- Главная
- Разное
- Образование
- Спорт
- Естествознание
- Природоведение
- Религиоведение
- Французский язык
- Черчение
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, фоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
Презентация, доклад на тему British Monarchy and Parliament
Содержание
- 1. British Monarchy and Parliament
- 2. to elect
- 3. Слайд 3
- 4. What do you think “ democracy” means?-
- 5. The United Kingdom has a three-tiered structure: the monarch the government Parliament
- 6. Слайд 6
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. What functions do the representatives
- 9. What functions do the representatives
- 10. Today the Queen is not only head
- 11. The present sovereign is Queen Elizabeth II.
- 12. Functions of the Queen. Opening and closing
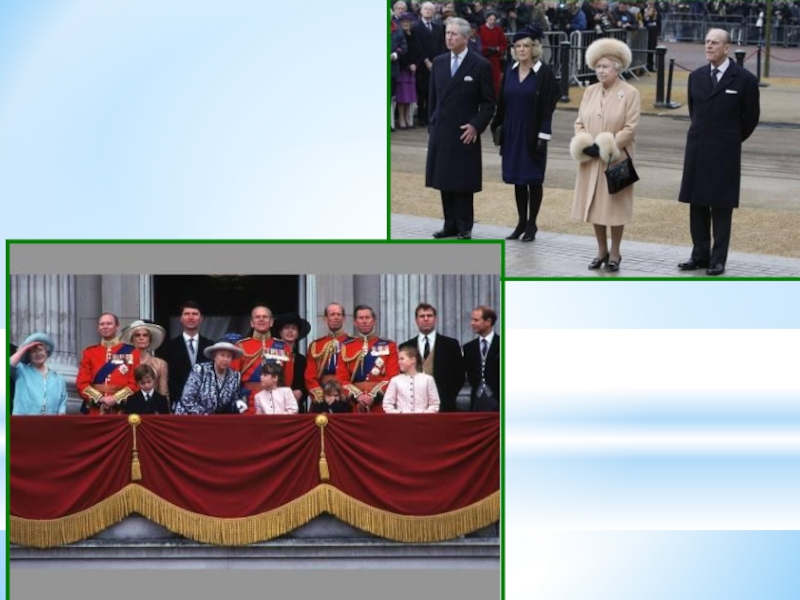
- 13. The Queen and the royal family continue to take part in many traditional ceremonies.
- 14. Слайд 14
- 15. The official ceremony the State Opening of Parliament
- 16. The proceedings of both Houses of Parliament are broadcast on television and radio.
- 17. Parliament:Parliament, Britain's legislature, comprises the House of
- 18. The debating chamber of the House of Commons
- 19. The UK
- 20. Match the words and their definitions.Monarchy
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. 1. How many parts does the
- 23. Слайд 23
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. Thank you for your work. Good luck!
Слайд 2
to elect
to vote personal achievement
to approve state
to inherit common
to represent
to consist of
Lord Chancellor
to be called
Labour Party
to preside
Conservative Party
chamber
to debate
Arch
Speaker
Слайд 4What do you think “ democracy” means?
- People do what they
- People rule the country.
- People do what they want within the framework
of law.
- People elect their representatives to rule the country.
- People elect the head of state directly.
- People say what they think.
- People can live in any place they choose.
- The head of state guarantees the rights of citizens.
- All people and authorities follow the constitution.
Слайд 6
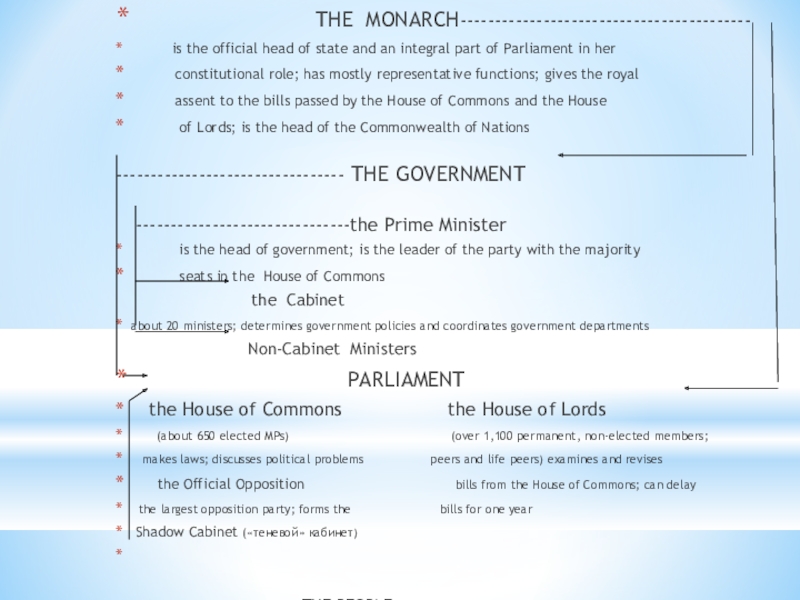
is the official head of state and an integral part of Parliament in her constitutional role; has mostly representative functions; gives the royal assent to the bills passed by the House of Commons and the House of Lords; is the head of the Commonwealth of
Nations
THE GOVERNMENT
the Prime Minister
is the head of government; is the leader of the party with the majority seats in the
House of Commons
the Cabinet
about 20 ministers; determines government policies and coordinates government departments
Non-Cabinet Ministers
PARLIAMENT
the House of Commons the House of Lords
(about 650 elected MPs - members of Parliament) (over 1,100 permanent, non-elected members;
makes laws; discusses political problems peers and life peers) examines and revises
the Official Opposition bills from the House of Commons; can delay
the largest opposition party; forms the bills for one year
Shadow Cabinet («теневой» кабинет)
THE PEOPLE
(all men and women over 18)
Слайд 7
is the official head of state and an integral part of Parliament in her
constitutional role; has mostly representative functions; gives the royal
assent to the bills passed by the House of Commons and the House
of Lords; is the head of the Commonwealth of Nations
--------------------------------- THE GOVERNMENT
-------------------------------the Prime Minister
is the head of government; is the leader of the party with the majority
seats in the House of Commons
the Cabinet
about 20 ministers; determines government policies and coordinates government departments
Non-Cabinet Ministers
PARLIAMENT
the House of Commons the House of Lords
(about 650 elected MPs) (over 1,100 permanent, non-elected members;
makes laws; discusses political problems peers and life peers) examines and revises
the Official Opposition bills from the House of Commons; can delay
the largest opposition party; forms the bills for one year
Shadow Cabinet («теневой» кабинет)
----------------------------------- THE PEOPLE
(all men and women over 18)
