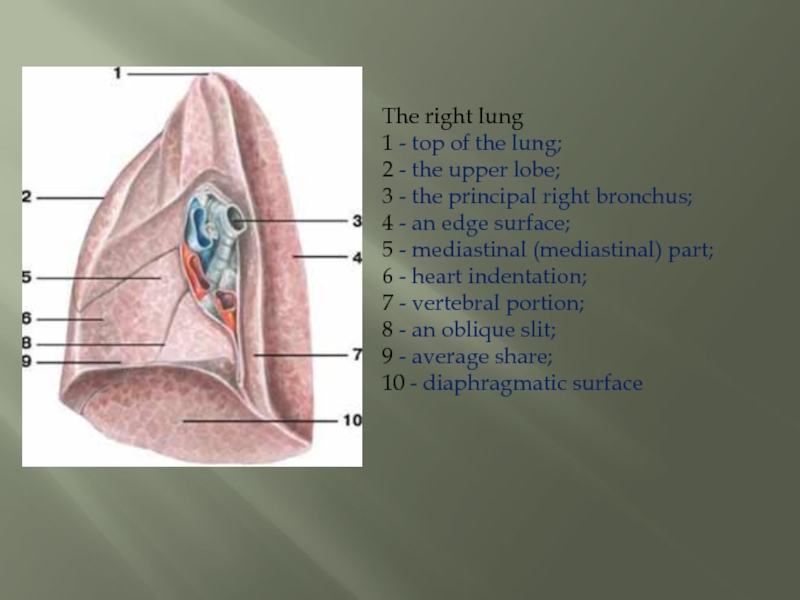
Слайд 8The right lung 1 - top of the lung; 2 - the upper
lobe;
3 - the principal right bronchus;
4 - an edge surface;
5 - mediastinal (mediastinal) part;
6 - heart indentation;
7 - vertebral portion;
8 - an oblique slit;
9 - average share;
10 - diaphragmatic surface
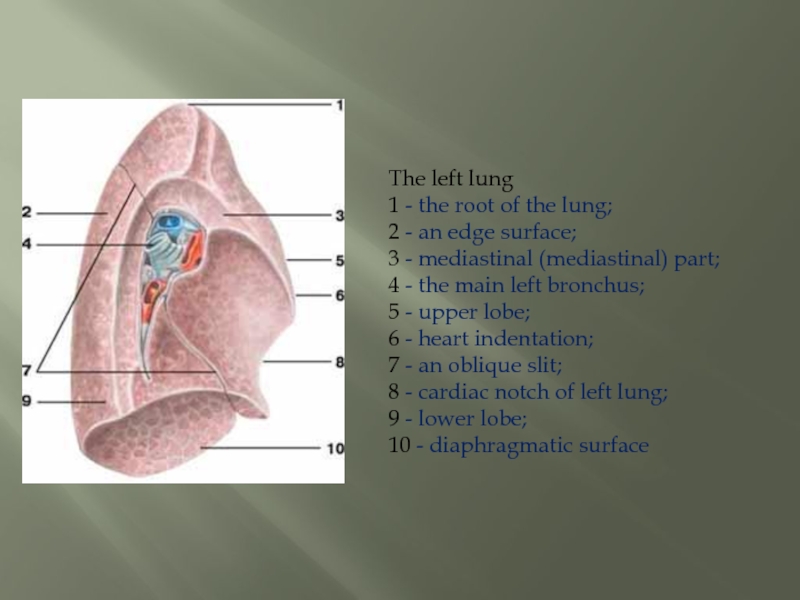
Слайд 9The left lung 1 - the root of the lung; 2 - an
edge surface;
3 - mediastinal (mediastinal) part;
4 - the main left bronchus;
5 - upper lobe;
6 - heart indentation;
7 - an oblique slit;
8 - cardiac notch of left lung;
9 - lower lobe;
10 - diaphragmatic surface
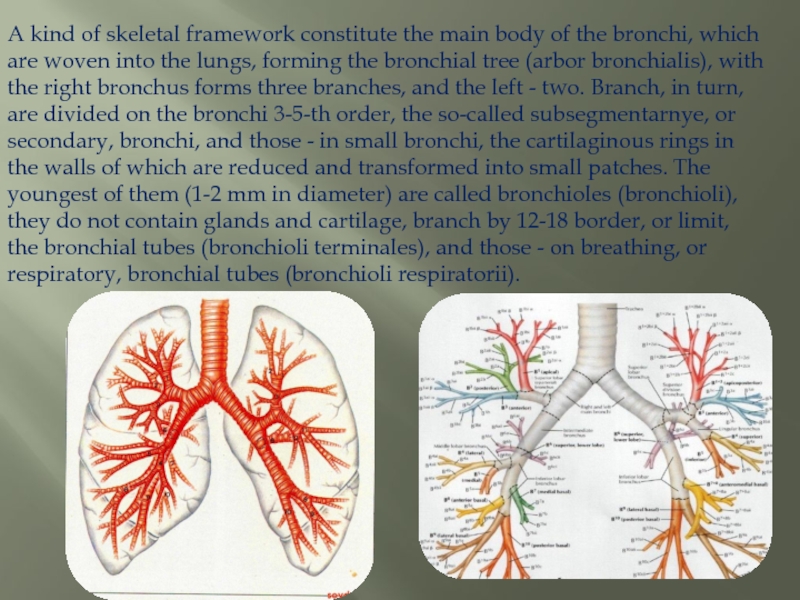
Слайд 10A kind of skeletal framework constitute the main body of the
bronchi, which are woven into the lungs, forming the bronchial tree (arbor bronchialis), with the right bronchus forms three branches, and the left - two. Branch, in turn, are divided on the bronchi 3-5-th order, the so-called