Слайд 8
What functions do the representatives of power perform? Use
1. A. The Queen votes on the bills.
B. The Queen signs the bills
2. A. The Queen has mostly representative functions.
B. The Queen rules the country in fact.
3. A. The government represents the legislative branch of power.
B. The government represents the executive branch of power.
4. A. The Cabinet is responsible for government policies.
B. The Cabinet Ministers revise bills from Parliament.
5. A. Parliament represents the legislative branch of power.
B. Parliament represents the executive branch of power.
6 A. The House of Commons controls the government.
B. The government controls the House of Commons.
7. A. The House of Lords has the power to delay bills for one year.
B. The House of Lords opposes the decisions of the House of Commons.
8. A. The Cabinet coordinates the work of the government departments.
B. The Cabinet makes laws.
Слайд 9
What functions do the representatives of power perform? Use
1. A. The Queen votes on the bills.
B. The Queen signs the bills
2. A. The Queen has mostly representative functions.
B. The Queen rules the country in fact.
3. A. The government represents the legislative branch of power.
B. The government represents the executive branch of power.
4. A. The Cabinet is responsible for government policies.
B. The Cabinet Ministers revise bills from Parliament.
5. A. Parliament represents the legislative branch of power.
B. Parliament represents the executive branch of power.
6 A. The House of Commons controls the government.
B. The government controls the House of Commons.
7. A. The House of Lords has the power to delay bills for one year.
B. The House of Lords opposes the decisions of the House of Commons.
8. A. The Cabinet coordinates the work of the government departments.
B. The Cabinet makes laws.
Слайд 10
Today the Queen is not only head of State, but also
Слайд 11The present sovereign is Queen Elizabeth II. She was born on
Слайд 12Functions of the Queen.
Opening and closing Parliament
Approving the appointment
Giving the Royal Assent to bills
Giving honours such as peerages, knighthoods and medals
Head of the Commonwealth
Head of the Church of England
Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces.
Слайд 17Parliament:
Parliament, Britain's legislature, comprises the House of Commons, the House of
The Commons has 651 elected Members of Parliament (MPs), each representing a local constituency (избирательный округ).
The Lords is made up of 1,185 hereditary and life peers, and the two archbishops and the 24 most senior bishops of the established Church of England.
Слайд 19 The UK is governed by the
of ministers. About 20 Ministers compose
the Cabinet , which meets
regularly under the chairmanship
of the Prime Minister.
David Cameron
10, Downing Street
Слайд 20Match the words and their definitions.
Monarchy
Parliamentary monarchy
Absolute
To become a monarch
To restore a monarchy
Royalty
Royal
a form of government in which the head of state is a monarch
a monarch does what Parliament tells her (him)
the power of a monarch is complete, total without limits
to become a king or queen
to bring back a monarchy
members of royal families (either individually or collectively)
a member of a royal family relating to or suitable for a king or queen
Слайд 21
a) one
b) two
c) three
2. What are the main colours of the Houses of Parliament?
a) gold, red, blue
b) gold, green and red
c) red and green
3. Who writes the Queen's Speech?
a) the Queen
b) the Government
c) the Lord Chancellor
4. Which are Britain's two main political parties?
a) Democratic, Republican and Conservative
b) Conservative and Democratic
c) Labour and Conservative
5. Whose shoe should a Conservative touch?
a) David Lloyd George’s
b) Winston Churchill's
c) The Queen’s
6. Why do MPs sometimes sit on the steps?
a) There are more MPs than seats in the House of Commons,
b) It’s a part of an old tradition.
c) it’s a punishment for those who are late.
7. When can you see the Mace in the House of Commons?
a) It’s always there.
b) Only when the Queen comes
c) When the House is debating.
8. How old is Westminster Hall?
a) more than a thousand years old
b) more than a hundred years old
c) more than four hundred years old
Слайд 221. How many parts does the Palace of Westminster consist
c) three
2. What are the main colours of the Houses of Parliament?
b) gold, green and red
3. Who writes the Queen's Speech?
b) the Government
4. Which are Britain's two main political parties?
c) Labour and Conservative
5. Whose shoe should a Conservative touch?
b) Winston Churchill's
6. Why do MPs sometimes sit on the steps?
a) There are more MPs than seats in the House of Commons,
7. When can you see the Mace in the House of Commons?
c) When the House is debating.
8. How old is Westminster Hall?
a) more than a thousand years old