subsegmentarnye, or secondary, bronchi, and those - in small bronchi, the cartilaginous rings in the walls of which are reduced and transformed into small patches. The youngest of them (1-2 mm in diameter) are called bronchioles (bronchioli), they do not contain glands and cartilage, branch by 12-18 border, or limit, the bronchial tubes (bronchioli terminales), and those - on breathing, or respiratory, bronchial tubes (bronchioli respiratorii).
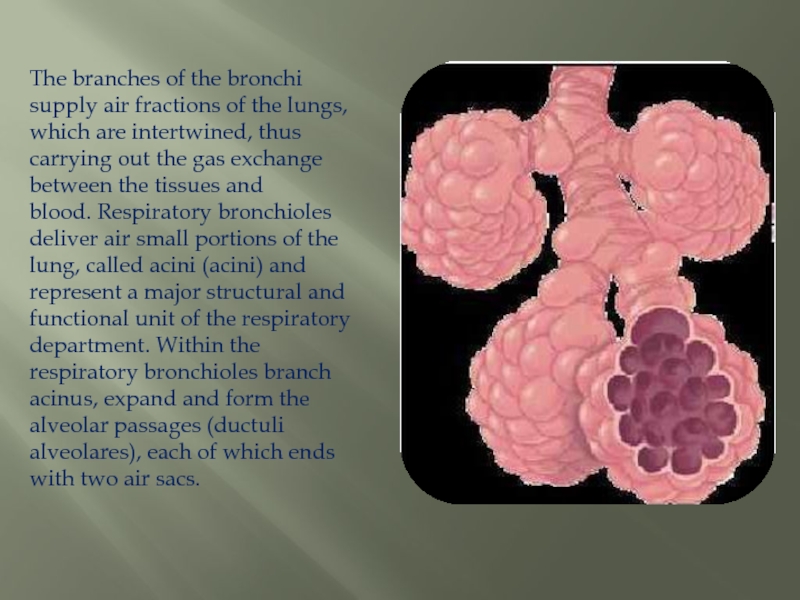
Слайд 11The branches of the bronchi supply air fractions of the lungs,
which are intertwined, thus carrying out the gas exchange between the tissues and blood. Respiratory bronchioles deliver air small portions of the lung, called acini (acini) and represent a major structural and functional unit of the respiratory department. Within the respiratory bronchioles branch acinus, expand and form the alveolar passages (ductuli alveolares), each of which ends with two air sacs.
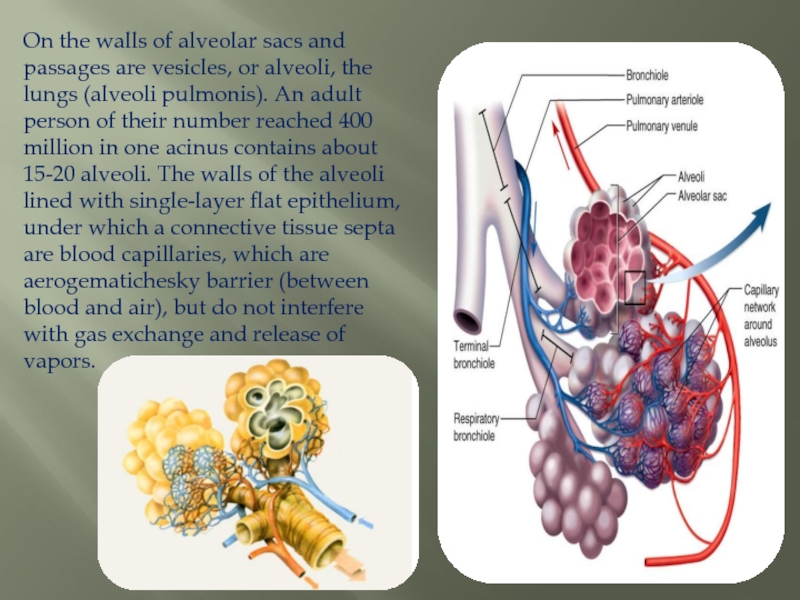
Слайд 12On the walls of alveolar sacs and passages are vesicles, or
alveoli, the lungs (alveoli pulmonis). An adult person of their number reached 400 million in one acinus contains about 15-20 alveoli. The walls of the alveoli lined with single-layer flat epithelium, under which a connective tissue septa are blood capillaries, which are aerogematichesky barrier (between blood and air), but do not interfere with gas exchange and release of vapors.
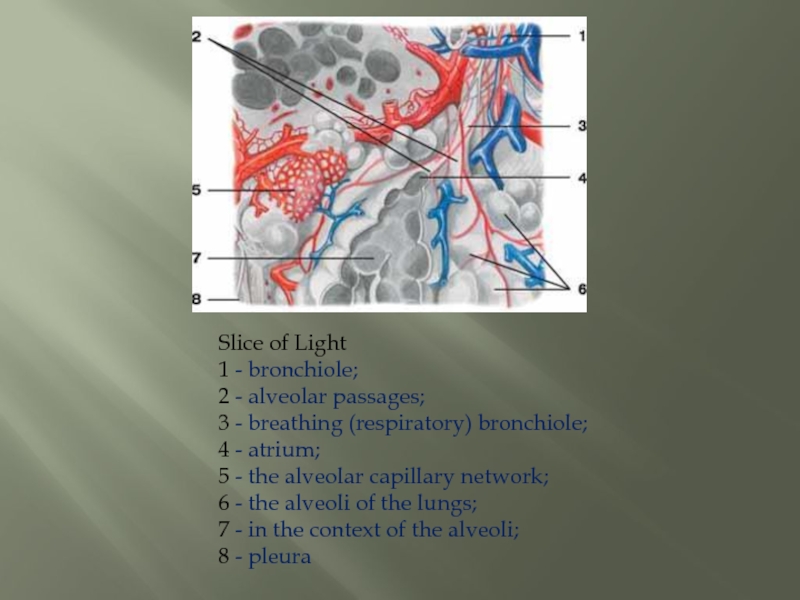
Слайд 13Slice of Light 1 - bronchiole; 2 - alveolar passages; 3 - breathing (respiratory)
bronchiole;
4 - atrium;
5 - the alveolar capillary network;
6 - the alveoli of the lungs;
7 - in the context of the alveoli;
8 - pleura
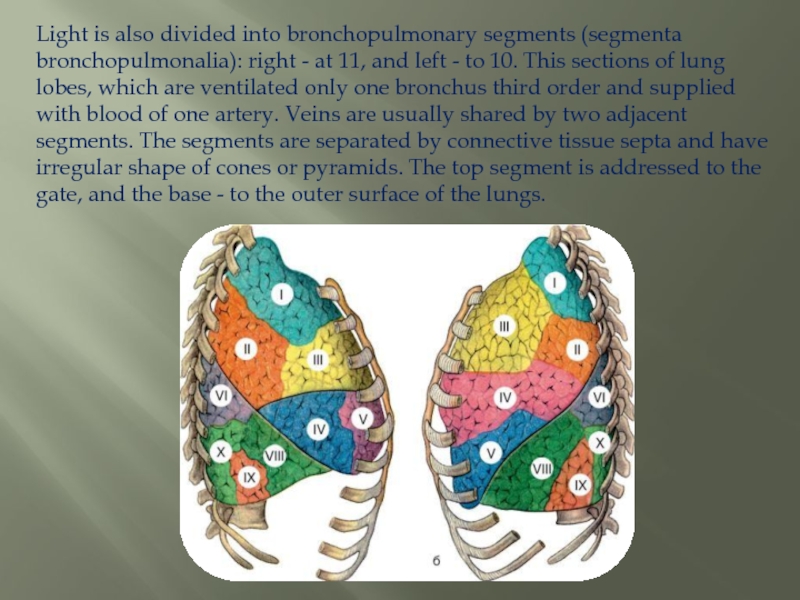
Слайд 14Light is also divided into bronchopulmonary segments (segmenta bronchopulmonalia): right -
at 11, and left - to 10. This sections of lung lobes, which are ventilated only one bronchus third order and supplied with blood of one artery. Veins are usually shared by two adjacent segments. The segments are separated by connective tissue septa and have irregular shape of cones or pyramids. The top segment is addressed to the gate, and the base - to the outer surface of the lungs.
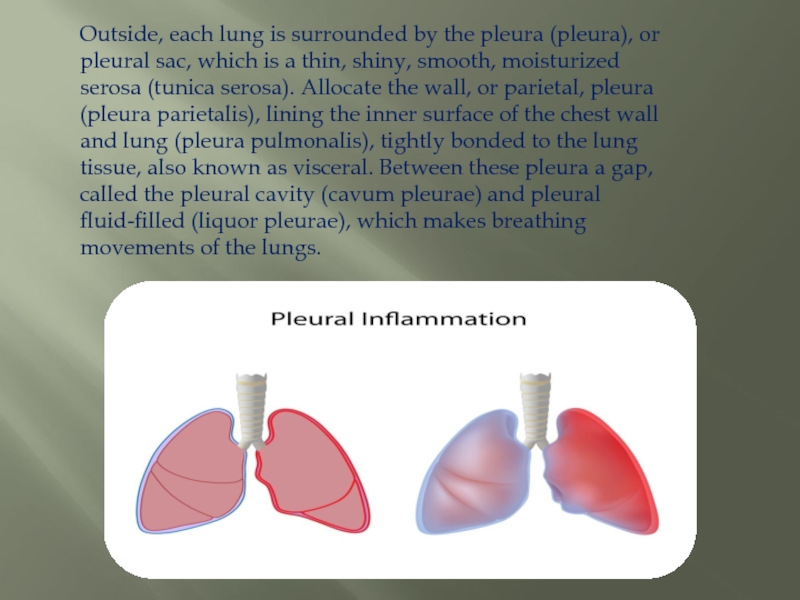
Слайд 15Outside, each lung is surrounded by the pleura (pleura), or pleural
sac, which is a thin, shiny, smooth, moisturized serosa (tunica serosa). Allocate the wall, or parietal, pleura (pleura parietalis), lining the inner surface of the chest wall and lung (pleura pulmonalis), tightly bonded to the lung tissue, also known as visceral. Between these pleura a gap, called the pleural cavity (cavum pleurae) and pleural fluid-filled (liquor pleurae), which makes breathing movements of the lungs.
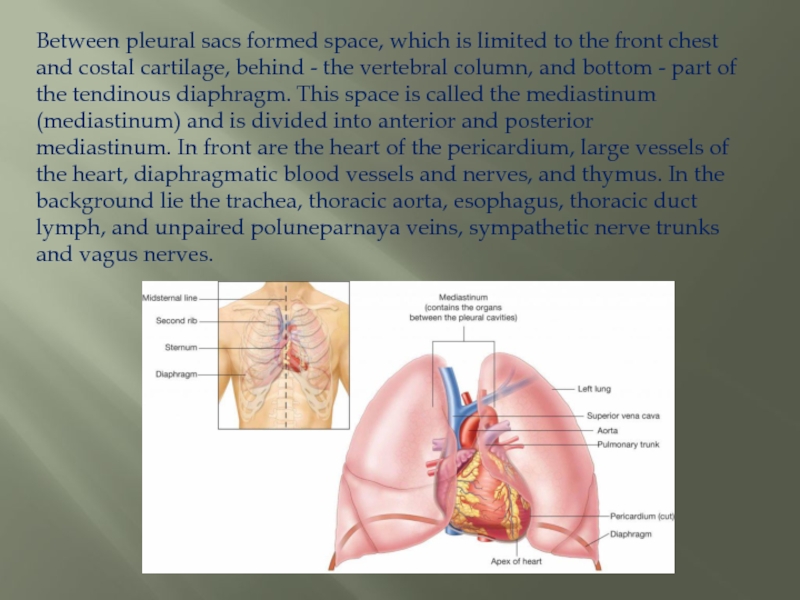
Слайд 16Between pleural sacs formed space, which is limited to the front
chest and costal cartilage, behind - the vertebral column, and bottom - part of the tendinous diaphragm. This space is called the mediastinum (mediastinum) and is divided into anterior and posterior mediastinum. In front are the heart of the pericardium, large vessels of the heart, diaphragmatic blood vessels and nerves, and thymus. In the background lie the trachea, thoracic aorta, esophagus, thoracic duct lymph, and unpaired poluneparnaya veins, sympathetic nerve trunks and vagus nerves.